38 heteronuclear molecular orbital diagram
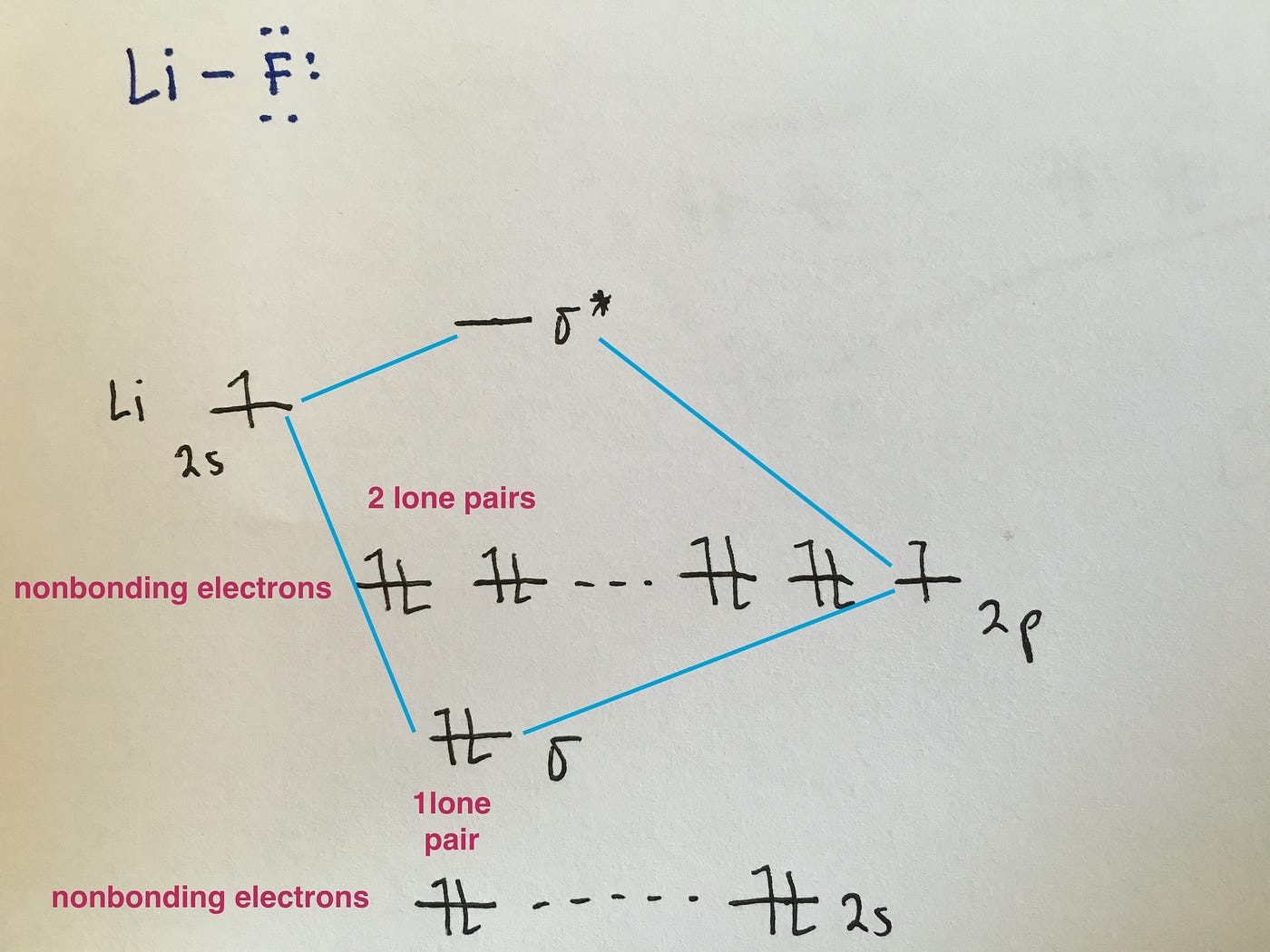
Heteronuclear Molecular orbital diagram - Summarized by ... Heteronuclear Molecular orbital diagram. Collected from the entire web and summarized to include only the most important parts of it. Can be used as content for research and analysis. PDF MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
PDF Heteronuclear Molecules Heteronuclear Molecules • The relative energy of the bonding orbitals determines the magnitude of the covalent bond energy (∆Ecov): 2-44 Energy Level Diagram of CO
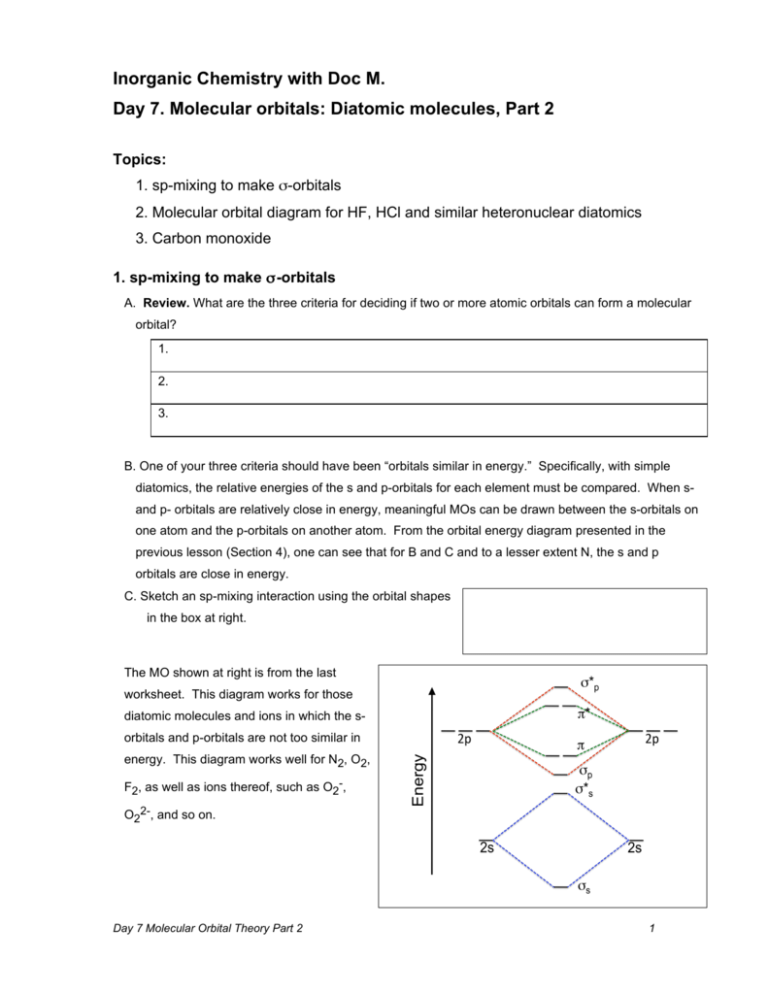
Heteronuclear molecular orbital diagram
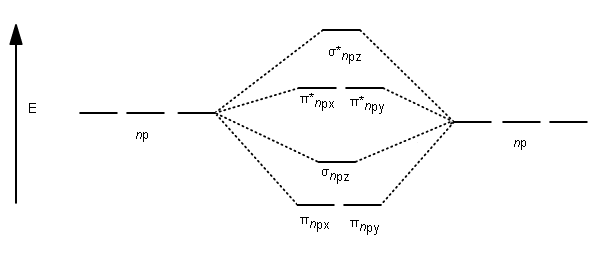
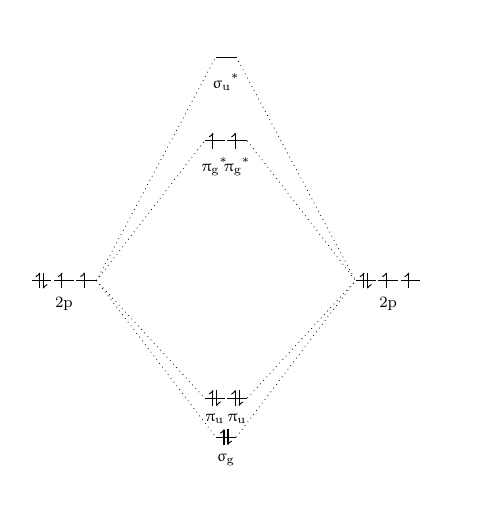
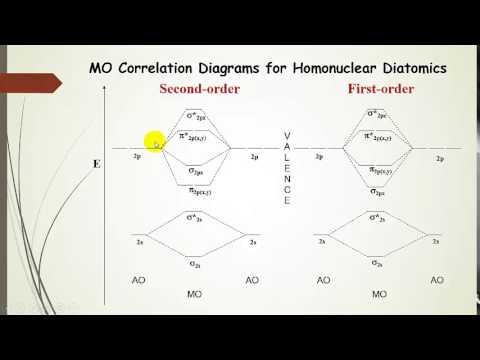
2: Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry LibreTexts Be able to construct molecular orbital diagrams for homonuclear diatomic, heteronuclear diatomic, homonuclear triatomic, and heteronuclear triatomic molecules. Understand and be able to articulate how molecular orbitals form - conceptually, visually, graphically, and (semi)mathematically. PDF The molecular orbital - Darbhanga College of Engineering and heteronuclear diatomic molecular orbital diagrams. These steps may then be extrapolated