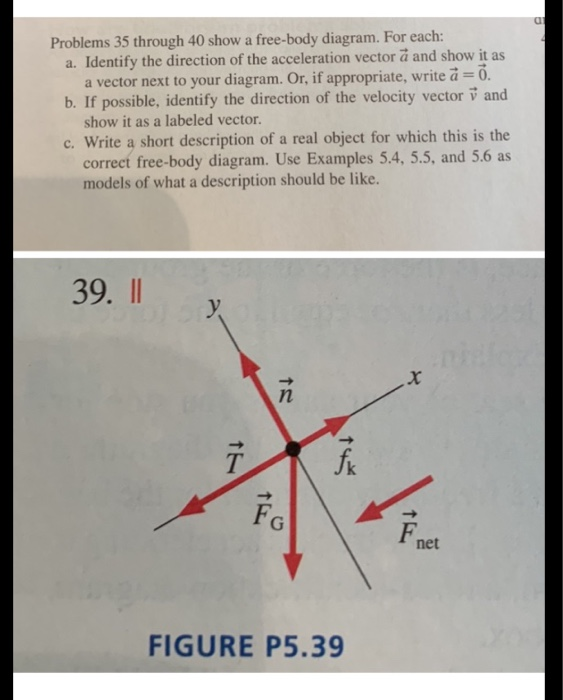
38 free body diagram acceleration
Accelerations in a Free Body Diagram - Physics Stack Exchange As we know the acceleration is downwards the net resultant force will be downwards. The vector sum of M g and T is M g − T (downwards) and is equal to M × (acceleration i.e. a) Hence. M g − T = M a. Alternative Let us consider direction of acceleration -ve We will write equation as. − M g + T = − M a (net external force=mass× ... DOC Free Body Diagrams Worksheet - Reynolds School District A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: A flying squirrel is gliding (no wing flaps) from a tree to the ground at constant velocity. Consider air resistance. A free-body diagram for this situation looks like this: A rightward force is applied to a book in order to move it across a desk with a rightward acceleration.
3-3 Constant Velocity, Acceleration, and Force - WebAssign WebAssign is an online learning platform built by educators that provides affordable tools to empower confident students in a virtual learning environment.

Free body diagram acceleration
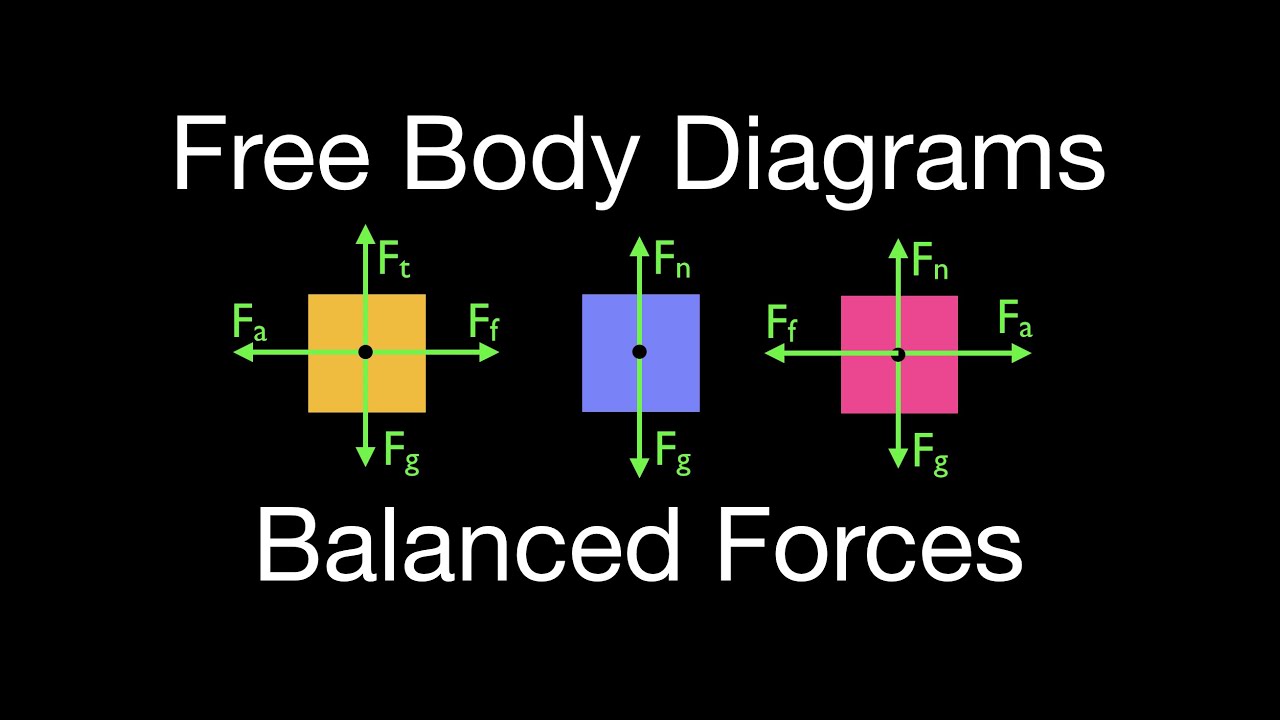
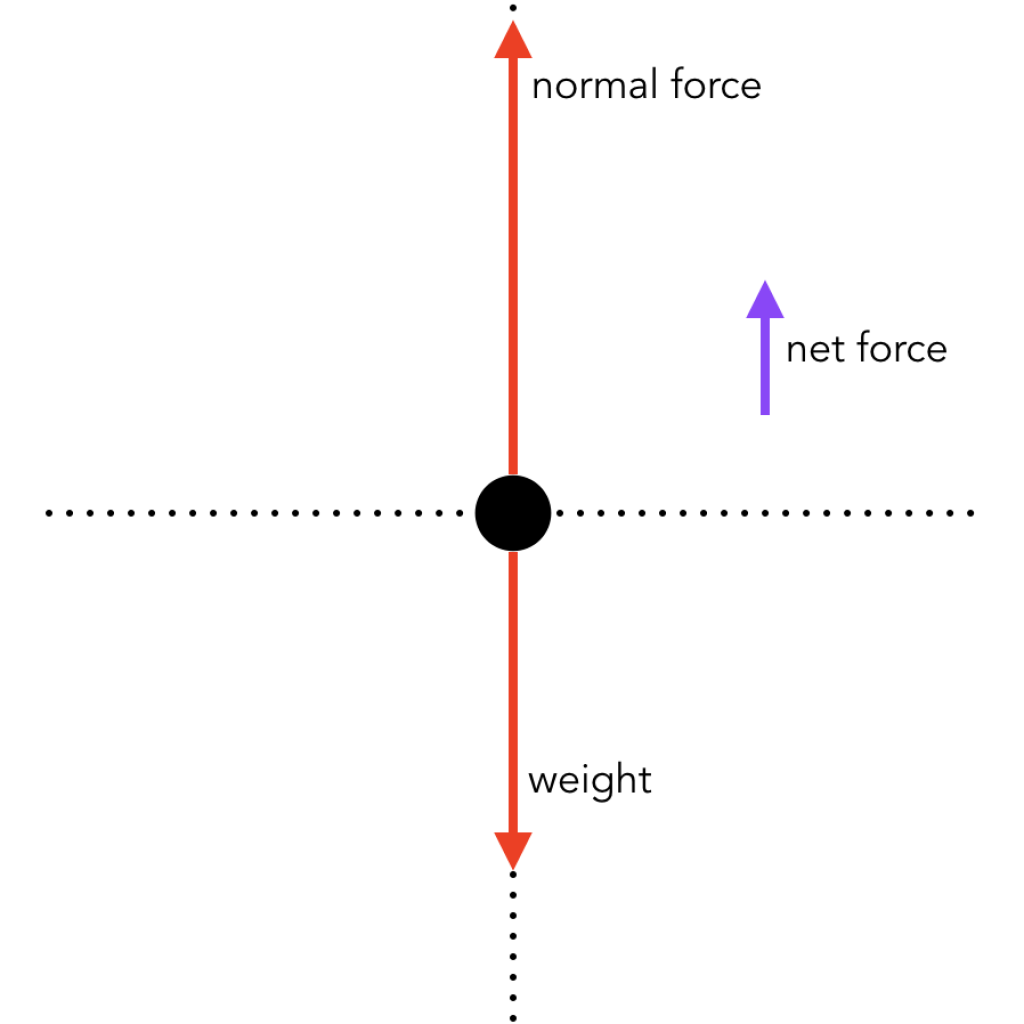
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - Physics Classroom Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. Free body diagram - Wikipedia In statics all forces and moments must balance to zero; the physical interpretation is that if they do not, the body is accelerating and the principles of statics do not apply. In dynamics the resultant forces and moments can be non-zero. Free body diagrams may not represent an entire physical body. Net acceleration, free body diagrams, velocity, force ... Net acceleration, free body diagrams, velocity, force normal Thread starter alexandria; Start date Mar 29, 2016; Mar 29, 2016 #1 alexandria. 169 2. Homework Statement . Homework Equations relevant equations are provided with each question below The Attempt at a Solution
