37 first class lever diagram
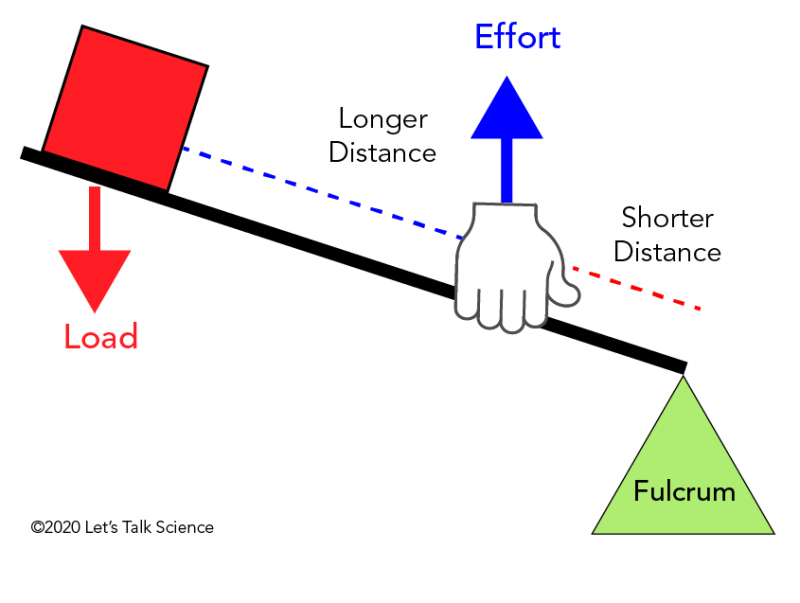
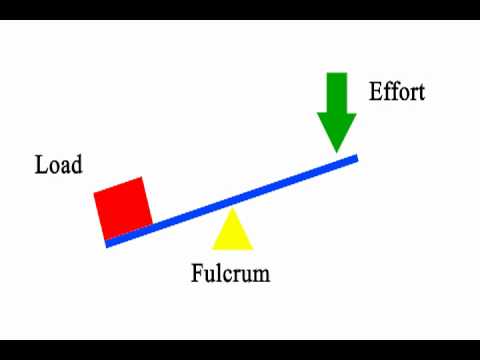
Simple Machines - Levers - Let's Talk Science In a first class lever, the fulcrum is located between the load and the effort. In a first class lever, the fulcrum is located between the load and the effort. When the fulcrum is closer to the load, then less effort is needed to move the load (©2020 Let's Talk Science). ... First class lever on free end RPD. | Download Scientific ... Download scientific diagram | First class lever on free end RPD. from publication: Mastication force analysis on the fulcrum point of first class lever on lower jaw distal free end denture | The ...
gizmos.explorelearning.com › indexLevers Gizmo : Lesson Info - ExploreLearning Identify the parts of a lever. Discover that a lever can be used to lift heavy objects using less force. Describe the relationship between the applied force (effort) needed to lift a load and the distance from the fulcrum to the applied force. Calculate mechanical advantage. Diagram a first, second, and third-class lever. VOCABULARY:

First class lever diagram
First Class Lever | ClipArt ETC First Class Lever. "The lever of the first class has the fulcrum between the power and the weight.". Examples: a common crowbar, a pump handle, scissors, a seesaw. -Foster, 1921. Simple Machines: How Does a Lever Work? - Owlcation First Class Lever. The effort is on one side of the lever and the load is on the other side. The fulcrum is in the middle. ... How Levers Work - The Physics. In the diagram below, two forces act on the lever. This is a schematic or diagram, but it symbolically represents any of the real life levers mentioned above. Levers - Engineering ToolBox A lever mechanism where the input effort is higher than than the output load is often characterized as a third-class lever mechanism. Example - Third-Class (Order) Lever. A force (weight) of 1 pound is exerted at a distance of 2 ft from the fulcrum. The effort force at a distance of 1 ft from the fulcrum can be calculated as. F e = F l d l / d ...
