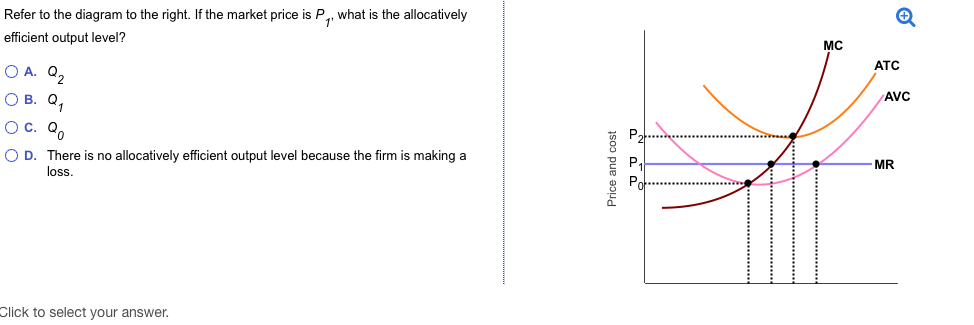
39 refer to the diagram. equilibrium output is
Refer to the above diagram. If the equilibrium price level is P1, then: A) aggregate demand is AD2 C) the equilibrium output level is Q2 B) the equilibrium output level is Q3 D) producers will supply output level Q1. Refer to the information provided in Figure 11.3 below to answer the questions that follow. Figure 11.3 31) Refer to Figure 11.3. A decrease in nominal aggregate output, ceteris paribus , will likely 31) A) increase the equilibrium interest rate without changing equilibrium money holdings.
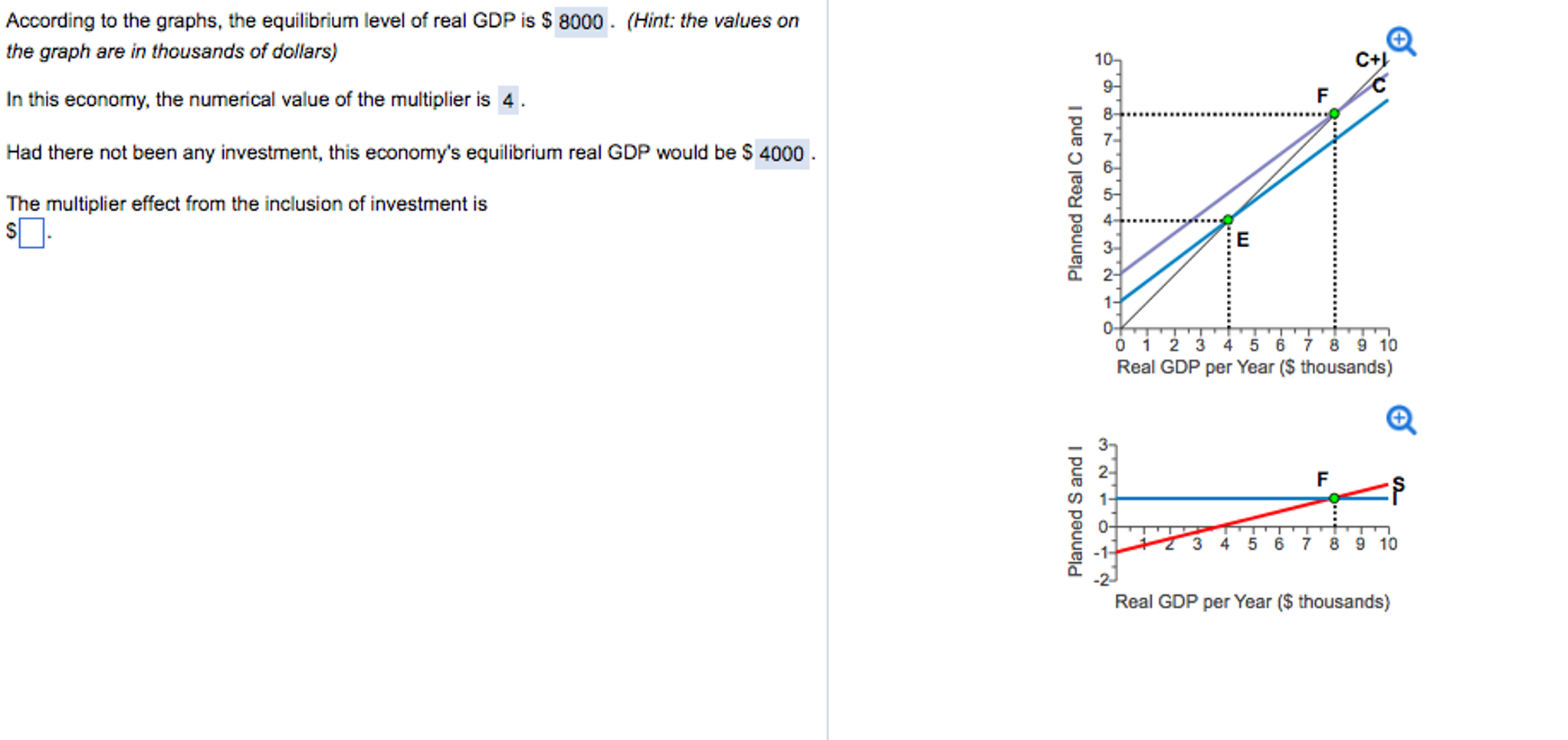
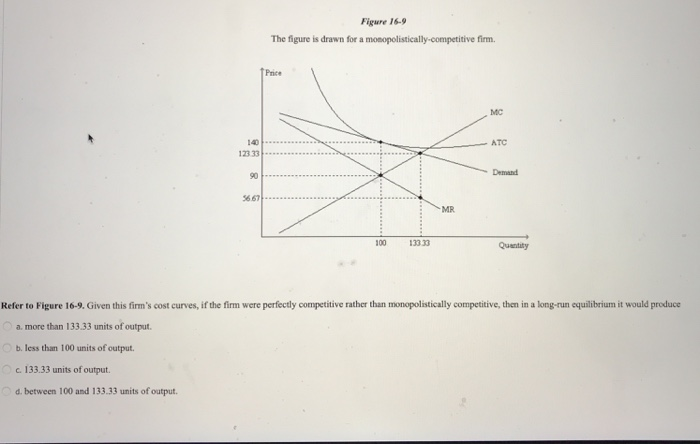
Refer to the figure above. Based on the figure and starting from an initial short-run equilibrium where output equals 20,000, if autonomous consumption spending decreases by 1,000, then the new short-run equilibrium is at an output (Y) equal to:

Refer to the diagram. equilibrium output is
Solved Example on Equilibrium Price. Q: How can we graphically represent the equilibrium? Ans: The equality of quantity demanded and quantity supplied is an indicator of the established of the equilibrium. When we draw the demand and supply curves on a single diagram, the point of intersection of these two curves is the point of equilibrium. LR equilibrium. Individual firm. SR Supply. Demand. Q*. In the long run, the market price p and each individual firm's output q, must be such that:.21 pages Refer to the diagram. If equilibrium real output is Q2, then: A. Aggregate demand is AD1 B. The equilibrium price level is P1 C. Producers will supply output level Q1 D. The equilibrium price level is P2
Refer to the diagram. equilibrium output is. 14. Refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy. The equilibrium level of GDP is: A) $400. B) $300. C) $200. D) $100. Answer: B. Type: G Topic: 2 E: 175-176 MA: 175-176 15. Refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy. At the equilibrium level of GDP, investment and saving are both: A) $50. In the case of monopoly, one firm produces all of the output in a market. ... Refer to the diagram below, which illustrates the demand, marginal revenue, ... Refer to the above diagram. If AD1 shifts to AD2, then the equilibrium output and price level are: A) P1Q3. B) P2Q3. C) P1Q2. D) P2Q2. Type: G Topic: 4 Level: Moderate E: 196-198 MA: 196-198. 128. Refer to the above diagram. When AD1 shifts to AD2, then at P1Q3 output demanded will: A) equal output supplied. C) be less than output supplied. B ... Once we have a short-run equilibrium output, we can then compare it to the full ... Negative output gaps mean that an economy is producing less than full ...