Free body diagram acceleration. PDF Free Body Diagrams Practice Problems Free Body Diagrams Practice Problems Construct free-body diagrams for the various situations described below. Use the following forces. 1. A book is at rest on a table top. Diagram the forces acting on the book. 2. A girl is suspended motionless from a bar which hangs from the ceiling by two ropes. Diagram the forces acting on the girl. 3. Determining the Net Force The net force concept is critical to understanding the connection between the forces an object experiences and the subsequent motion it displays. In this Lesson, The Physics Classroom describes what the net force is and illustrates its meaning through numerous examples. Free Body DIagrams - e=mc2andallthat In diagram C, the the apple and scales are in an elevator that is accelerating downwards at 1.00 metres per second per second. The resultant upward force must therefore be smaller than the downward weight as shown in the free body diagram. The scales show a reading of 0.881/9.81 - 0.089 806 kg = 89.806 g. Forces, Free Body Diagrams, and Newton's First Law of ... If you were asked to make that box accelerate, what would you do to it? You might think to push it (applied force), or attach a string to it and pull it (tension force). But before the box began to move, it would have to overcome the force of friction. If you pushed on it a little, the box’s free-body diagram ...
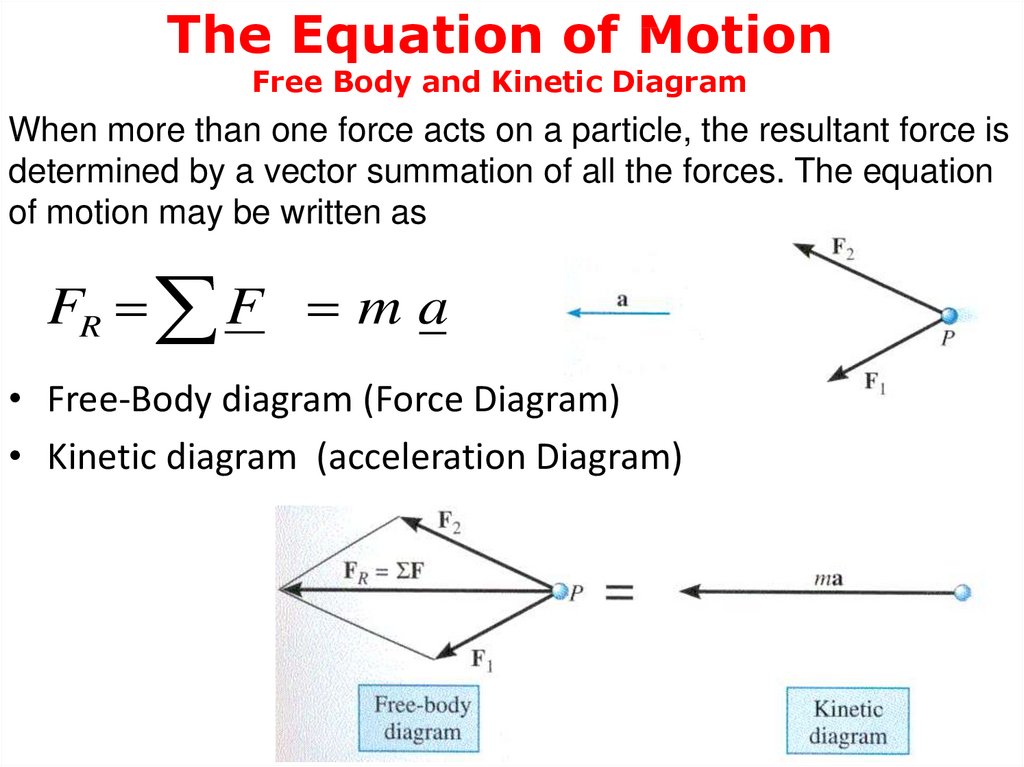
Solved The free-body diagram shows the all of the forces ... Part. Question: The free-body diagram shows the all of the forces acting on an object of mass m = 6.22 kg. The three forces have magnitudes F1 = 13.3 N, F2 = 27.9 N, and F3 = 19.8 N, with directions as indicted in the diagram, where θ = 35.3 degrees. Part (a) Write an expression for the x-component of the acceleration in terms of the symbols ... Applications - Newton's Laws of Motion As always, begin with a "free body diagram". Tension T acts upward on the lamp while the