36 pv diagram constant temperature
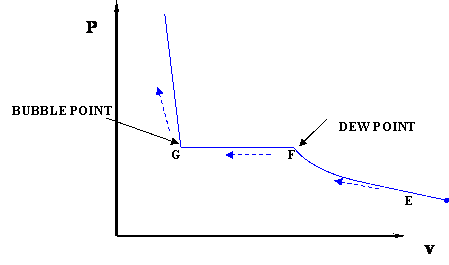
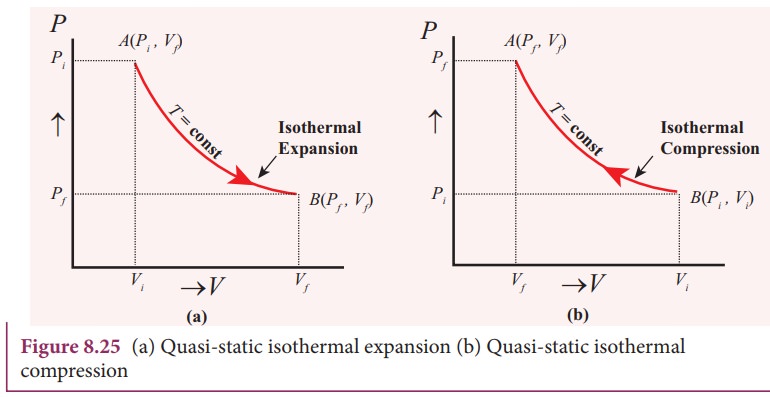
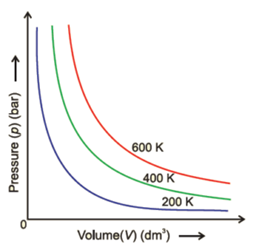
Figure 3.4: P-v Diagram For A Pure Component. In this case temperature is being held constant; our substance is undergoing an isothermal compression process. Starting at E (all-vapor condition), an increase in pressure will result in a rather significant reduction in volume since the gas phase is compressible. 9 Oct 2020 — The PV diagram models the relationship between pressure (P) and ... This diagram is showing an ideal gas exhibiting constant temperature.
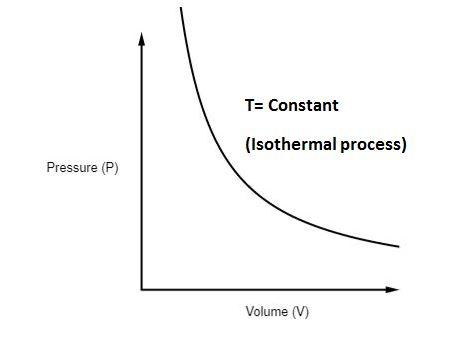
An isothermal process is a process that takes place under constant temperature conditions. For an ideal gas, the temperature only depends on the internal ...

Pv diagram constant temperature
> One mole of a diatomic ideal gas performs a transformation from an initial state for which temperature and volume are, respectively, 291 K and 21000 cc to a final state in which temperature and volume are 305 K and 12700 cc. The transformation is represented on the (V, p) diagram by a straight line. To find the work performed and the heat absorbed by the system. OK so to find first the work L performed ON the system by the surroundings just integrate P dV; since the transformation is repre... I'm tutoring someone who is struggling with topics from content category 5E. I already recommended Leah4Sci and they are already using Jack Westin. What other resources did you like for learning these topics besides simply reading a review book? ​ ***Content Category 5E: Principles of chemical thermodynamics and kinetics*** **Enzymes (BC, BIO)** * [Classification by reaction type](https://jackwestin.com/resources/mcat-content/enzymes/classification-by-reaction-type) * [Mechanism]... (1) A cylinder contains 3.25 mol of a diatomic gas at 20.0◦C and pressure of 1.1 atm. A scientist heats the gas at constant volume, adding 1.6 × 104 J of heat. Then, he heats it further at constant pressure to twice its original volume. a. Draw a clear and neat pV diagram of the experiment. b. Calculate the final temperature of the gas. c. Calculate the amount of work done by the gas. d. Calculate the amount of heat added to the gas while it is expanding. e. Calculate the change in interna...