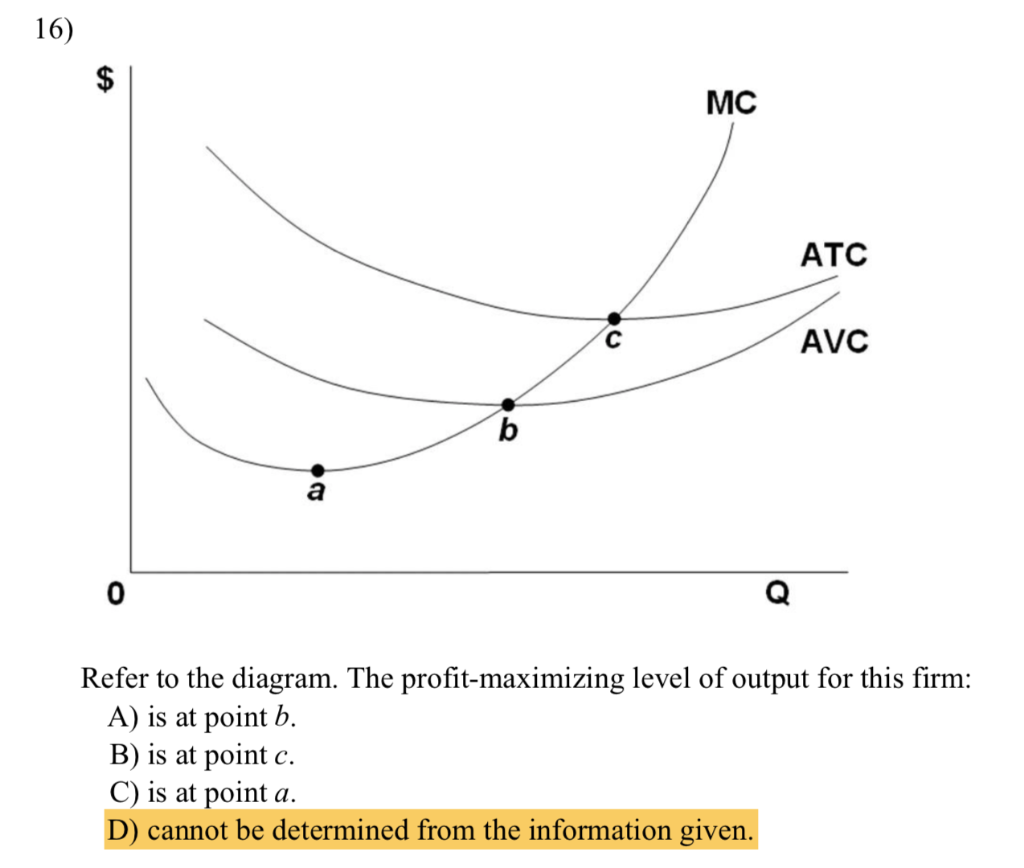
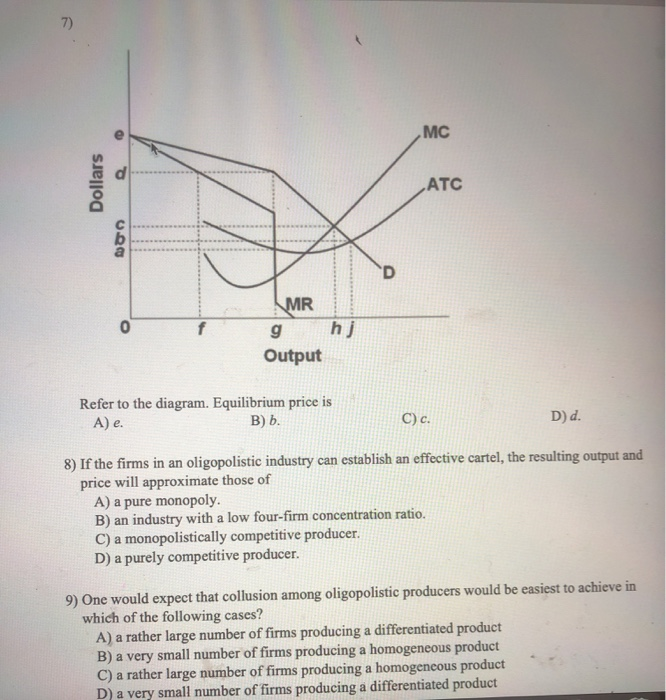
C16Read.pdf 3 The Model in Words: Equilibrium (defined as a state in which there is no tendency to change or a position of rest) will be found when the desired amount of output demanded by all the agents in the economy exactly equals the amount produced in a given time period. There are three classes of demanders or buyers of goods: consumers, firms, and the Refer to the above diagram of the market for product X. Curve S t embodies all costs (including spillovers) and Dt embodies all benefits (including spillovers) associated with the production and consumption of X. Assuming the equilibrium output is Q 1, we can conclude that the existence of spillover: More precisely, a short run competitive equilibrium consists of a price p and an output yi for each firm i such that, given the price p, the amount each firm i ... Economics questions and answers. MC ATC MR g hj Output 39. Refer to the above diagram. Equilibrium price is: С.С. D. b 40. Refer to the above diagram. This firm's demand and marginal revenue curves are based on the assumption that: A. the firm has no immediate rivals. B. rivals will match both a price increase and a price decrease.
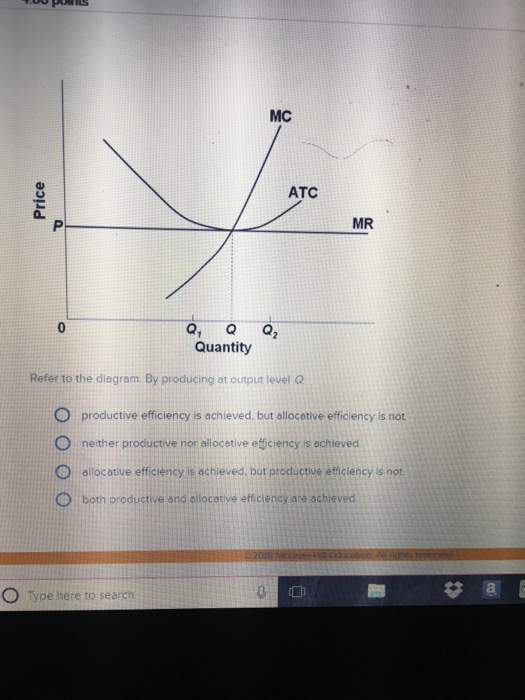
Consider a simple macro model with demand-determined output. Suppose the level of exports decreases unexpectedly by $6 billion. If the government wants to restore the initial equilibrium level of output it could, all other things equal A) decrease its purchases by $6 billion. B) increase its net tax revenues by $6 billion. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue: A. is $10. B. is $40. C. is $400. D. cannot be determined from the information provided. C. is $400. 8. The above diagram shows the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's economic profit: A. is zero. Question 2 1 out of 1 points Refer to the above diagram. Equilibrium output is: Selected Answer: g. Correct Answer: g. Question 3 1 out of 1 points Answer the next question (s) on the basis of the following demand and cost data for a specific firm: Refer to the above data. If columns (1) and (3) of the demand data shown above are this firm's ... Refer to the above diagram. Equilibrium output is: A. j. B. h. C. g. D. f . 6. ... Refer to the above diagram. This firm's demand and marginal revenue curves are based on the assumption that: A. the firm has no immediate rivals. B. rivals will match both a price increase and a price decrease. C. rivals will match a price increase, but ignore a ...
At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's economic profit: A. is zero. B. is $400. ... Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Rating: 5 · 2 reviews
Determination of Economic Equilibrium Level of Output! Output is at its equilibrium when quantity of output produced (AS) is equal to quantity demanded (AD). The economy is in equilibrium when aggregate demand represented by C + I is equal to total output. Under short run fixed price, equilibrium level of output is determined solely by level of ...