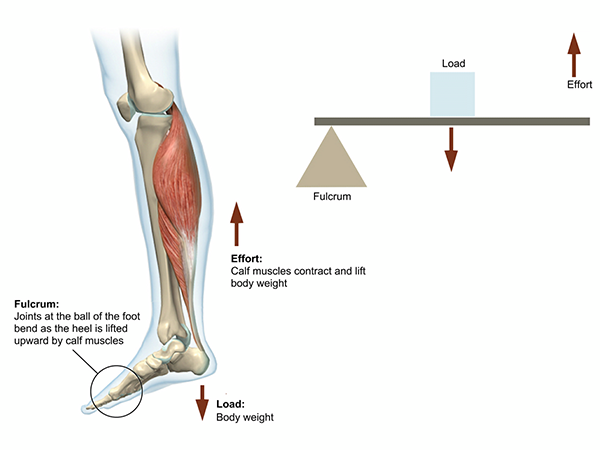
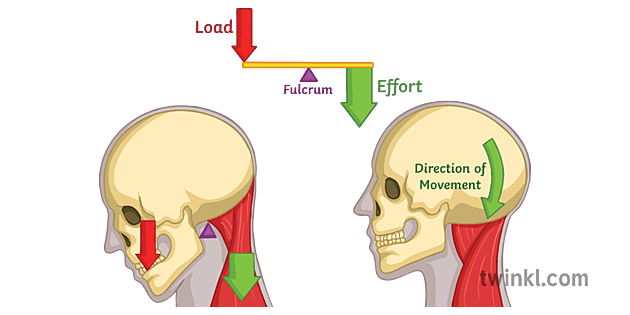
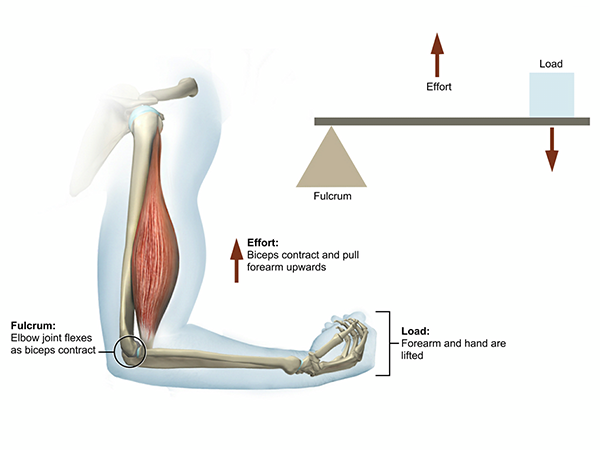
First class lever diagram. cbsepython.in › artificial-intelligence-sampleArtificial Intelligence Sample Paper Class 9 Code 417 - CBSE Oct 27, 2021 · Artificial Intelligence Sample Paper Class 9 Code 417 2021-22 Term-1. SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER FOR TERM -1. Max. Time Allowed: 1 Hour . Max. Marks: 25. General Instructions: 1. This Question Paper is divided into 03 sections, viz., Section A, Section B and Section C. 2. Section A is of 05 marks and has 06 questions on Employability Skills. 3. Examples of a first-class lever | Download Scientific Diagram Download scientific diagram | Examples of a first-class lever from publication: ERGONOMICS IN BRIDGE ENGINEERING | Ergonomics is the study of people while they use equipment in specific ... 1st Class Lever Anatomy and Physiology - Innerbody The first class lever is one of three classes of levers and is one possible arrangement of muscles, bones, and joints found in the human body. While less common in the body than second and third class levers, the first class lever system is found in the neck at the atlanto-occipital joint and in the elbow joint. Anatomy First, second and third class levers in the body ... First class lever This type of lever is found in the neck when raising your head to head a football. The neck muscles provide the effort, the neck is the fulcrum, and the weight of the head is the...
