40 newton's second law diagram
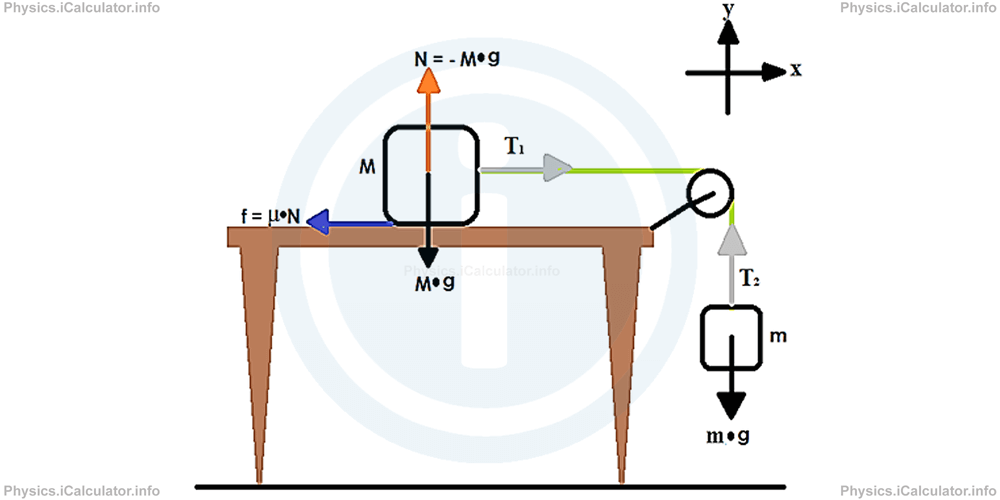
A Kinetic Diagram is a diagram that represents the acceleration vector of Newton's Second Law, or the right hand side of the F = ma equation. On a kinetic ... In the horizontal direction, the tension in the string acts in the + x direction on the cart while the friction force between the cart's tires and the surface of the track acts in the − x direction. Newton's second law, in the x and y directions, respectively, are ( 7 ) Fnet,2x = T − f = m2a ( 8 ) Fnet,2y = FN − m2g = 0
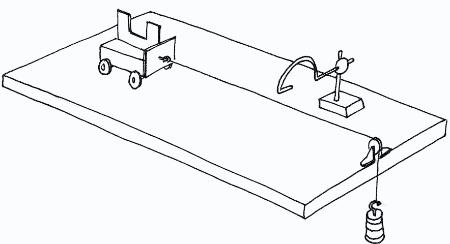
Newton's Second Law 3 Figure 2: Free-Body Diagram of Forces on Cart and Hanging Mass Since force is a vector quantity, it is necessary to decide what are the positive and negative directions so that each force can be labelled as being either positive or negative. A useful rule is to say that the direction of motion is the positive direction.
Newton's second law diagram
Shows how to draw free body diagrams for simple one dimensional motion. Free-body diagrams show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upo... Mission NL7: Newton's Second Law. Mission NL7 pertains to Newton's Second Law. You must understand how alterations in mass and net force would affect the acceleration of an object. The mission consists of 32 questions organized into 9 Question Groups. You must answer one question from each Question Group to complete the mission. Newton's Second Law Objective The Newton's Second Law experiment provides the student a hands on demonstration of "forces in motion". A formulated analysis of forces acting on a ... Free-body diagrams of the forces on the cart and hanging mass are shown in Figure 4. Figure 3: Inclined Track with Hanging Mass .