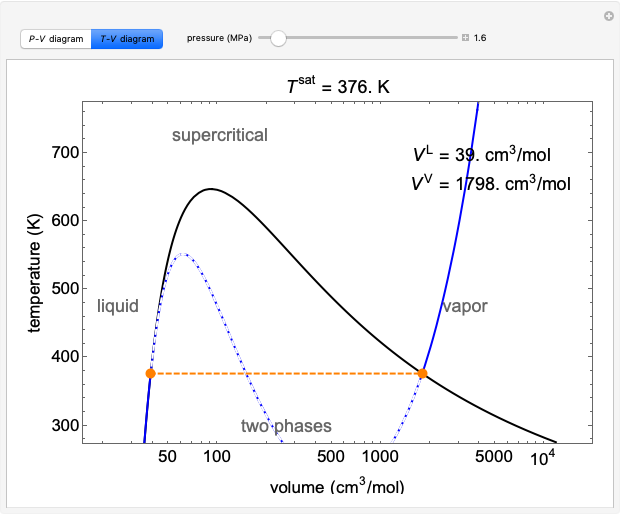
Pv diagram constant temperature. 12 Sept 2018 — The isothermal process is represented by a P-V curve at constant temperature. As pressure changes and volume changes within a closed system, ... Air with volume 0.45m^3, pressure 1.1MN/m^2, and temperature 36 deg C has 2.7MJ of energy supplied to it via heating at constant pressure. The air is then allowed to expand to a volume of 1.8m^3 according to the law pV^1.4 = a constant. _____________________________________________ Sketch the two seperate processes on a pV diagram, then for EACH process calculate: a) The final temperature b) The work done c) The change in internal energy For air, take R=8.314 J/mol.K and molar heat capac... Looking at how general chemistry concepts are currently organized, my attempt at making a diagram devolved into a cascade of concepts overlaid onto an overlapping series of circles. The official course of instruction starts in the middle and makes multiple passes through the same concepts, which opens up plenty of possible questions on the exams but makes everyone’s life more difficult. I would instead start from the sub-subatomic particles and move up from there, allowing the rest of the concep... temperature) constant, the gas must be absorbing heat from the water. As long as the energy lost (by the gas doing work) equals the heat gained from the water, the internal energy will not change and the temperature stays the same. U=Q W U=−W W U=0 The PV diagram we get shows a curved line as the pressure and volume both change.
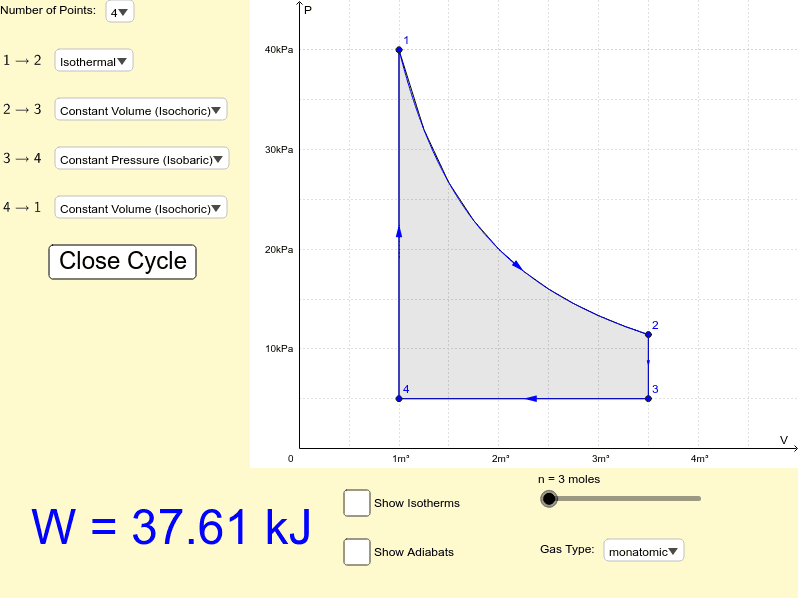
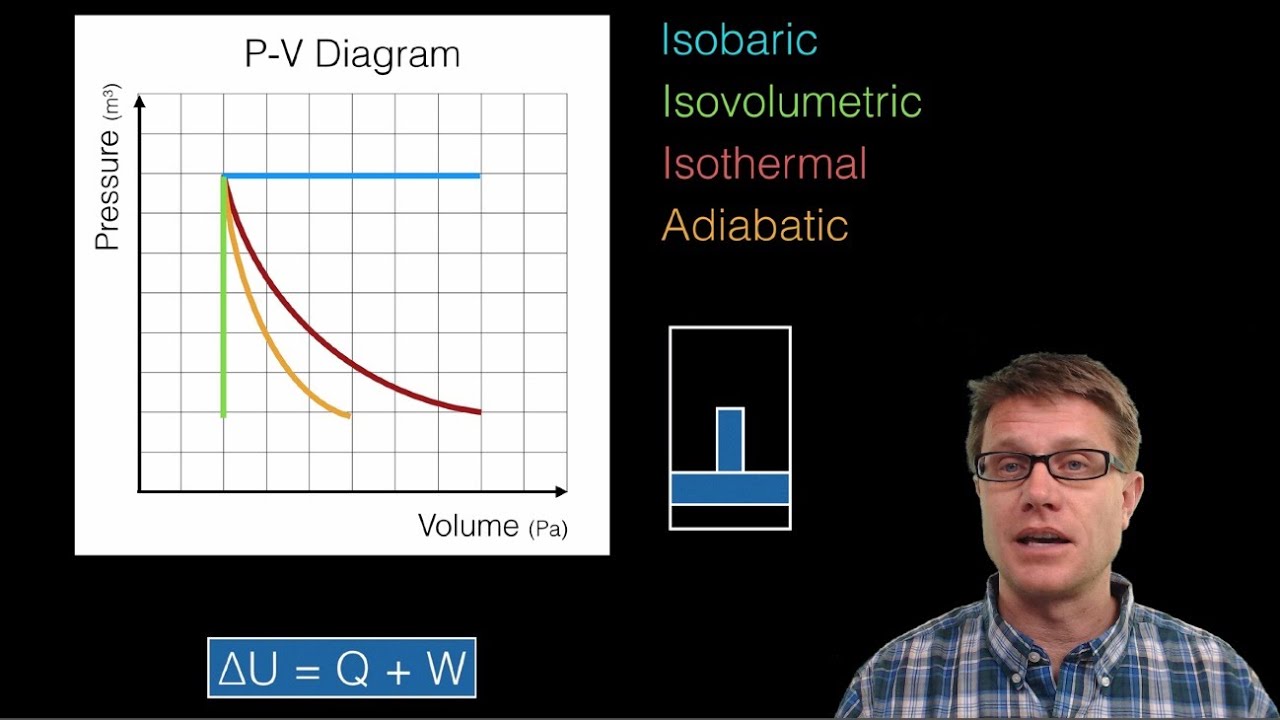
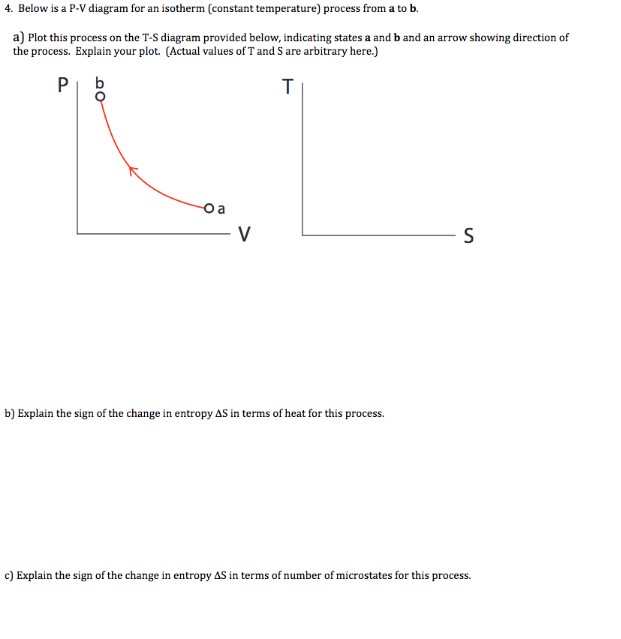
So if the temperature increases, the internal energy must also increase. Now, if the gas we're considering is an ideal gas we also know that,. isotherm, a line of constant temperature. Key Ideas about P-V diagrams: The P-V diagram (the graph of pressure as a function of volume) for a system can convey significant information about the