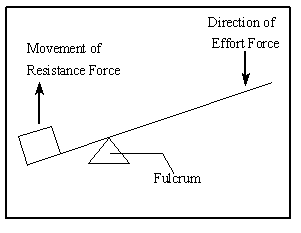
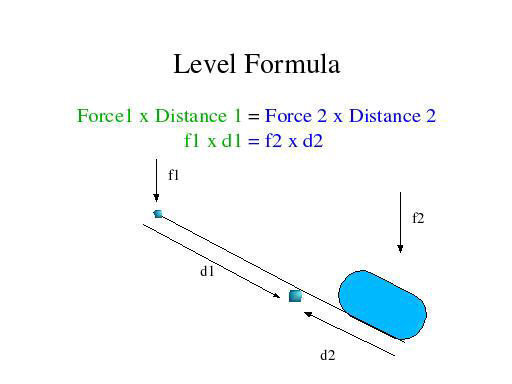
PDF Simple Machines : Lever There are three classes of levers. In first class levers as shown in diagram 1: · the fulcrum is positioned between the effort and the load · the effort is smaller than the load There are six simple machines that all other machines are made out of. Lever | Engineering | Fandom A First-Class Lever is a lever in which the fulcrum is located in between the Effort Force and the Resistance Force, and works by having a force be applied by pulling or pushing onto a section of the bar, which causes the lever to swing about the fulcrum, overcoming the resistance force. Examples: Seesaw (also known as a teeter-totter) Lever - LEGO® Education This model shows a first class lever. It has the effort and load at opposite ends with the pivot in between. This model uses the least effort to move the load. A2 This model shows a second class lever. It has the effort and pivot at opposite ends and the load in between. The effort needed to move the load is about half the load force. byjus.com › physics › wheel-and-axleWheel And Axle - Mechanism & Working | Simple Machines Observed as drawings in technological Greek texts, it is one of the first six simple machines identified by the Renaissance scientists. The simple concept of force transformation gives shape to this machine where two segments i.e. a wheel is attached to a smaller axle and their rotations create the force.
Types Of Lever - Examples, Mechanism, Application, Definition First Class Lever This is a type of lever which has the fulcrum in between the weight and the force applied. Its order is represented as force-fulcrum-weight. This is the most basic type of lever. Example: Our hand pushing an object or seesaws, crowbars. Using scissors represents the use of two first-class levers. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Social_impact_bondSocial impact bond - Wikipedia History. The social impact bond is a non-tradeable version of social policy bonds, first conceived by Ronnie Horesh, a New Zealand economist, in 1988. Since then, the idea of the social impact bond has been promoted and developed by a number of agencies and individuals in an attempt to address the paradox that investing in prevention of social and health problems saves the public sector money ... Types of levers:first, second, third class lever examples ... The three types of levers are as follows: (1) First Class lever or class I lever, (2) Second Class lever or class II lever, and. (3) Third Class lever or class III lever. These types are based on the relative position of the fulcrum, load, and effort in the lever body. Examples of a First-Class Lever | Download Scientific Diagram A pair of scissors is a double lever of the first class. The first-class lever is illustrated in Figure 1. Second-class levers have the load between the effort and the fulcrum. A wheelbarrow is a ...