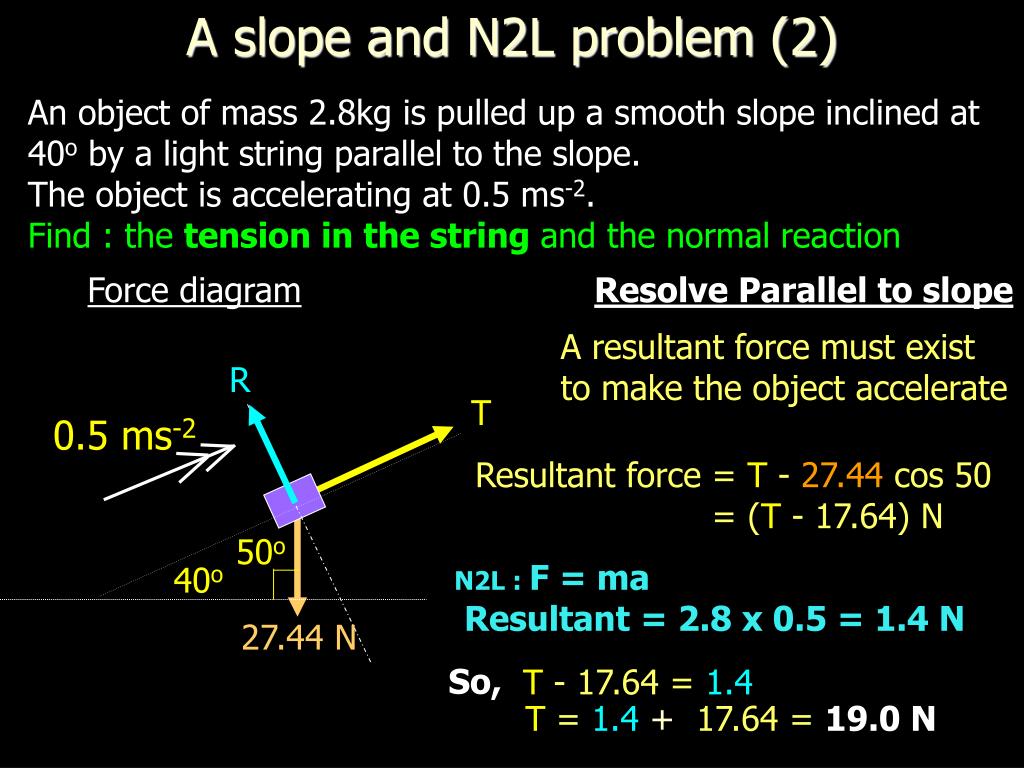
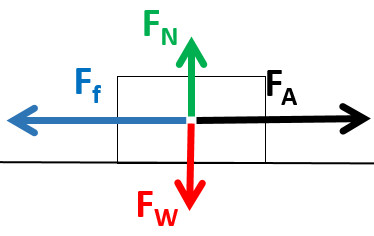
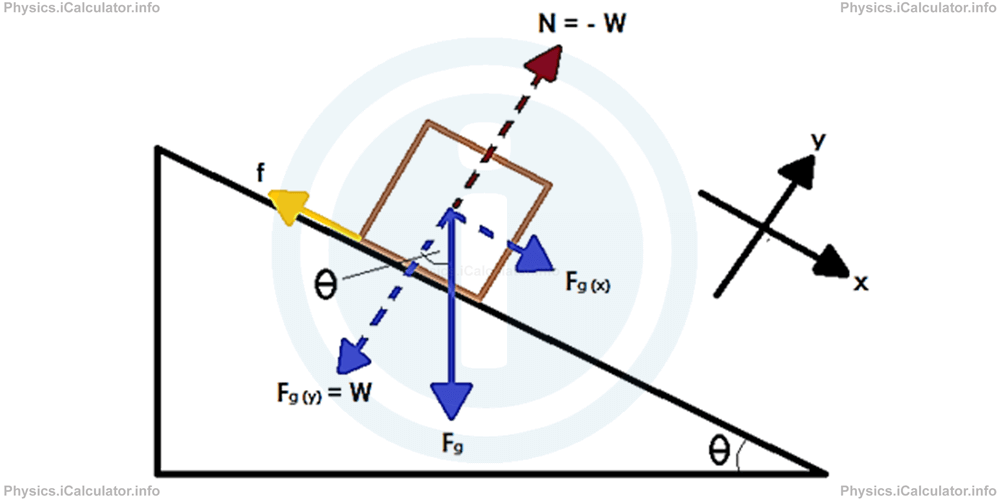
Newton's second law diagram. Newton's Second Law "Change of motion is proportional to the force applied, and take place along the straight line the force acts." Newton's second law for the gravity force - weight - can be expressed as. W = F g = m a g = m g (1) where. W, Fg = weight, gravity force (N, … Once a free-body diagram is drawn, we apply Newton's second law. This is done in Figure 6.2(d) for a particular situation. In general, once external forces are clearly identified in free-body diagrams, it should be a straightforward task to put them into equation form and solve for the unknown, as done in all previous examples. The free-body diagram shows all of the forces acting on the system of interest. The dot represents the center of mass of the system. Each force vector extends ... 28 Experiment 5: Newton's Second Law FREE-BODY DIAGRAM SOLUTION METHOD: INSTRUCTIONS Step 1: Sketch the problem/situation and specify the coordinate system for each object in your system. Step2: Draw all forces (arrows that represent these vectors) acting on each object in the system you are investigating.
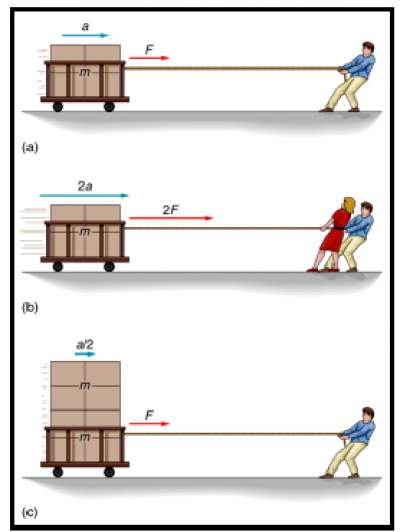
Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting upon the object and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. The law is often expressed in the form of the following two equations. Newton's Second Law and a Force Analysis. In Unit 2 of The Physics Classroom, Newton's second law was used to analyze a variety of physical ... Newton's Second Law Figure 4.2: Diagram of the apparatus 4.7 Procedure 1. Set up the air track as shown in Figure4.2. With the hanging mass disconnected from the glider and the air supply on, level the air track by carefully adjusting the air track leveling feet. The glider should sit Nov 5, 2020 — Newton's second law of motion says that the net external force on an object ... The free-body diagram shows all of the forces acting on the ... Newton's Three Laws of Motion. 