to construct more difficult polyatomic diagrams. Molecular Orbitals The region an electron is most likely to be found in a molecule. A MO is defined as the combination of atomic orbitals. Homonuclear Diatomic Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A heteronuclear diatomic molecule is composed of two atoms of two different elements. Examples include CO, HCl, and NO . Dihydrogen H2 Molecular Orbital Diagram MO diagram of dihydrogen Bond breaking in MO diagram The smallest molecule, hydrogen gas exists as dihydrogen (H-H) with a single covalent bond between two hydrogen atoms.
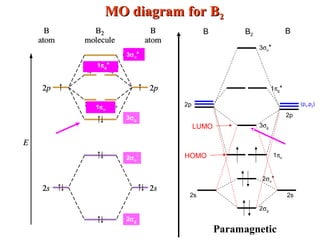
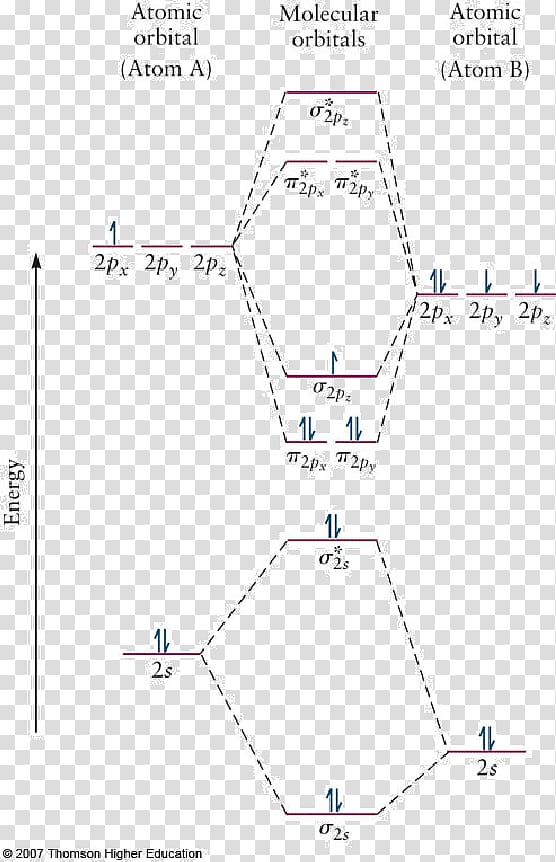
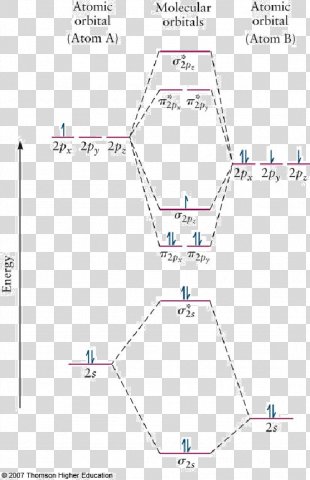
Heteronuclear molecular orbital diagram. PDF Module 2 : Molecular Structure Lecture 8 : Hetenuclear ... Module 2 : Molecular Structure Lecture 8 : Hetenuclear Diatomics Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Construction of molecular orbitals of heteronuclear diatomics from the constituent atomic orbitals. Qualitative sketches of contours of MOs. The energy level diagrams. The electronic configurations. Which statement regarding stable heteronuc... - Organic ... Which statement regarding stable heteronuclear diatomic molecules is false? a) All have bond orders greater than zero b) Their molecular orbital diagrams are more symmetrical than those of homonuclear diatomic molecules c) The antibonding molecular orbitals have more of the character of the more electropositive element than of the more electronegative element d) The bonding molecular orbitals ... PDF Practice Test Questions 3 Molecular Orbital Theory ... Molecular Orbital Theory: Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules . 1. Energy Values for the Atomic Orbitals of Hydrogen and Helium Atoms . Hydrogen Helium 1s -1.00 Ry -1.81 Ry (a) Use the energy values in the table above to help you develop a valencemolecular orbital energy level diagram for the helium protonate ion (𝐻𝐻𝐻𝐻𝐻𝐻+). Molecular Orbitals - Introductory Chemistry - 1st Canadian ... We can focus further on two very important types of molecular orbitals: the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) and the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO), also referred to collectively as the frontier molecular orbitals (Figure 9.26 "Frontier molecular orbitals HOMO and LUMO"). As their names imply, the HOMO is the molecular orbital that has the highest energy and contains electrons, while the LUMO is the lowest energy molecular orbital that does not contain electrons.
Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules - CHEMISTRY COMMUNITY Re: Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules. Electronegativity is the electron pulling power of an atom, and an atom with a higher electronegativity will pull the shared electrons pair more towards itself. This is true for bonding orbitals, where the more electronegative atom will dominate. However, this is not true for antibonding orbitals. Molecular Orbitals - Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear ... Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Molecules. The molecular orbitals which describe the motion of a single electron in a molecule containing two unequal nuclear charges will not exhibit the g and u symmetry properties of the homonuclear diatomic case. The molecular orbitals in the heteronuclear case will in general be concentrated more around one nucleus than the other. The molecular orbital diagram shown below ... | Clutch Prep The molecular orbital diagram shown below belongs to an interhalogen compound, bromine chloride (BrCl). Assuming that the molecular orbitals of interhalogen compounds are analogous to diatomic halogen molecules (such as Cl 2 or Br 2), determine the number of electrons that occupy this molecular orbital. PDF Molecular orbital DiagraM - Magadh University Basis of molecular orbital (MO) approach: Overlap of orbitals occurs for the whole molecule-bonding is thereforeDELOCALISED. Atomic orbitals: Orbitals that are localized on single atoms. Molecular orbitals: Orbitals that span two or more atoms. These are constructed by overlapping atomic orbitals (AOs) which match in symmetry and size. In principle, To construct MO diagram of a any Molecule, first, set up