What Is a First-Class Lever? - Reference.com A first-class lever is a beam, rod or stick with the load at one end, the fulcrum in the middle and the force applied on the other end. A good example of a first-class lever is a child's see-saw. Levers are simple machines — apparatuses composed of few or no moving parts that make performing a task easier by one or more of four methods:
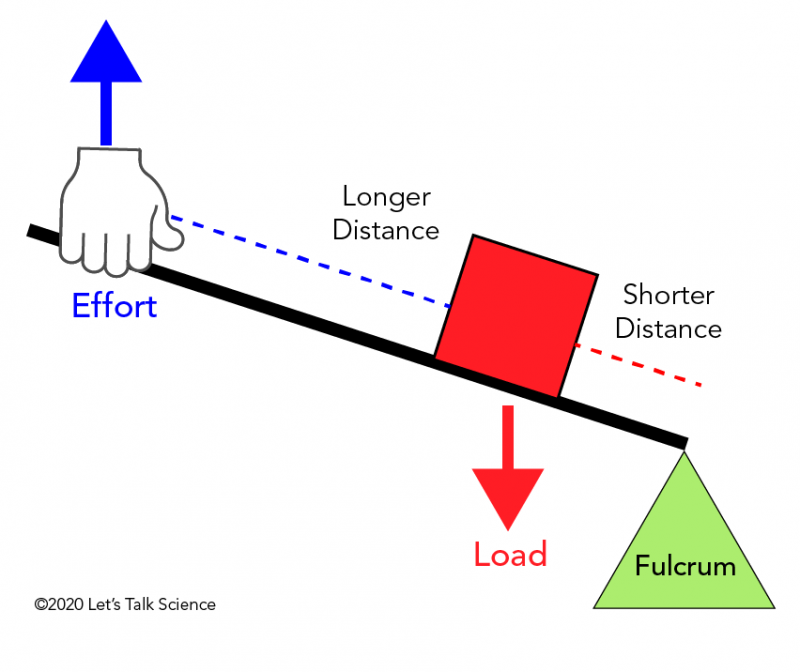
PDF Levers - Polytech High School "First Class Lever" • A first-class lever is a lever in which the fulcrum is located between the input effort and the output load. • In operation, a force is applied (by pulling or pushing) to a section of the bar, which causes the lever to swing about the fulcrum, overcoming the resistance force on the opposite side. Examples:
First Class Lever Worksheets - Kiddy Math First Class Lever - Displaying top 8 worksheets found for this concept.. Some of the worksheets for this concept are Levers, , Misp simple machineslevers work 2 l1 clever lever 3, Misp simple machineslevers work 1 l3 clever lever 1, Levers, Name simple machines work section 83, Simple machines, The 6 simple machines.
Class One Lever Examples - Softschools.com The image below is an example of a Class One Lever, sometimes called a First Class Lever. Examples of Class One Lever: All classes of levers have four basic parts: Beam- The lever, a wooden plank or metal bar resting on the fulcrum. Fulcrum- the pivot or the turning point.
TIphysics.com Physics Bell Ringer: First-Class Levers - ID ... Draw a force diagram for the first-class lever shown on the previous page. Draw the diagram in the Graphs & Geometry application below or on a blank piece of paper. A. A sample force diagram is shown below. Here N is the normal force, F r is the resistance force (and is equal to W, the weight of the load), and F e is the effort force.
Mechanical Advantage of a Lever, Mechanical Advantage ... The mechanical advantage of a lever is the ratio of the load the lever overcomes and the effort a person or system applies to the lever to overcome some load or resistance. In simple words and as per the formula, it's the ratio of load and effort. The formula of the mechanical advantage(MA) of a lever is given as MA = load/effort. Another form of this ma formula is MA = Effort Arm/Load Arm ...
Movement Analysis First, second and third class levers. 2. Mechanical advantage. 3. The planes of movement and axes of rotation when performing sporting movements ...25 pages
Levers - Coggle Diagram A teeter-totter, a car jack, and a crowbar are all examples of first class levers. First class levers are very useful for lifting large loads with little effort. In a second class lever, the load is located between the effort and the fulcrum. If the load is closer to the fulcrum than the effort, then less effort will be required to move the load.