3. To every action there is always an equal and opposite reaction. 2. The force exerted on a body equals the resulting change in the body's momentum divided by the time elapsed in the process. 1. Law of Inertia: An object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same ...
7. Newton's 2nd Law in More Complicated Problems and Friction The Atwood's Machine is used below to help in understanding how Newton's 2nd law applies to a system of two connected masses. It is not a practical machine. Suppose two different masses M 1 and M 2 are attached to a rope which is placed over a pulley as indicated in the diagram below. Newton's Second Law of Motion gives the following relation: F ∝ p f - p i t. Here F is the applied force. p i is the initial momentum. p f is the final momentum and. t is the time for which the force acts on the body to bring the change in momentum of the body. But we know that, p i = m u and p f - m v. where, Newton's second law of motion pertains to the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are not balanced. The second law states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables - the net force acting upon the object and the mass of the object. Dec 17, 2012 - This diagram illistrates Newton's second law. It shows that a smaller mass will always have a greater acceleration compated to a large mass ...
Newton's Second Law Video Tutorial. The Newton's Second Law Video Tutorial uses five example problems to demonstrate the use of a free-body diagram, Newton's second law, and circular motion equations to solve a problem related to an object moving in a circle. The video lesson answers the following question:
Newton's Second Law: Force The acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied. His second law defines a force to be equal to change in momentum (mass times velocity) per change in time. Momentum is defined to be the mass m of an object times its velocity V.