state of the system, including the pressure, volume, and temperature of the system when it is in a particular state. It can be helpful to sketch isotherms on the P-V diagram to convey temperature The problem is: > 2.0mol of gas are at 30∘C and a pressure of 1.5atm. How much work must be done on the gas to compress it to one third of its initial volume at constant temperature? constant pressure? Show both processes on a single pV diagram. [Picture of provided graph with my attempted solution](http://imgur.com/2ZamL7Z) Now for the first two parts, I solved it quite easily and got the correct rounded values of 5500 J for constant temperature and 3400 J for constant pressure. Now when ... Temperature is the slave of pressure and volume on a pressure-volume graph (PV graph). Function of State. ∆U = 3 2 nR∆T. Function of Path: Work. W = ∫ F · ds = ∫ P dV. W = − area on PV graph. Function of Path: Heat. Q = ∆U + W = nc∆T
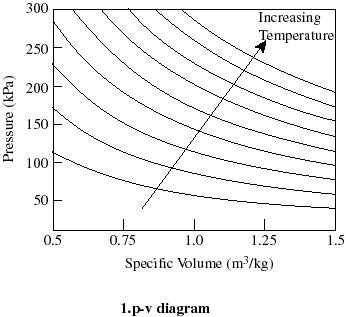
May 13, 2021 · On a p-V diagram, lines of constant temperature curve from the upper left to the lower right. A process performed at constant temperature is called an isothermal process . During an adiabatic process no heat is transferred to the gas, but the temperature, pressure, and volume of the gas change as shown by the dashed line. Disclaimer: I'm not interested in debating the science of climate change. If you don't believe in climate change please argue it elsewhere. Thanks! I have an idea for combating climate change, but it involves multiple engineering disciplines which puts most of the feasibility assessment of my idea outside of my expertise. I know myself well enough to know that I'm not cut-out to be an entrepreneur or leader of any sort. My hope is that posting the idea here might inspire some of my fellow engin... PV Diagrams. We can examine aspects of the behavior of a substance by plotting a graph of pressure versus volume, called a PV diagram.When the substance behaves like an ideal gas, the ideal gas law describes the relationship between its pressure and volume. P-V diagram. The Pressure-Volume (PV) diagram. Volume. 