First Class Lever First Class Lever. Examples: • See-saw • Top of a Hammer to get out nails • Oars • Scissors. Lever Definition: a simple machine consisting of a bar that pivots at a fixed point, called a fulcrum. First Class Lever Definition: The fulcrum is located between the input force and the load. Mechanical Advantage: • MA will be equal to, greater
What are examples of 1st, 2nd, and 3d class levers ... First Class Lever. This is a type of lever which has the fulcrum in between the weight and the force applied. Its order is represented as force-fulcrum-weight. This is the most basic type of lever. Examples. Our hand pushing an object or seesaws, crowbars. Using scissors represents the use of two first-class levers. A wheel and axle is also an ...
1st,2nd,and 3rd Class Levers Diagram | Quizlet First Class lever. fulcrum in the middle between the effort force and the resistance arm. Lever-A beam on a fulcrum-Smaller force can move more weight. First class lever examples. Scissors, Can opener. Second Class lever. The load is between the fulcrum and the effort force.
Three Lever Classes by Ron Kurtus - Succeed in ... A fulcrum is an object about which the lever pivots. There are three classes levers, according to the position of the fulcrum. Class 1 has the fulcrum placed between the effort and load. Class 2 has the load between the effort and the fulcrum. Class 3 has the effort between the load and the fulcrum. Each has its own uses and advantages.
› category › tvTV Archives - Hollywood.com Click to get the latest TV content. Sign up for your weekly dose of feel-good entertainment and movie content!
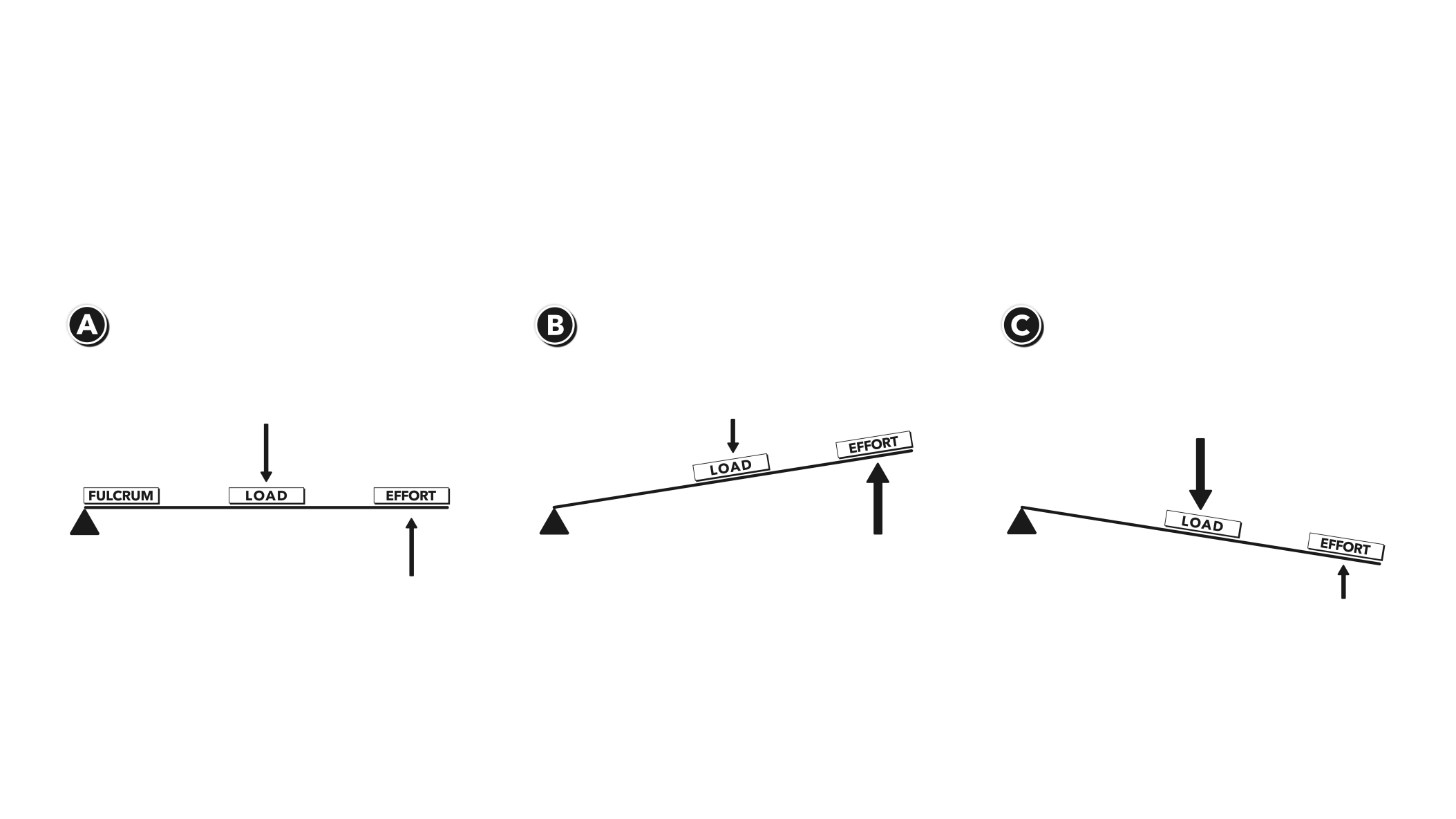
Click on the diagram that shows a first-class lever. Question #85010. Click on the diagram that shows a first-class lever. General. 1837 students attemted this question. Bookmark. Add Comment. Share With Friends. Report.
The diagram shows a first class lever. How far down will ... Get an answer for 'The diagram shows a first class lever. How far down will the effort side have to move to lift the load 1 m?' and find homework help for other Science questions at eNotes