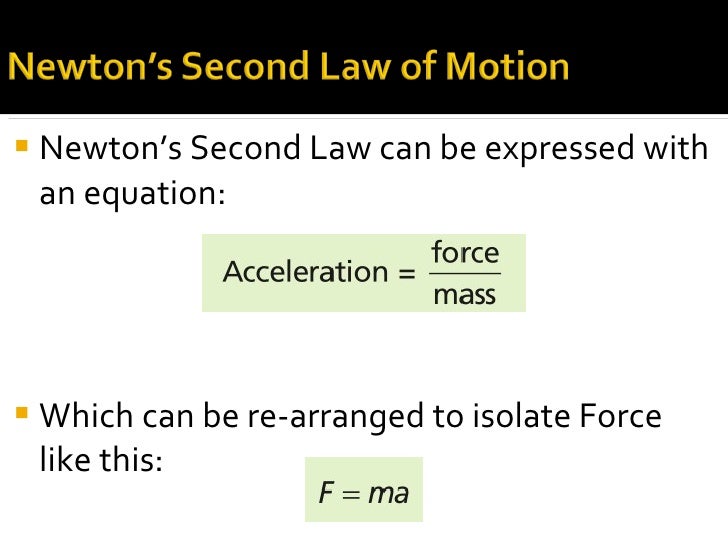
Newton's second law can be formally stated as, The acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. This statement is expressed in equation form as, a = F ne
Newton's Second Law Video Tutorial. The Newton's Second Law Video Tutorial uses five example problems to demonstrate the use of a free-body diagram, Newton's second law, and circular motion equations to solve a problem related to an object moving in a circle. The video lesson answers the following question:
When we apply Newton's Second Law to a suitable group of objects, we call the group "the system." In this experiment, a small mass is connected to the cart by a string that hangs down over a pulley. To apply Newton's Second Law to this situation, the system mass (the m in F = ma) and the net
The Physics Classroom serves students, teachers and classrooms by providing classroom-ready resources that utilize an easy-to-understand language that makes learning interactive and multi-dimensional. Written by teachers for teachers and students, The Physics Classroom provides a wealth of resources that meets the varied needs of both students and teachers.