force of gravity pulls down with force w, the weight of the lamp. The net force is the vector sum of these two forces. The lamp is not accelerating so the force up must equal the force down. 6.4: Free-Body Diagrams - Physics LibreTexts November 6, 2020 - The figure below shows, as an example, a free-body diagram for block 1 in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\), in the presence of both a nonzero acceleration and a kinetic friction force. The diagram includes all the forces, even gravity and the normal force, which were left out of the picture in Figure ... Free Body Diagram - Examples, Problems and Solutions Your acceleration vector should be drawn and labelled to the side of the dot, not touching it. Write a=0 if there is no acceleration. Free Body Diagram Problems and Solutions Problem 1. The pulley in the mechanism depicted in the figure is smooth. String is massless and inextensible. Find acceleration of the system a, tensions T1 and T2 .
Free Body Diagrams - What are They and How are They Used ... Making a Free Body Diagram is a process of drawing a component or system as one simple, immovable solid. Identify the external forces that act upon the body as well as their magnitude and direction. For rigid bodies add dimensions that locate forces. Add in the reactions and rotate the coordinate system if needed. 1. Draw the object Force | Free Body Diagrams | Physics | Don't Memorise ... Understanding free body diagrams is crucial to understanding the concept of Net Force. Watch this video to know more! To learn more about Force, enrol in our... What is a Free-Body Diagram and How to Draw it (with ... A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. The external environment (other objects, the floor on which the object sits, etc.), as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects, are omitted in a free-body diagram. Below you can see an example of a free-body diagram: 5.7: Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - Physics LibreTexts
