36 incline free body diagram
9 Feb 2021 — In this tutorial, we will draw a free body diagram of an inclined plane with a load resting on top of it in LaTeX using TikZ package.
https://www.positivephysics.org Free-Body Diagram Drawing - Incline Forces - positivephysics.org positivephysics.org
Free-Body Diagram. Solving the Free-Body Diagram In order to solve the problem, the force on the rope necessary to move the box up the incline must be found. This is the tension force. Finding this force requires a system of equations. Although there is currently one known variable, the weight, there are three unknown variables; therefore,
Incline free body diagram
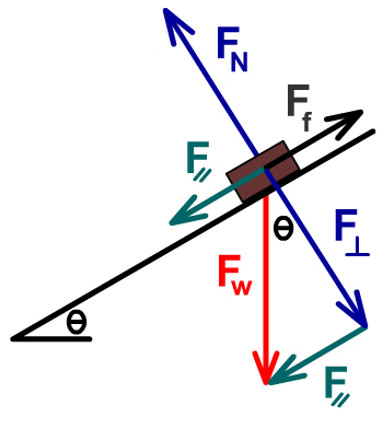
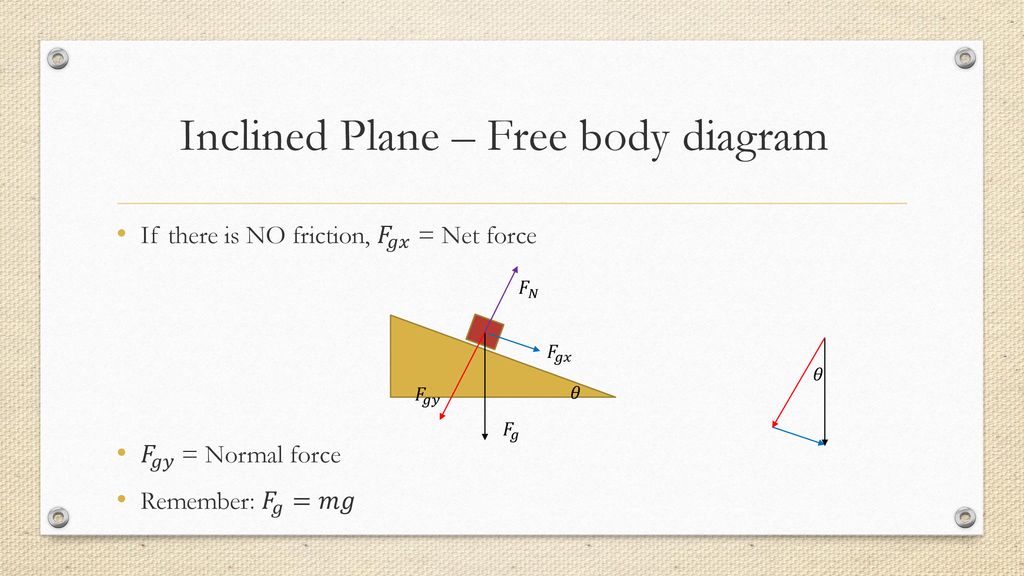
Free-body diagrams for objects on an incline must (at the minimum) depict: Gravity's downward force and the corresponding translated downhill force parallel to the surface. The surface exerts a Normal force that is perpendicular to the surface and both equal and opposite to gravity's perpendicular surface component.