1 L 6 L. 3.0. Temperature: This simulation introduces the P-V (pressure-volume) diagram. See what happens when the temperature of the ideal gas or the volume is changed (at constant temperature). You can also sketch a pressure vs. volume graph for a given temperature, by choosing a temperature and then using the volume slider to cover the full range of volumes.
(1) A cylinder contains 3.25 mol of a diatomic gas at 20.0◦C and pressure of 1.1 atm. A scientist heats the gas at constant volume, adding 1.6 × 104 J of heat. Then, he heats it further at constant pressure to twice its original volume. a. Draw a clear and neat pV diagram of the experiment. b. Calculate the final temperature of the gas. c. Calculate the amount of work done by the gas. d. Calculate the amount of heat added to the gas while it is expanding. e. Calculate the change in interna...
I'm tutoring someone who is struggling with topics from content category 5E. I already recommended Leah4Sci and they are already using Jack Westin. What other resources did you like for learning these topics besides simply reading a review book? ​ ***Content Category 5E: Principles of chemical thermodynamics and kinetics*** **Enzymes (BC, BIO)** * [Classification by reaction type](https://jackwestin.com/resources/mcat-content/enzymes/classification-by-reaction-type) * [Mechanism]...
> One mole of a diatomic ideal gas performs a transformation from an initial state for which temperature and volume are, respectively, 291 K and 21000 cc to a final state in which temperature and volume are 305 K and 12700 cc. The transformation is represented on the (V, p) diagram by a straight line. To find the work performed and the heat absorbed by the system. OK so to find first the work L performed ON the system by the surroundings just integrate P dV; since the transformation is repre...















0 Response to "36 pv diagram constant temperature"
Post a Comment