› selina-solutions › icseICSE Selina Solutions for Class 9 Physics ICSE Chapter 4 ... The diagram below in Fig. 4.12 shows a device which makes the use of the principle of transmission of pressure. (i) Name the parts labelled by the letters X and Y. (ii) Describe what happens to the valves A and B and to the quantity of water in the two cylinders when the lever arm is moved down (iii) Give reasons for what happens to the valves ...
Pivot diagram of a Class 1 lever - Science Learning Hub Different classes of levers are identified by the way the joint and muscles attached to the bone are arranged. For the Class 1 lever the pivot lies between the effort and load. A see saw in a playground is an example of a Class 1 lever where the effort balances the load.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › ArchimedesArchimedes - Wikipedia Archimedes was born c. 287 BC in the seaport city of Syracuse, Sicily, at that time a self-governing colony in Magna Graecia.The date of birth is based on a statement by the Byzantine Greek historian John Tzetzes that Archimedes lived for 75 years before his death in 212 BC.
Human Body Levers And Vector Diagrams - Studying Diagrams Anatomy In a first class lever system the fulcrum or pivot point is located on the lever between the effort force and load or resistance being moved. Free body diagrams A free body diagram models the forces acting on an object. In the human body third-class levers have the pivot point at one end.
Levers - Engineering ToolBox A lever mechanism where the input effort is higher than than the output load is often characterized as a third-class lever mechanism. Example - Third-Class (Order) Lever. A force (weight) of 1 pound is exerted at a distance of 2 ft from the fulcrum. The effort force at a distance of 1 ft from the fulcrum can be calculated as. F e = F l d l / d ...
Simple Machines: How Does a Lever Work? - Owlcation First Class Lever. The effort is on one side of the lever and the load is on the other side. The fulcrum is in the middle. ... How Levers Work - The Physics. In the diagram below, two forces act on the lever. This is a schematic or diagram, but it symbolically represents any of the real life levers mentioned above.
First Class Lever | ClipArt ETC First Class Lever. "The lever of the first class has the fulcrum between the power and the weight.". Examples: a common crowbar, a pump handle, scissors, a seesaw. -Foster, 1921.




















0 Response to "37 first class lever diagram"
Post a Comment