Newton's second law of motion describes that, when a force is applied to an object, it produces acceleration in the object (i.e rate of change of velocity). For an object at rest, the applied force produces acceleration in the object and makes the object move in the direction of applied force.
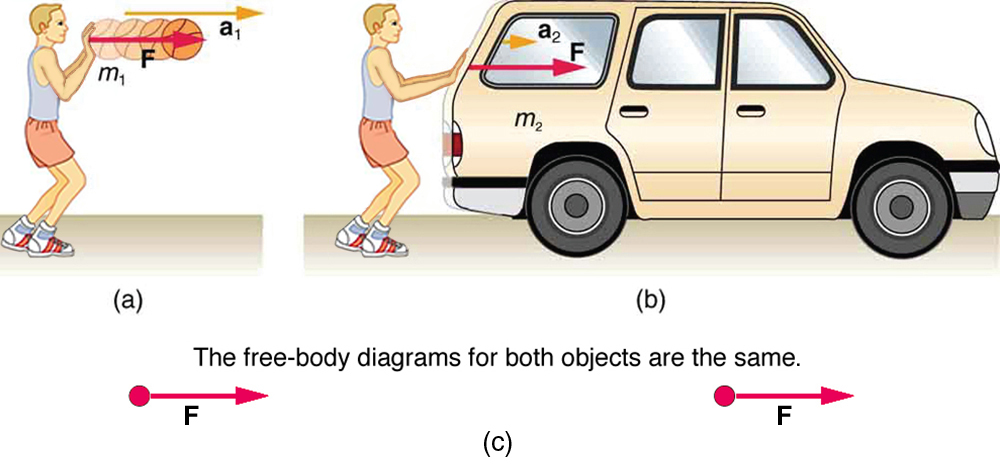
Figure (b): a free-body diagram that shows the horizontal forces acting on the car. In the diagram, the car is represented as a black dot, and its motion is along the +x axis. The free - body diagram is very helpful when applying Newton's second law and to determine the net force (F net). 17
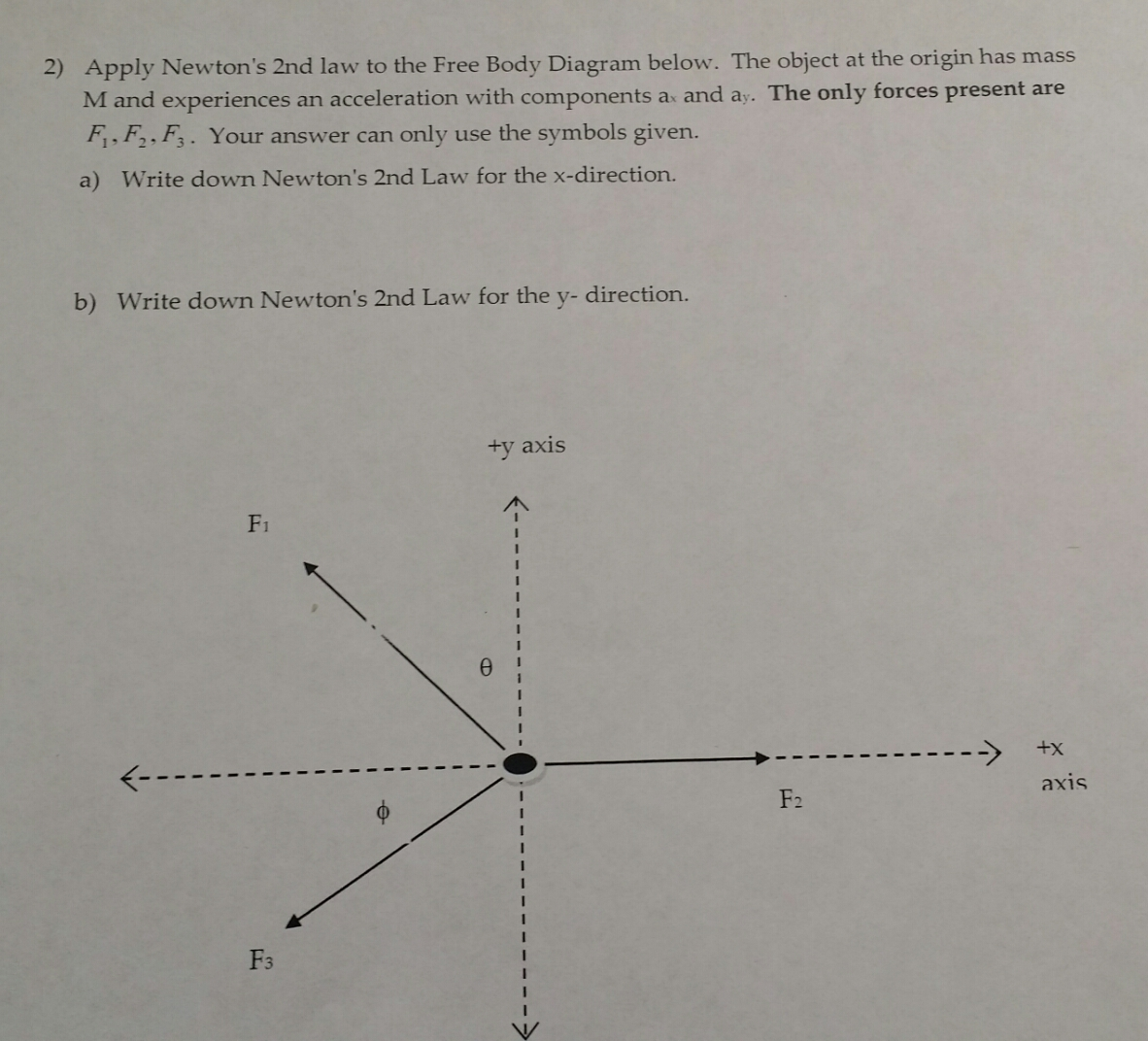
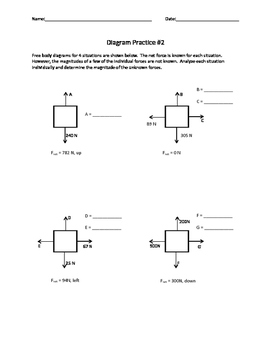
Reread it carefully. "A 1.2 kg turtle named Newton has four forces exerted on it as shown in the diagram below." There are 4 forces applied to the turtle, that is what the 4 vectors are in the diagram. Since they are asking for the acceleration in the vertical and horizontal directions, you need to find the net force in each of those directions.