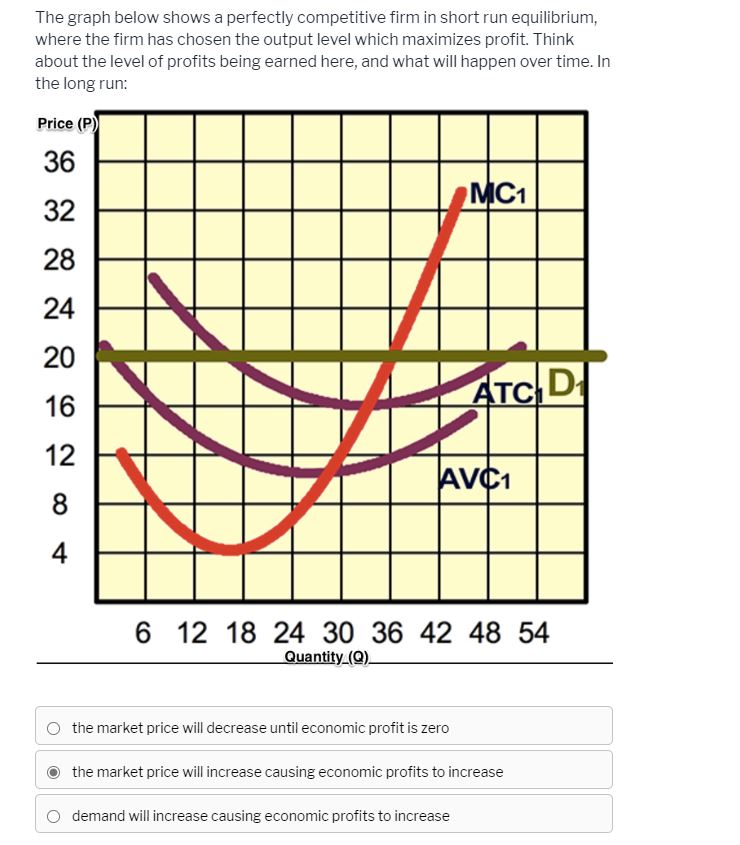
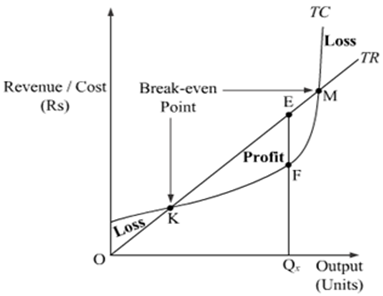
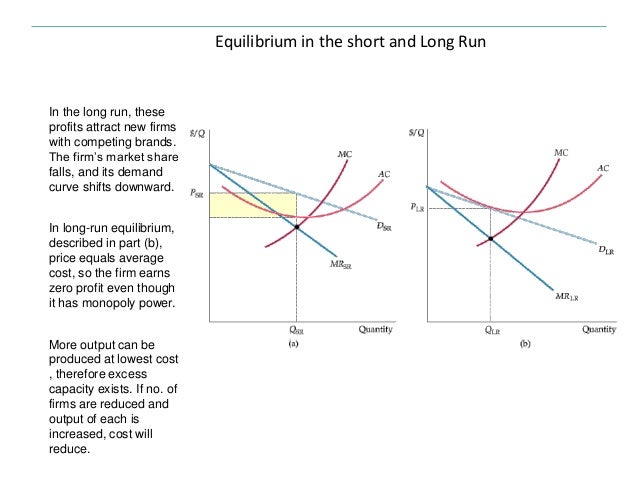
The firm should increase output as long as marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost ... The industry is not in long-run equilibrium, since profit is positive.
In macroeconomics an equilibrium output is a stable output, one that is neither expanding nor contracting. We can illustrate the concept of equilibrium output with the circular-flow diagram in Exh. 3.