Braingenie | Calculating the acceleration of an object using ... Engaging math & science practice! Improve your skills with free problems in 'Calculating the acceleration of an object using free-body diagrams and Fnet = ma' and thousands of other practice lessons.
Free Body DIagrams - e=mc2andallthat Situation diagram for a person stepping off an unmoored boat; and free body force diagrams for the person and the boat. Note different style of arrow for forces and acceleration. The person pushes back on the boat (gripping the boat with friction as above).
Force Calculations Free Body Diagram: A sketch where a body is cut free from the world except for the forces acting on it. In the bridge example the free body diagram for the top of the tower is: ... The acceleration due to gravity on Earth is 9.81 m/s 2, so a = 9.81 m/s 2. F = 80 kg × 9.81 m/s 2. F = 785 N.
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams The motion of objects is determined by the relative size and the direction of the forces that act upon it. Free-body diagrams showing these forces, their direction, and their relative magnitude are often used to depict such information. In this Lesson, The Physics Classroom discusses the details ...
402-C: Finding Acceleration: Finding Acceleration from a ... Draw a free-body diagram that illustrates those forces, then find the net force, and acceleration acting on the object. If you have gone ahead and you know how to calculate specific forces such as weight, normal force, and friction, please do not include these forces in your free-body diagrams.
Free Body Diagram - Definition, Examples, Solved Problems ... Bodies other than the free body diagram Constraints Internal Forces Velocity and Acceleration Vectors What is the purpose of a free body diagram? Free body diagrams are tools that are used to visualize the force and moments applied to a body and to calculate the resulting reactions in many types of mechanics problems.