The presence of an unbalanced force will accelerate an object - changing either its speed, its direction, or both its speed and direction. In terms of an ...
Newton's Second Law states that acceleration of an object relies on two factors, the mass of the object and the force being applied to the object. The Acceleration of an object will rely directly...
Newton's second law of motion says that the net external force on an object with a certain mass is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the acceleration of the object. Newton's second law can also describe net force as the instantaneous rate of change of momentum. Thus, a net external force causes nonzero acceleration.
In the world of introductory physics, Newton's second law is one of the most important laws you'll learn. It's used in almost every chapter of every physics textbook, so it's important to master this law as soon as possible. We know objects can only accelerate if there are forces on the object. Newton's second law tells us exactly how much an ...
Newton actually stated his second law in terms of momentum: "The instantaneous rate at which a body's momentum changes is equal to the net force acting on the body." ("Instantaneous rate" implies that the derivative is involved.) This can be given by the vector equation. F → net = d p → d t. F → net = d p → d t. 5.6.
Newtons First Law: Law of Inertia. An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an outside force. (More mass more inertia or resistance to change) Newtons Second Law: Force causes acceleration (F=ma) Newtons Third Law: All forces are paired, equal and opposite.
Newton's Second Law of Motion The acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external force acting on the system, and inversely proportional to its mass. In equation form, Newton's second law of motion is a = Fnet m a = F net m. This is often written in the more familiar form Fnet = ma.
Newton's 2nd law states that the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the object's mass. Newton's second law describes precisely how much an object will accelerate for a given net force.
Newton's Second Law Lab Newton's second law of motion explains the relationship among force, mass, and acceleration. In this activity, you will study the relationship between acceleration and mass, while keeping force constant. A car carrying different masses will be pulled across a table by a hanging weight—the constant force.
Newton's Second Law Objective The Newton's Second Law experiment provides the student a hands on demonstration of "forces in motion". A formulated analysis of forces acting on a ... Free-body diagrams of the forces on the cart and hanging mass are shown in Figure 4. Figure 3: Inclined Track with Hanging Mass .
Mission NL7: Newton's Second Law. Mission NL7 pertains to Newton's Second Law. You must understand how alterations in mass and net force would affect the acceleration of an object. The mission consists of 32 questions organized into 9 Question Groups. You must answer one question from each Question Group to complete the mission.
Shows how to draw free body diagrams for simple one dimensional motion. Free-body diagrams show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upo...