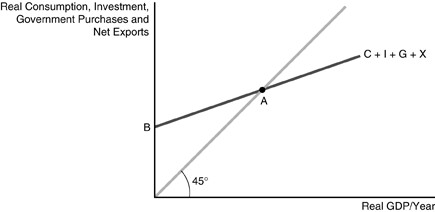
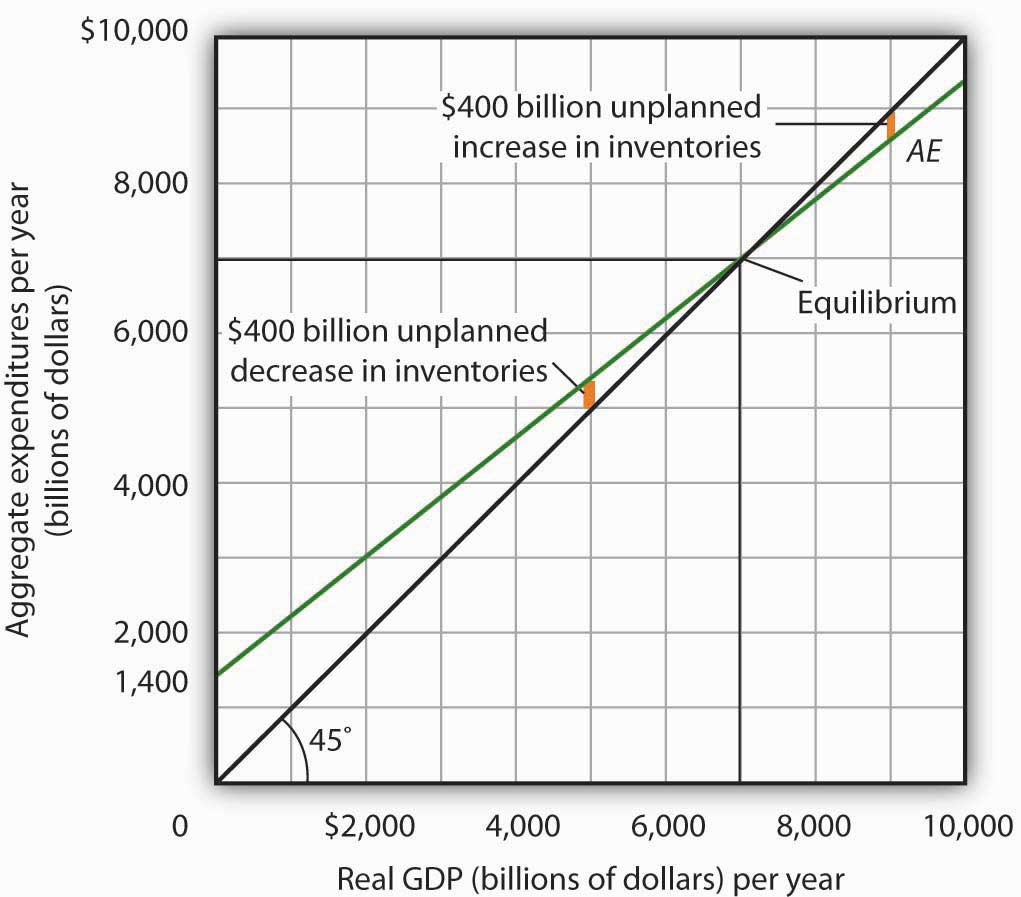
The equilibrium in the diagram will occur where the aggregate expenditure line crosses the 45-degree line, which represents the set of points where aggregate expenditure in the economy is equal to output (or national income). Equilibrium in a Keynesian cross diagram can happen at potential GDP, or below or above that level.
The expenditure-output model, sometimes also called the Keynesian cross diagram, determines the equilibrium level of real GDP by the point where the total or aggregate expenditures in the economy are equal to the amount of output produced.