Elevator Physics - Boston University Sketch separate free-body diagrams for you, the elevator by itself, and the combined system of you plus the elevator for these three situations: the elevator has no acceleration (standing still or moving with constant velocity) the elevator has an upward acceleration (accelerating upward, or decelerating while on the way down)
Free Body Diagrams: Calculating Net Force And Acceleration ... Quiz Flashcard. To calculate net force: add vectors in the same direction; subtract vectors in the opposite direction. To calculate acceleration: acceleration = net force / mass Use the following abbreviations for units: newtons = N meters per second squared = m/ss Use the following for directions: right, left, up, down. Questions and Answers. 1.
Question about a simple free body diagram | Page 2 ... 2,747. 957. sysprog said: the second diagram is a free-body diagram; No, it's not. A free body diagram contains only one body, and it shows all the forces acting on that one body. To analyze a situation with more than one body, you draw a separate free body diagram for each body.
Khan Academy Review the key concepts, equations, and skills for Newton's second law of motion, including how to analyze motion in the x- and y-directions independently.
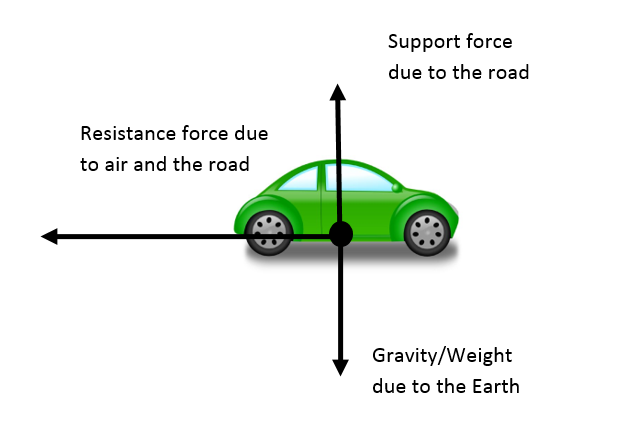
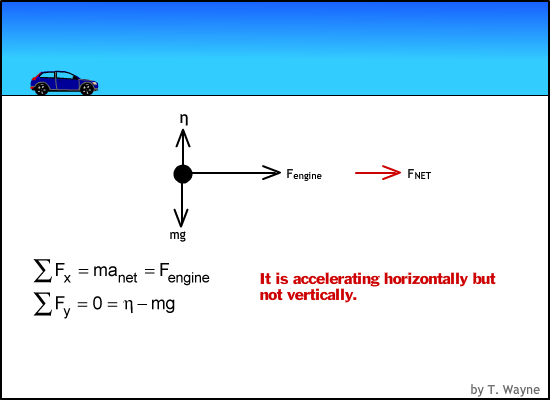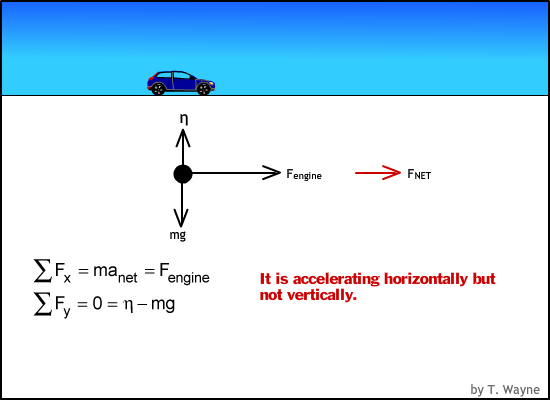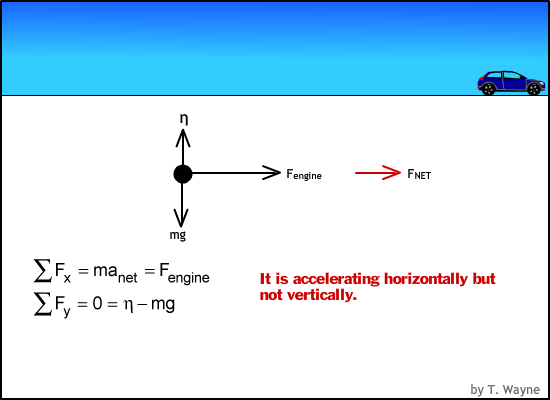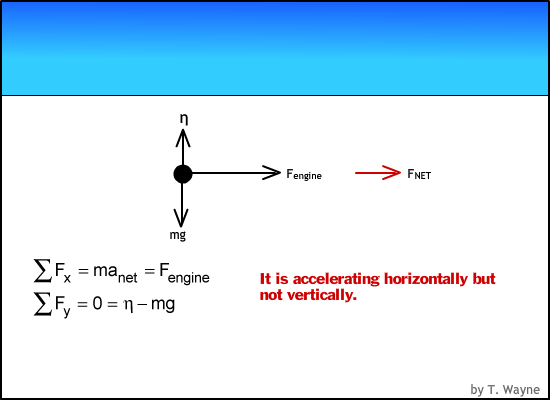
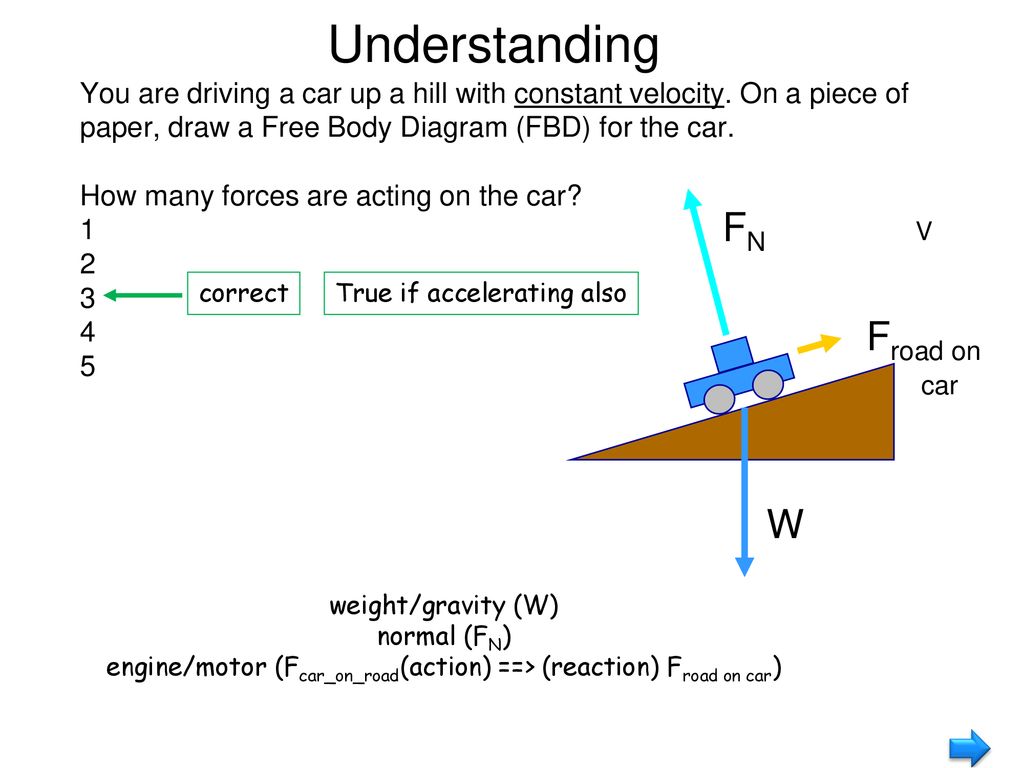
acceleration and force Physics Free Body Diagrams a Explanation Physics : acceleration and force Free Body Diagram • A free body diagram is a picture representation of all forces acting on an object. • We use arrows to represent the forces and indicate their direction and magnitude. • Magnitude expressed by number and arrow size.
5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams | University Physics Volume 1 Explain the effects with the help of a free-body diagram. Use free-body diagrams to draw position, velocity, acceleration, and force graphs, and vice versa.
Accelerating and braking - University of Illinois Urbana ... accelerate free body diagram components applies backwards moments to both wheels, causing them to slow down. To maintain non-slip, there is a backwards force from the ground at the point of contact. Because the wheel is slowing down, the car pushes forward on the axle.