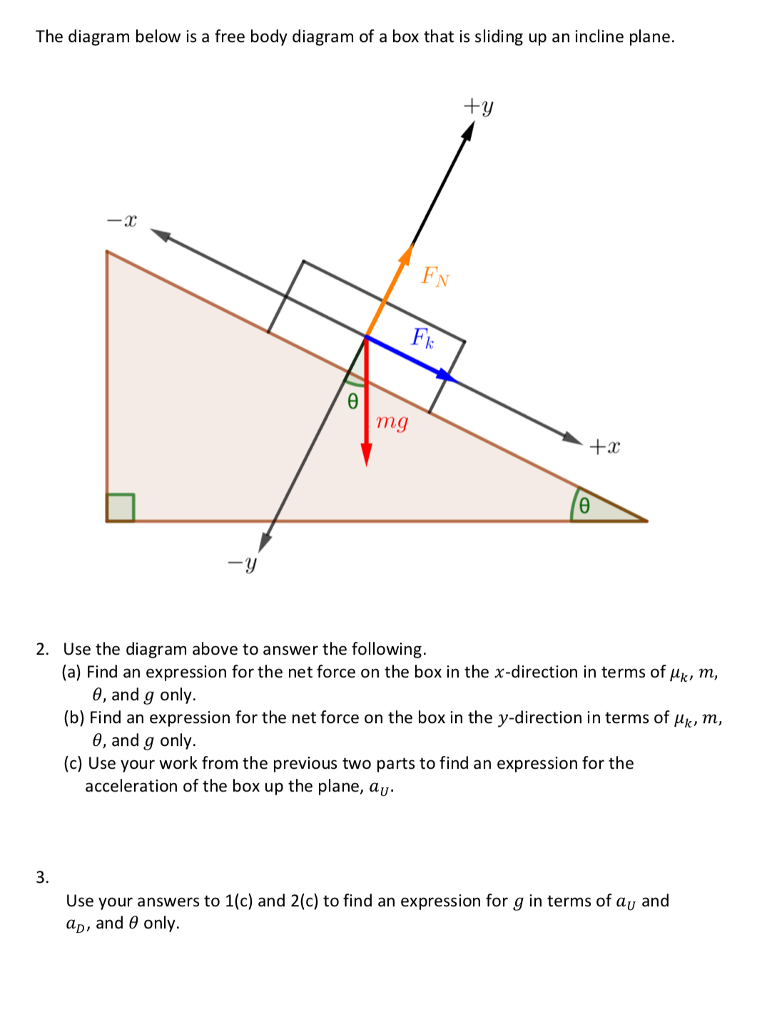
Force and Motion on an Incline An inclined plane is basically a ramp. It is a flat surface that is sloped rather than horizontal. When solving problems about objects on an incline, it is convenient to choose a coordinate system with axes ... Rotated free body diagram ...
Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
Incline free body diagram.
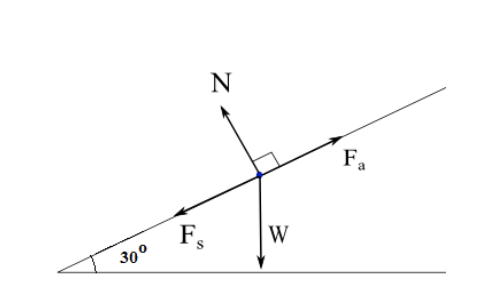
Solution a). Free Body Diagram The box is the small blue point. In the diagram below, W is the weight of the box, N the normal force exerted by the inclined plane on the box, F a is the force applied to have the box in equilibrium and F s the force of friction opposite F a. b) The box is at rest, hence its acceleration is equal to 0, therefore the sum of all forces acting on the box is equal ...
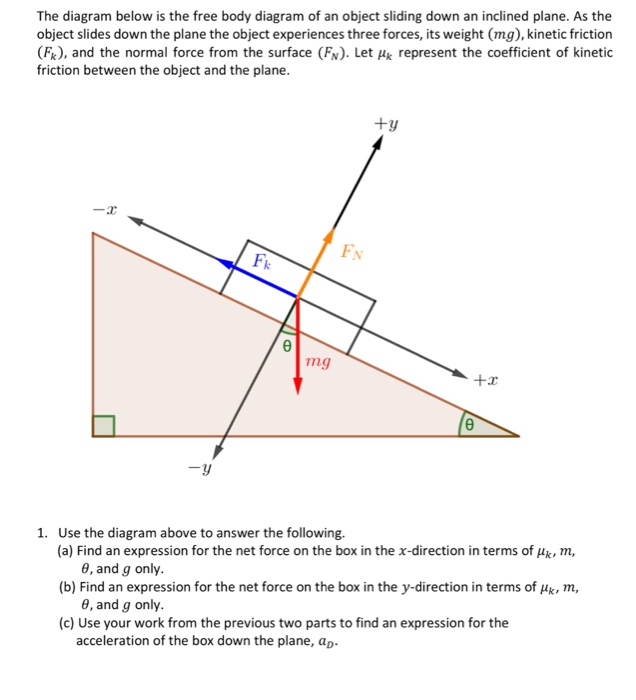
The net force is 5 N, directed along the incline towards the floor. Let us consider another example. The free-body diagram shows the forces acting upon a 100-kg crate that is sliding down an inclined plane. The plane is inclined at an angle of 30 degrees. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the incline is 0.3.