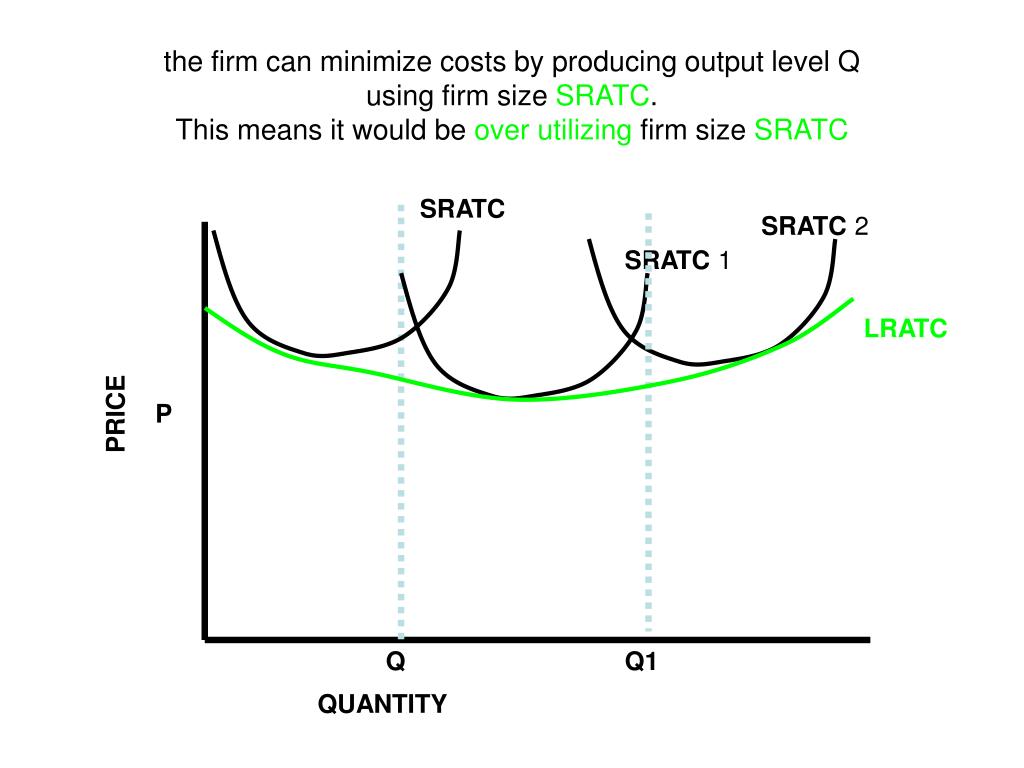
A firm under perfect competition in the long run is in equilibrium at output where Price = MC = Minimum LAC. This point is shown by E. It shows that the firm is making just normal profits. If the price is above the minimum long run average cost, the firms will be making super-normal profits.
Refer to the above diagram of the market for product X. Curve St embodies all costs (including externalities) and Dt embodies all benefits (including externalities) associated with the production and consumption of X. Assuming the equilibrium output is Q2, we can conclude that the existence of external:
The equilibrium in the diagram occurs where the aggregate expenditure line crosses the 45-degree line, which represents the set of points where aggregate expenditure in the economy is equal to output, or national income. Equilibrium in a Keynesian cross diagram can happen at potential GDP—or below or above that level. Critical-thinking questions
Refer to the above diagram. If AD1 shifts to AD2, then the equilibrium output and price level will be: asked Sep 3, 2019 in Economics by Eline. A. P1Q3. B. P1Q2. C. P2Q3. D. P2Q2. principles-of-economics; 0 Answers. 0 votes. answered Sep 3, 2019 by offed . Best answer ...
Refer to the above diagram. If this somehow was a costless product (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by: A) selling the product at the highest possible price at which a positive quantity will be demanded.