How to Calculate Acceleration With Friction | Sciencing December 5, 2020 - The friction force depends on the weight of an object plus the coefficient of friction between an object and the surface on which it slides.
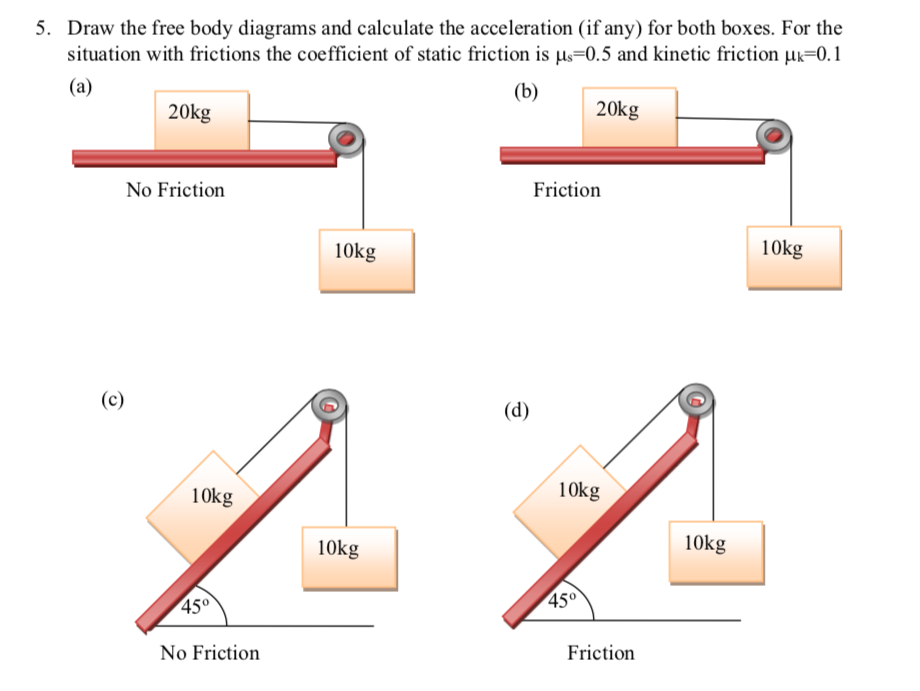
PDF Subject: Forces (Free Body Diagrams; F = ma) acceleration with which the blocks move. Assume there is no friction. The problem asks for the acceleration, and therefore "Forces" is the best way to approach this problem (because if we find the net force, we've found the acceleration - via ΣF = ma .). 1. Draw one Free Body Diagram for each object.
PDF Forces and Free-Body Diagrams acceleration. Draw a free-body diagram. The applied force arrow points to the right and is larger than the frictional force since the object is accelerating. Since the sled is on the ground, the normal and gravitational force are balanced. Problem 7 A football is moving upwards toward its
PDF Unit 4.2 Free Body Diagrams - SCASD Unit 4.2 Free Body Diagrams Teacher: Dr. Van Der Sluys Objectives •Net Forces •Free Body Diagrams •Problem Solving with Free Body Diagrams Vocabulary •Weight is the force that results from the acceleration of gravity on a mass. •A contact force results when two objects in contact with one another are exerting equal and opposite forces ...
Introduction to forces and free body diagrams review (article) ... Review the key concepts and skills for forces, including how to draw free body diagrams.
How to Use Free-Body Diagrams to Solve Motion Problems 11 Jan 2022 — Keeping track of the multitude of forces that are acting on an object is the challenge when solving problems related to force and acceleration.