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
Examples of drawing free-body diagrams. To better understand how to draw free-body diagrams using the 3 steps, let's go through several examples. Example 1. A box is pushed up an incline with friction which makes an angle of 20 ° with the horizontal. Let's draw the free-body diagram of the box. The first step is to sketch what is happening:
2. Draw the full free-body diagram of a block that is getting pulled UP an inclined plane by a force at an angle of degrees above the inclined surface. Assume that the incline has an angle of inclination of degrees and that it is NOT frictionless. F 3. A 100 kg block is sitting on an incline plane whose angle of inclination is 10o. Find:
This physics video tutorial explains how to draw free body diagrams for different situations particular those that involve constant velocity and constant acc...
A free body diagram is defined as an illustration that depicts all the forces acting on a body, along with vectors that are applied by it on the immediate environs. Apart from the acting forces and subsequent work done, the moment magnitudes are also considered to be a part of such diagrammatic representations.
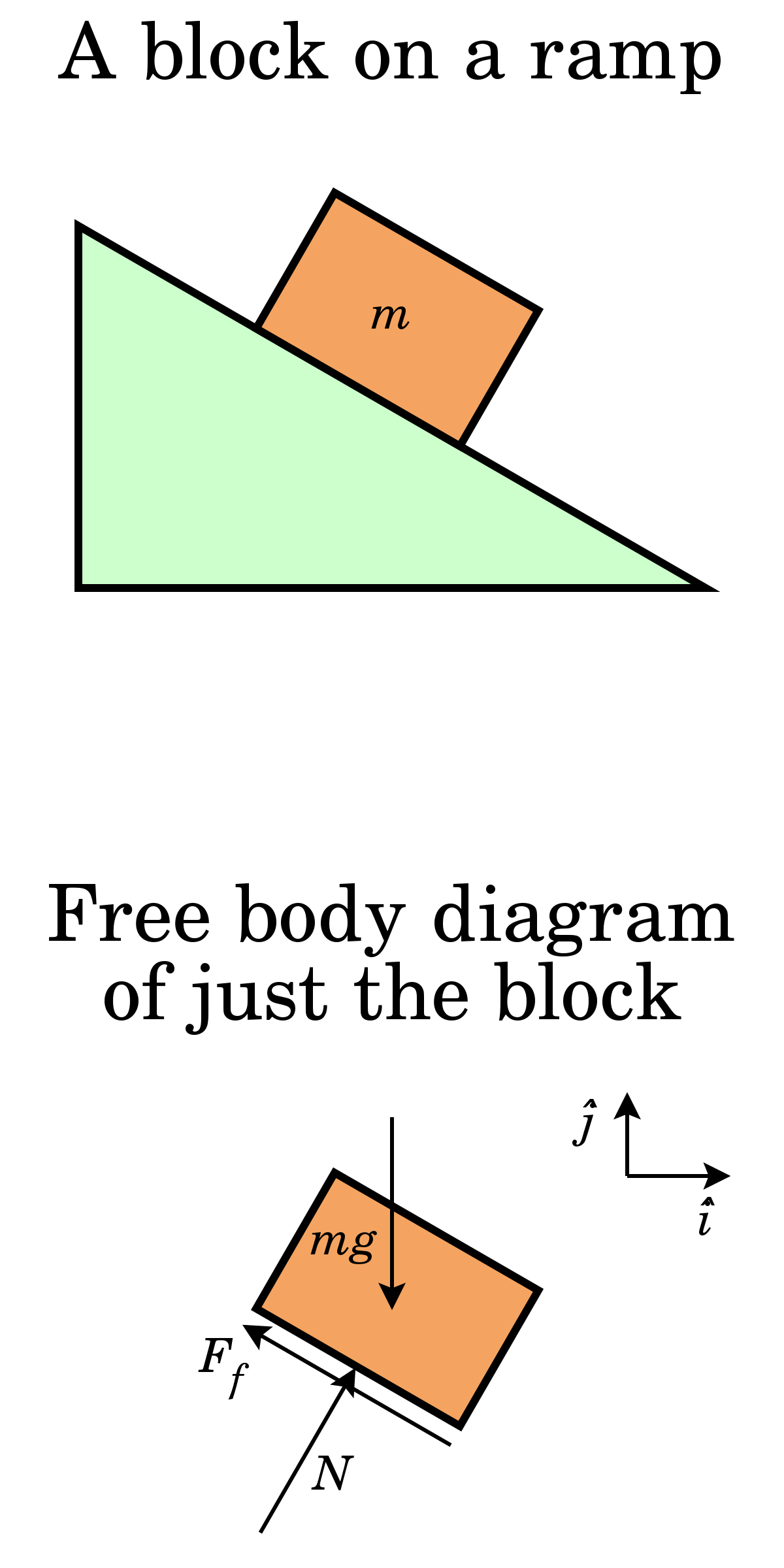
In this exercise we will draw a free body diagram that describes a block sliding down an inclined plane. The object is to identify all the forces and the ...
The corresponding force component along the incline (downhill force due to gravity) Any frictional forces (due to static friction or kinetic friction, if applicable) along the incline ... but will also display a labeled free body force diagram. All answers are provided to three decimal places. (These tools only support integers and decimals ...
24 Jul 2013 — Free Body Diagrams. Representation of all the forces acting on an object.