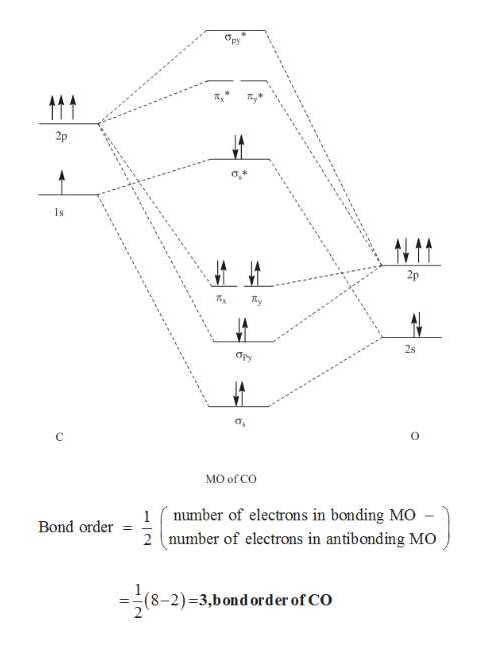
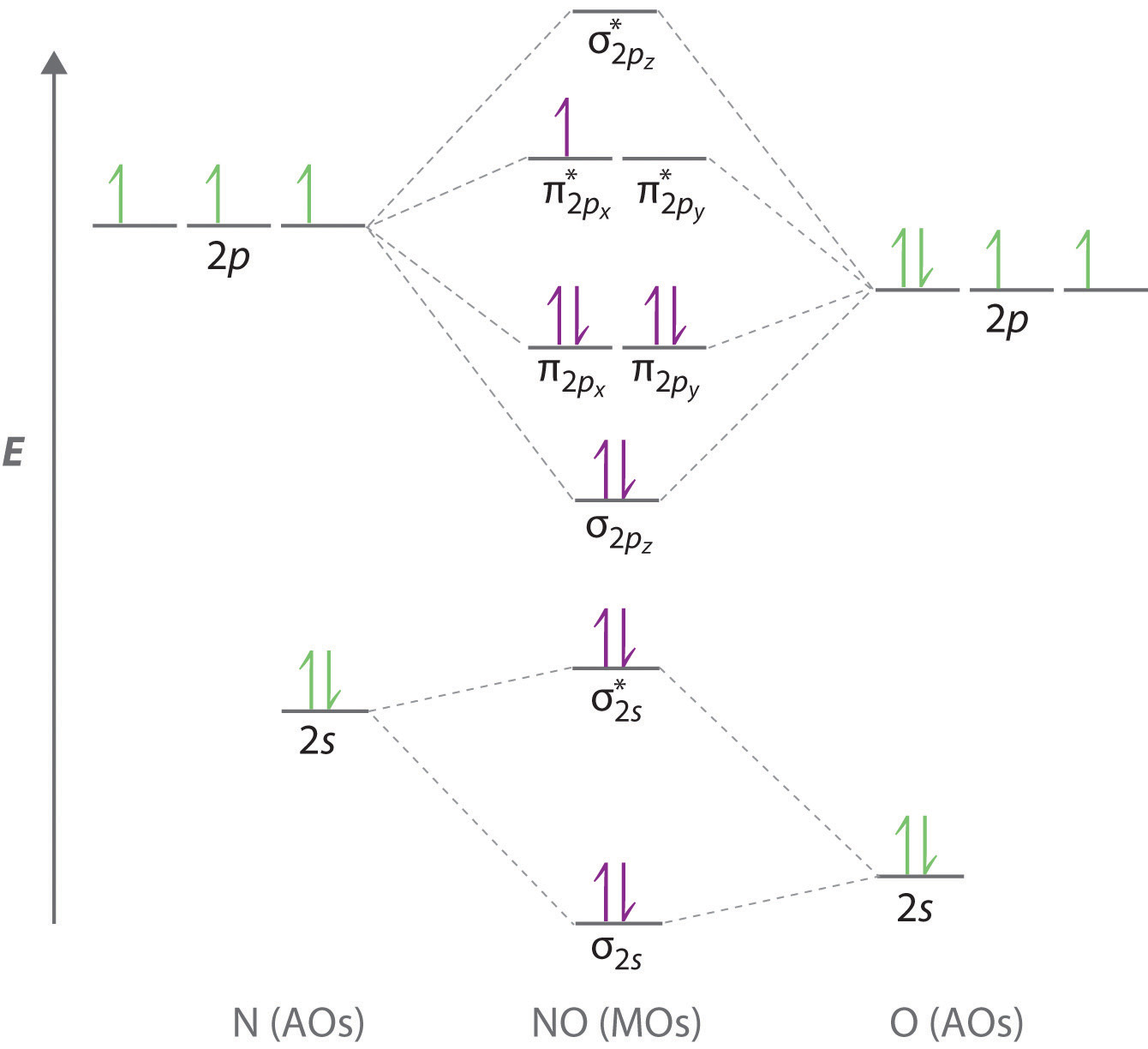
Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia Heteronuclear diatomics. In heteronuclear diatomic molecules, mixing of atomic orbitals only occurs when the electronegativity values are similar. In carbon monoxide (CO, isoelectronic with dinitrogen) the oxygen 2s orbital is much lower in energy than the carbon 2s orbital and therefore the degree of mixing is low. The electron configuration 1σ 2 1σ* 2 2σ 2 2σ* 2 1π 4 3σ 2 is identical ... PDF Molecular Orbital Diagram for a Homonuclear Diatomic The molecular orbital energy diagram is not shown to scale (that is, the 1s orbitals are the corresponding MOs are much lower in energy than the 2s or 2p orbitals). For homonuclear diatomic molecules formed from atoms with atomic numbers greater than that of nitrogen, including O. 2, F. inorganic chemistry - Molecular orbitals of heteronuclear ... Now, MO diagrams are only simple for elements of the second row of the periodic table ($\ce{Li}$ through $\ce{Ne}$). Involving heavier atoms makes it harder to guess at molecular orbital diagrams, and there is need for quantum chemistry calculations. Thus, the rule becomes: the further to the right your element is, the lower its energy levels are. D6.5 MOs for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules - Chemistry ... D6.5 MOs for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Diatomic molecules with two non-identical atoms are called heteronuclear diatomic molecules, examples include CO, NO and HCl. Molecular orbital diagrams for these molecules have one more layer of complexity, but they also serve to explain many bond and molecular properties we will encounter later on in the course.