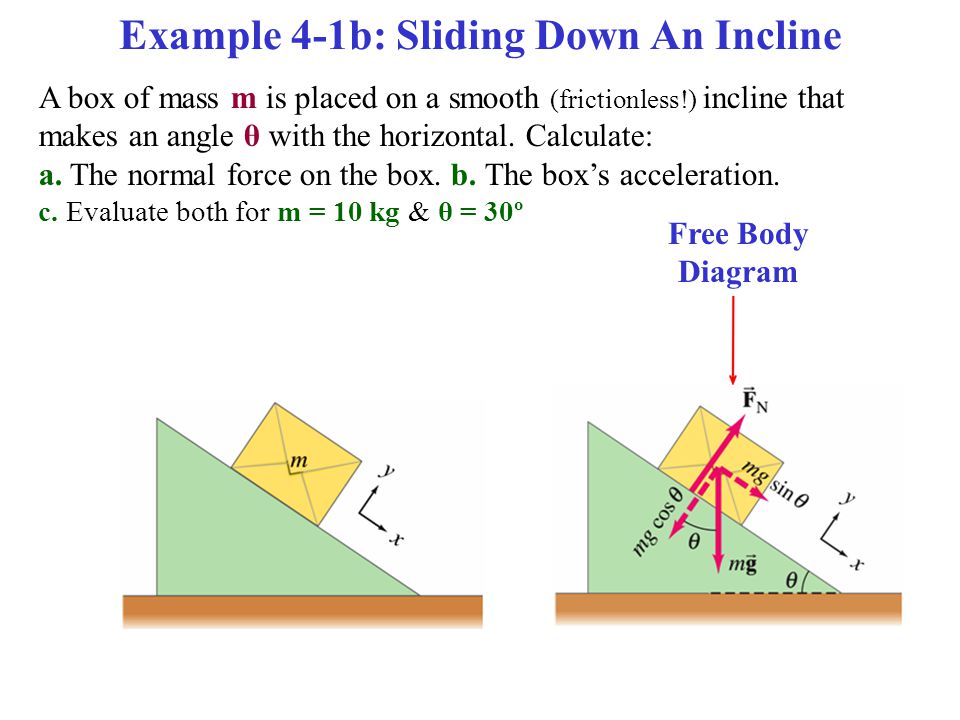
newtonian mechanics - Free body diagram of block on ... So when drawing the free-body diagram (still only containing w → and n → ), their sum will point along the acceleration. In the three cases mentioned above, this resulting force will change direction, according to how fast the incline moves leftwards, because n → is affected.
How to Draw a Free Body Diagram: 10 Steps (with Pictures) Since the Free Body Diagram shows the forces, if you know the mass you can use the equation F=ma. F is the force, M is the mass and A is the acceleration. The action reaction forces are equal to each other and are in opposite directions. Thanks! Yes No Not Helpful 5 Helpful 6 Question What are the best equations to solve a free body diagram?
Finding Acceleration - Physics Classroom Equipped with information about the forces acting upon an object and the mass of the object, the acceleration can be calculated. Using several examples, The Physics Classroom shows how to calculate the acceleration using a free-body diagram and Newton's second law of motion.
Weight and Free Body Diagrams. Weight; The weight of an object is the force with which a body is attracted to the earth.; Weight = mass x acceleration due to gravity (w = mg) Since "g" is approximately the same everywhere on the earth's surface, weight is often quoted in units of mass.
Finding Individual Force Values When the acceleration of an object is known and the mass is known, it is often possible to determine the values of the individual forces acting upon an object. In this Lesson, The Physics Classroom shows how this can be done through numerous examples.
5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - General Physics Using ... A free-body diagram is a useful means of describing and analyzing all the forces that act on a body to determine equilibrium according to Newton's first law or acceleration according to Newton's second law. Key Equations Conceptual Questions
5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - OpenStax September 19, 2016 - Note: If there is acceleration, we do not directly include it in the free-body diagram; however, it may help to indicate acceleration outside the free-body diagram. You can label it in a different color to indicate that it is separate from the free-body diagram.
Net acceleration, free body diagrams, velocity, force ... Net acceleration, free body diagrams, velocity, force normal Thread starter alexandria; Start date Mar 29, 2016; Mar 29, 2016 #1 alexandria. 169 2. Homework Statement . Homework Equations relevant equations are provided with each question below The Attempt at a Solution
Free body diagram - Wikipedia In statics all forces and moments must balance to zero; the physical interpretation is that if they do not, the body is accelerating and the principles of statics do not apply. In dynamics the resultant forces and moments can be non-zero. Free body diagrams may not represent an entire physical body.
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - Physics Classroom Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.

















0 Response to "38 free body diagram acceleration"
Post a Comment