A free-body diagram for the car is shown at left. Both the normal force, N (blue components) and the friction force, f (red components) have been resolved into horizontal and vertical components. Notice that the friction force acts up the incline, to keep the car from sliding toward the center of the turn.
Free Body Diagram On Incline. forces box on an inclined plane in this video mr bantz explains how to construct a free body force diagram and determine the magnitude and direction of all forces acting on free body diagram of a incline 1 the problem statement all variables and given known data draw a free body diagram of the incline build the free body diagram of the man which is the
Solution. Figure 11.7 A solid cylinder rolls down an inclined plane from rest and undergoes slipping. The coordinate system has x in the direction down the inclined plane and y upward perpendicular to the plane. The free-body diagram shows the normal force, kinetic friction force, and the components of the weight.
How to Calculate Normal Force on an Inclined Surface: Step 1: Draw a free-body diagram for the object on the incline. Step 2: Taking the direction parallel to the surface to be the x-axis and the ...
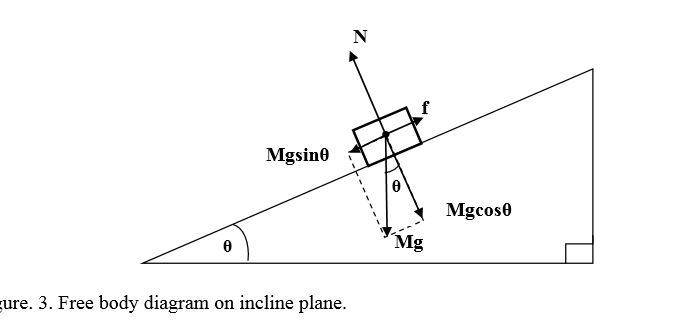
How to write Newton's second law for forces on an incline. 1) Draw a free body diagram for the object (see Figure 3). Remember to rotate the coordinate axes to ...
For a frictionless incline of angle degrees, the acceleration is given by the acceleration of gravity times the sine of the angle. Acceleration = m/s 2 compared to 9.8 m/s² for freefall. If the height of the incline is h= m, then the time to slide down the incline from rest would be t= seconds, compared to a time of t= seconds to drop from that height. . The speed at the bottom of the incline ...