MO Theory: Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules - Chemistry ... Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules are composed of 2 different elements bonded together. Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Heteronuclear Diatomics Concept #1: Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Heteronuclear Diatomics
8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams — Flux Science To make sense of the complexities introduced by antibonding, we build molecular orbital diagrams. These, however, also have their own depth; diagrams like these change according to if you're working with homonuclear molecules - molecules made of one element - or heteronuclear molecules - molecules made of different elements. Yes, readers, unfortunately, this is going to be similar to the functional groups section in its depth.
Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Lih - schematron.org Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Lih. We shall consider the molecular orbitals in LiH, CH and HF to illustrate how molecular orbital theory describes the bonding in heteronuclear molecules, and to. and 2p orbitals, but that is not how sodium chloride is made. Sodium atoms are Construct an MO diagram for LiH and suggest what type of bond it might have.
MO Diagram for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules ... Re: MO Diagram for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules [ENDORSED] We label a molecular orbital "sigma 2s" only when it correlates to two atomic 2s orbitals. With molecular orbitals that correlate to more than one type of atomic orbital, we have to use an alternative notation, where each set of molecular orbitals of a certain type (sigma, pi) is ...
PDF Answers to Practice Test Questions 3 Molecular Orbital ... • four sigma-symmetric orbitals close enough in energy to combine: 2𝑠𝑠(𝑁𝑁), 2𝑠𝑠(𝑂𝑂), 2𝑝𝑝. 𝑧𝑧 (𝑁𝑁) and 2𝑝𝑝. 𝑧𝑧 (𝑂𝑂). σ. 2p (b) The HOMO is labeled on the diagram in part (a). (c) The LUMO is labeled on the diagram in part (a). You need to show both 2𝜋𝜋∗ MOs. N NO+ O 2s 2s 1σ 2σ∗ 2p 3σ 4 ∗ 1π
Molecular orbital theory. Heteronuclear diatomics. CO ... 12-12 This video describes the molecular orbital theory diagram of CO, placing emphasis on how MO theory differs for homo and heteronuclear diatomics
Molecular Orbital Theory Heteronuclear Diatomic (Cyanide ... Molecular Orbital Theory Heteronuclear Diatomic (Cyanide, CN-) Example - YouTube. Molecular Orbital Theory Heteronuclear Diatomic (Cyanide, CN-) Example. Watch later. Share.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › J-couplingJ-coupling - Wikipedia The origin of J-coupling can be visualized by a vector model for a simple molecule such as hydrogen fluoride (HF).In HF, the two nuclei have spin 1 / 2.Four states are possible, depending on the relative alignment of the H and F nuclear spins with the external magnetic field.
What is molecular orbital diagram of CO? - handlebar ... What is molecular orbital diagram of CO? Carbon monoxide MO diagram. Carbon monoxide is an example of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule where both atoms are second-row elements. The valence molecular orbitals in both atoms are the 2s and 2p orbitals. The molecular orbital diagram for carbon monoxide (Figure 5.3. Is there SP mixing in CO?
Heteronuclear Molecules AB - TU Braunschweig Fig. 3 shows a correlation diagram for a heteronuclear diatomic molecule (comp. homonuclear case).Just σ and π appear as the g-u-classification is only relevant for homonuclear diatomics. Fig. 4 qualitatively shows the distribution of the wave function's amplitude for the single atoms and the orbitals of an hypothetical united atom as the two extremes in this approach.
PDF Lecture 2 MO theory for polyatomic molecules s/p mixing more important more bonding more antibonding s/p mixing less important Heteronuclear diatomics, AH: (HF vs HB) Protocol for constructing MO diagrams for AHn(H2O, NH3, CH4) 1) Identify symmetry equivalent atoms (hydrogens in this case) 2) Generate Symmetry Adapted Linear Combinations on these identical atoms 3) Combine SALCS with orbitals ...