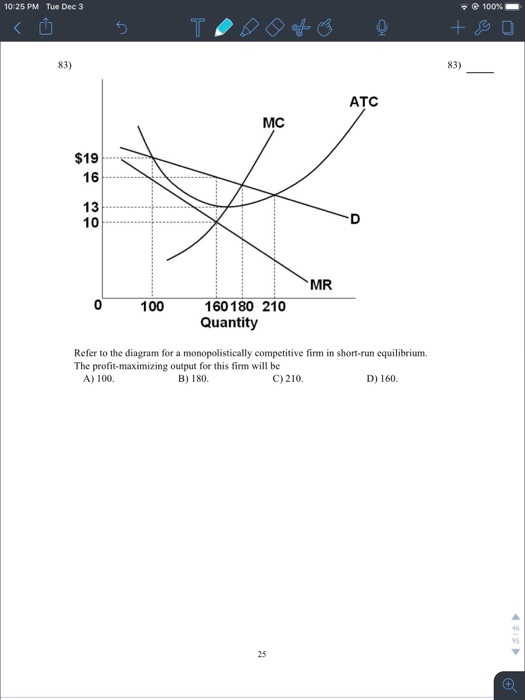
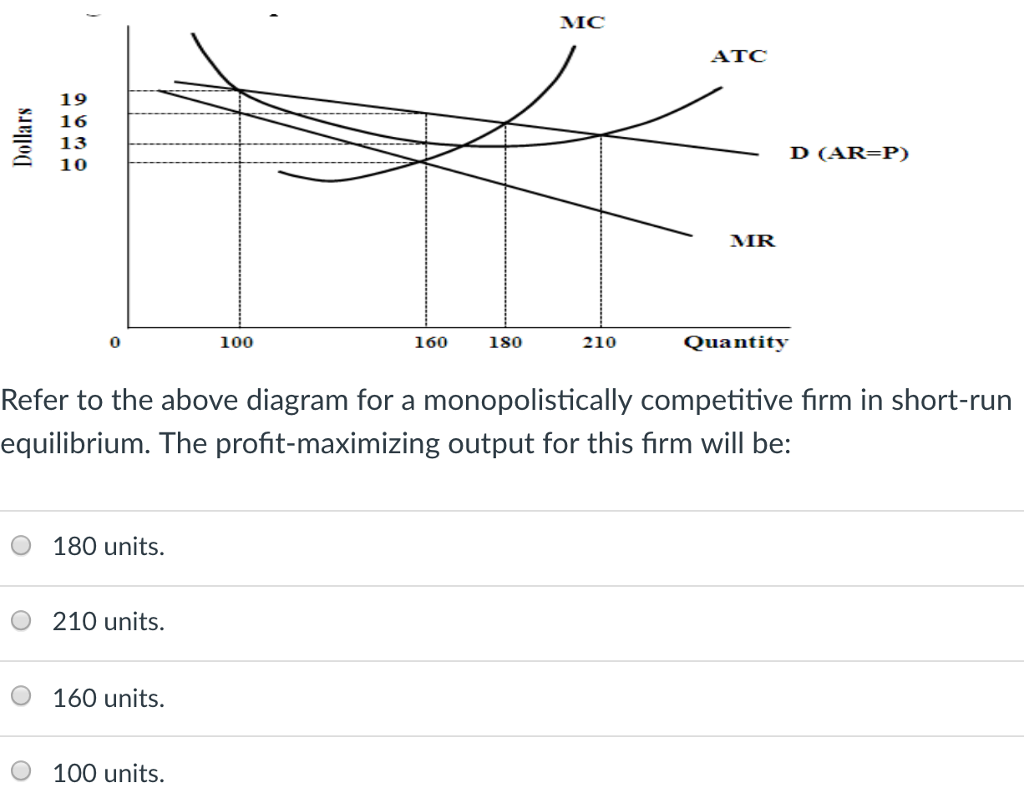
The profit-maximizing output for this firm will be: 160. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: profit of $480. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Short-run equilibrium entailing economic loss is shown by:
Refer to the diagram. If equilibrium real output is Q2, then: A. Aggregate demand is AD1 B. The equilibrium price level is P1 C. Producers will supply output level Q1 D. The equilibrium price level is P2
LR equilibrium. Individual firm. SR Supply. Demand. Q*. In the long run, the market price p and each individual firm's output q, must be such that:.21 pages
Solved Example on Equilibrium Price. Q: How can we graphically represent the equilibrium? Ans: The equality of quantity demanded and quantity supplied is an indicator of the established of the equilibrium. When we draw the demand and supply curves on a single diagram, the point of intersection of these two curves is the point of equilibrium.















0 Response to "39 refer to the diagram. equilibrium output is"
Post a Comment