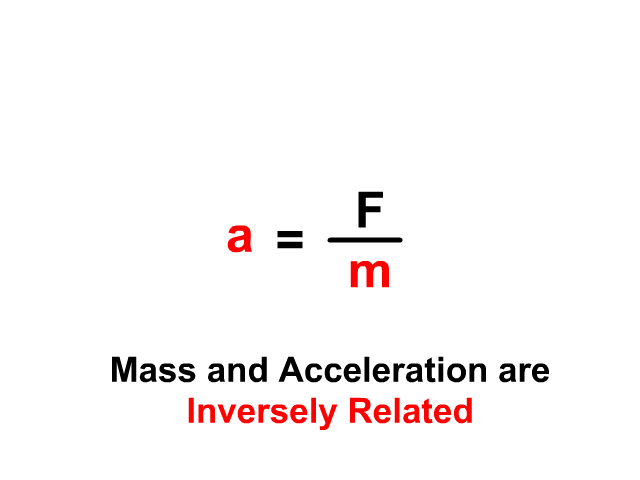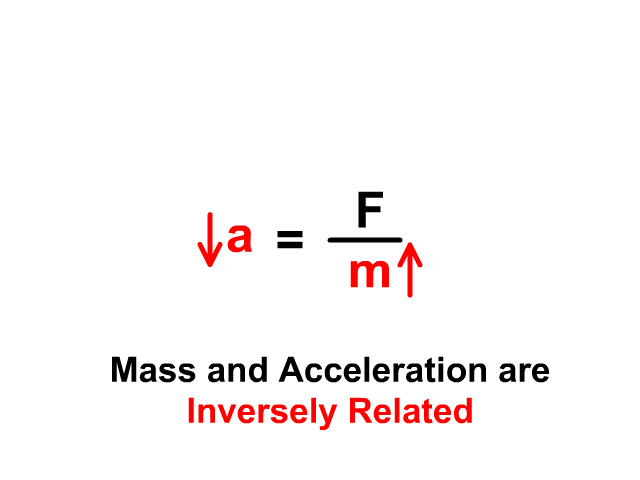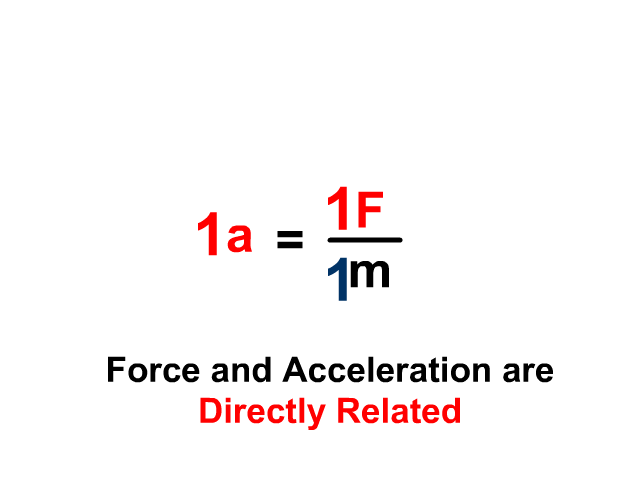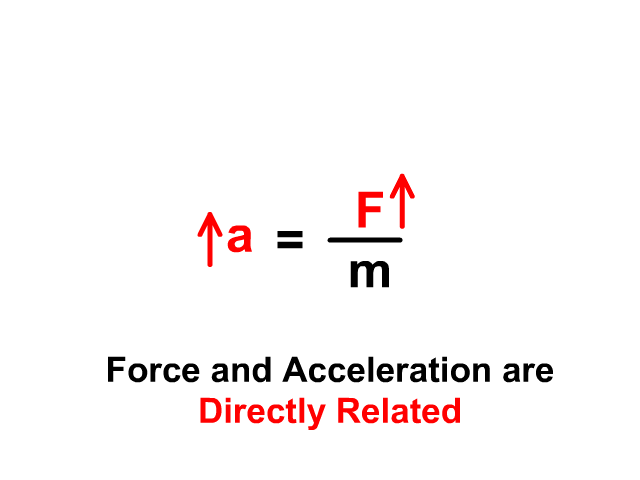












0 Response to "40 newton's second law diagram"
Post a Comment