Answer (1 of 10): First draw a free body diagram of the block. A free body diagram shows all the forces acting on the object. Notice that I have defined a rotated set of axes and I labelled them x' and y'. The x'-axis is parallel to the inclined plane and the y'-axis is perpendicular to the plan...
Draw a free-body diagram (which is a sketch showing all of the forces acting on an object) with the coordinate system rotated at the same angle as the inclined plane. Resolve the vectors into horizontal and vertical components and draw them on the free-body diagram.
Download scientific diagram | Free-body diagrams for a cylinder going up (a) and down (b) an incline. from publication: Rotation in secondary school: ...
Worksheet #1 Free Body or Force diagrams… Drawing Free-Body Diagrams . Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free -body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams; these diagrams will be used throughout your study of physics.
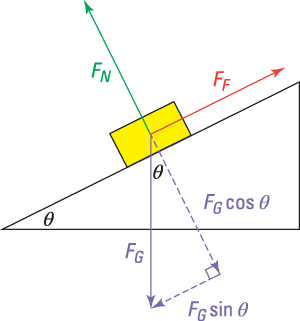
Answer: The free body diagram of the block resting on the incline is shown above. For equillibrium, N=mg\cos\theta F=mg\sin\theta Here, F is the fricti on al force between block and incline, and N is the Normal reacti on on the Block. By the definiti on of static fricti on, F\leq\mu N \implies ... Incline d plane force comp on ents.
Free Body Diagram Of Block On Incline. what is a free body diagram and how to draw it with 2 jack is pulling a box up an incline which makes an angle of 30° with the horizontal assuming there is no friction draw a free body diagram of the box finding forces acting upon objects on an inclined plane or in both high school physics and general college physics free body force diagrams are critical ...
the reaction from the box (or the man) does act on the incline, and so it does go on the free body diagram (also you've missed out the friction, though it would be easier if you simply said "reaction" (not "normal reaction"), since that includes the friction) Reply Jan 23, 2014 #8 thonwer 60 0 tiny-tim said: hi thonwer!
Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
B) free body diagram of point P; three forces (upper part of figure below) 1) Tension T 1 2) Tension T 2 3) Tension T 3 Example 8 : A system with two blocks, an inclined plane and a pulley A) free body diagram for block m 1 (left of figure below) 1) The weight W 1 exerted by the earth on the box.
The free-body diagram shows the forces acting upon a 100-kg crate that is sliding down an inclined plane. The plane is inclined at an angle of 30 degrees. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the incline is 0.3. Determine the net force and acceleration of the crate.
Free body diagram of an incline Thread starter speakout; Start date Nov 22, 2014; Tags free body digram Nov 22, 2014 #1 speakout. 7 0. Homework Statement For the maximum angle for which you have data draw a free body diagram and explain how the forces add to give the resultant (net) force and show the calculations required to determine the ...
Graded Exercises in Drawing and Utilizing Free-Body Diagrams Using a ruler, draw free-body diagrams (FBD's) showing all forces acting on each body. Coordinate directions are indicated in the leading diagram of a sequence. Forces that are replaced by their x-and y-components should be shown canceled out.















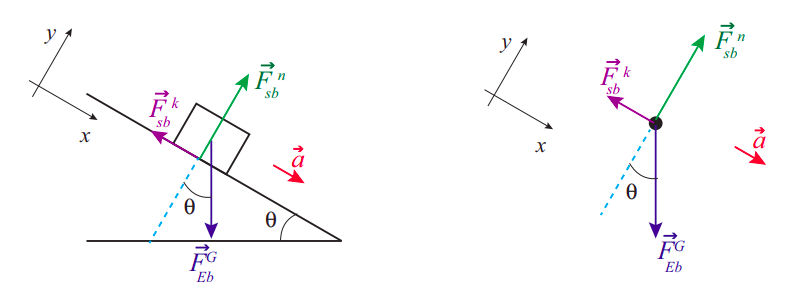


0 Response to "36 incline free body diagram"
Post a Comment