7.3: How to Build Molecular Orbitals - Chemistry LibreTexts STEP 2: Heteronuclear molecule; "F" will be lower on the diagram. STEP 3: Fill the MOs with electrons: STEP 4: Check; Do the number of AO's = number of MO's? Now more difficult MO diagrams can be derived using the four simple step above. Keep the energies of atomic/molecular orbitals when arranging the diagram!
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Oxidation_stateOxidation state - Wikipedia when the isolated tandem of a heteronuclear and a homonuclear bond leads to a bonding compromise in between two Lewis structures of limiting bond orders. An example is N 2 O: The typical oxidation state of nitrogen in N 2 O is +1, which also obtains for both nitrogens by a molecular orbital approach.
Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A heteronuclear diatomic molecule is composed of two atoms of two different elements. Examples include CO, HCl, and NO . Dihydrogen H2 Molecular Orbital Diagram MO diagram of dihydrogen Bond breaking in MO diagram The smallest molecule, hydrogen gas exists as dihydrogen (H-H) with a single covalent bond between two hydrogen atoms.
PDF The molecular orbital - Darbhanga College of Engineering and heteronuclear diatomic molecular orbital diagrams. These steps may then be extrapolated to construct more difficult polyatomic diagrams. Molecular Orbitals The region an electron is most likely to be found in a molecule. A MO is defined as the combination of atomic orbitals. Homonuclear Diatomic
2: Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry LibreTexts Be able to construct molecular orbital diagrams for homonuclear diatomic, heteronuclear diatomic, homonuclear triatomic, and heteronuclear triatomic molecules. Understand and be able to articulate how molecular orbitals form - conceptually, visually, graphically, and (semi)mathematically.
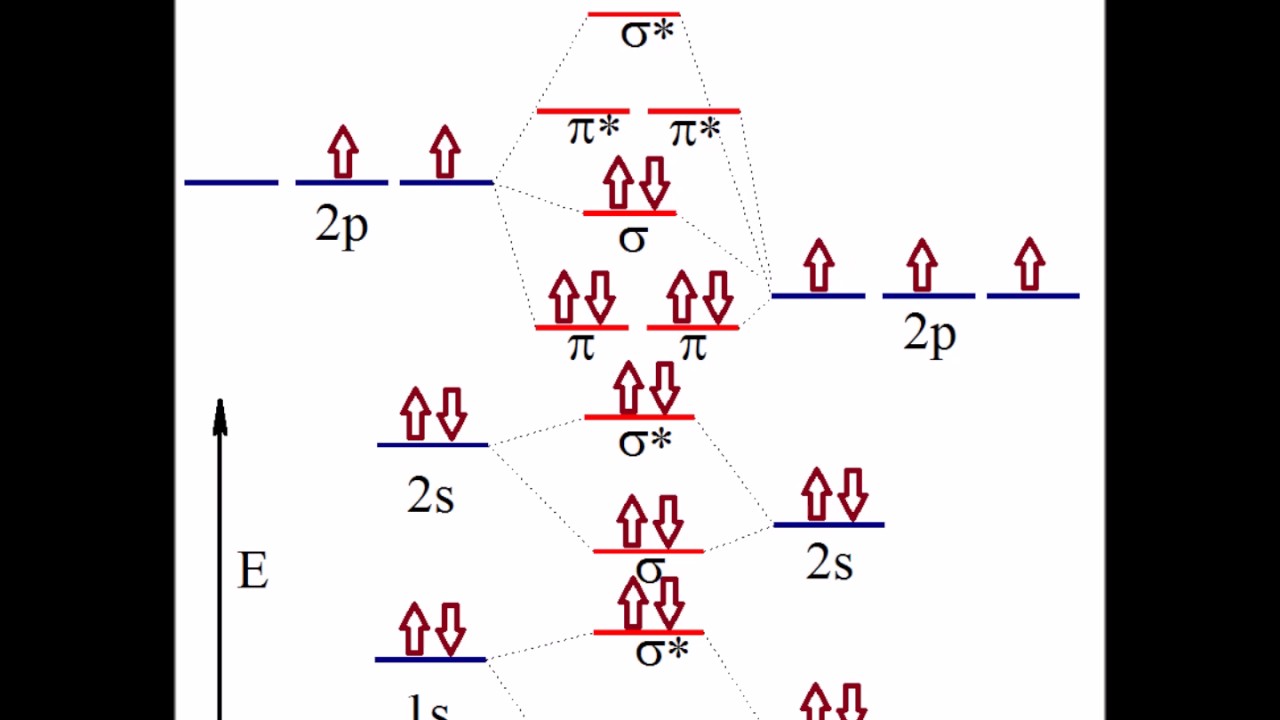

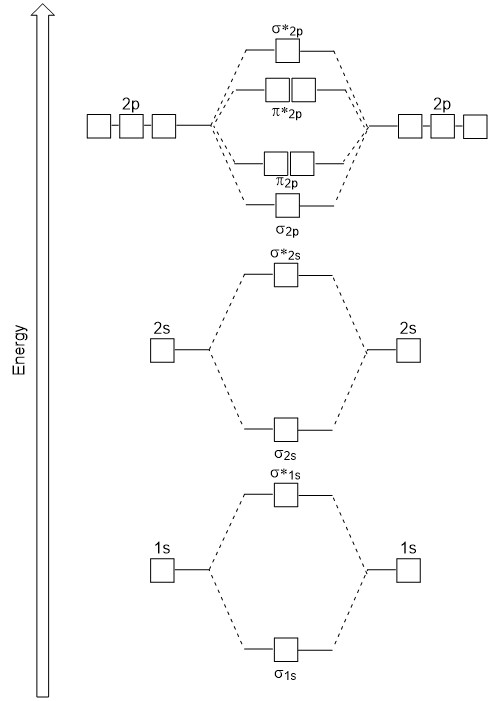


![SOLVED:5.0 [20 pts] Consider the heteronuclear diatomic ...](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/1d261a94a8c543ecb38c77d0d5a38b69.jpg)


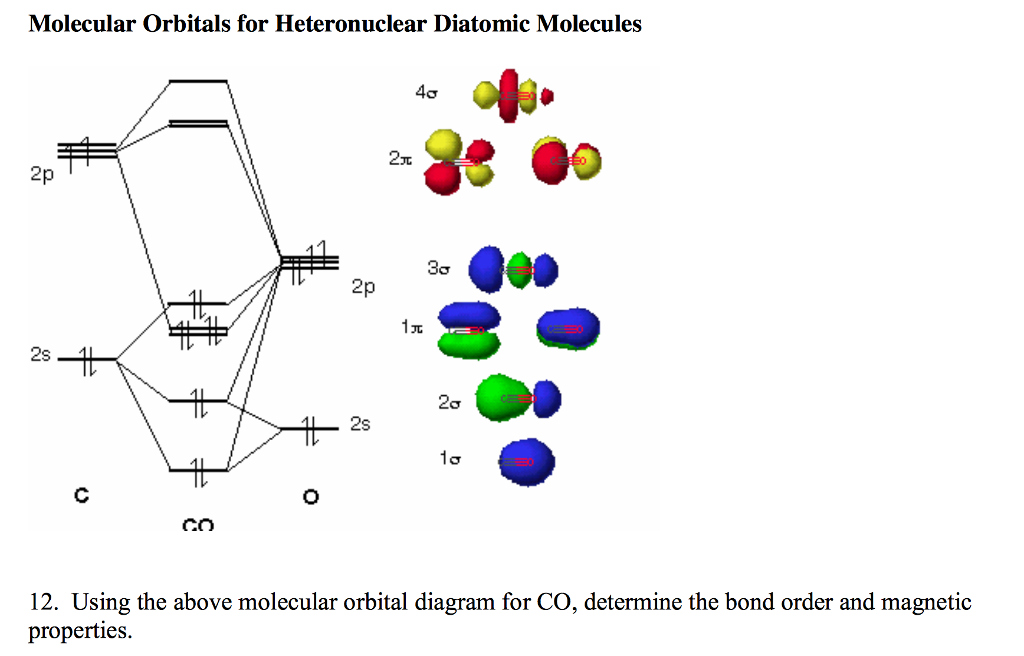









0 Response to "38 heteronuclear molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment