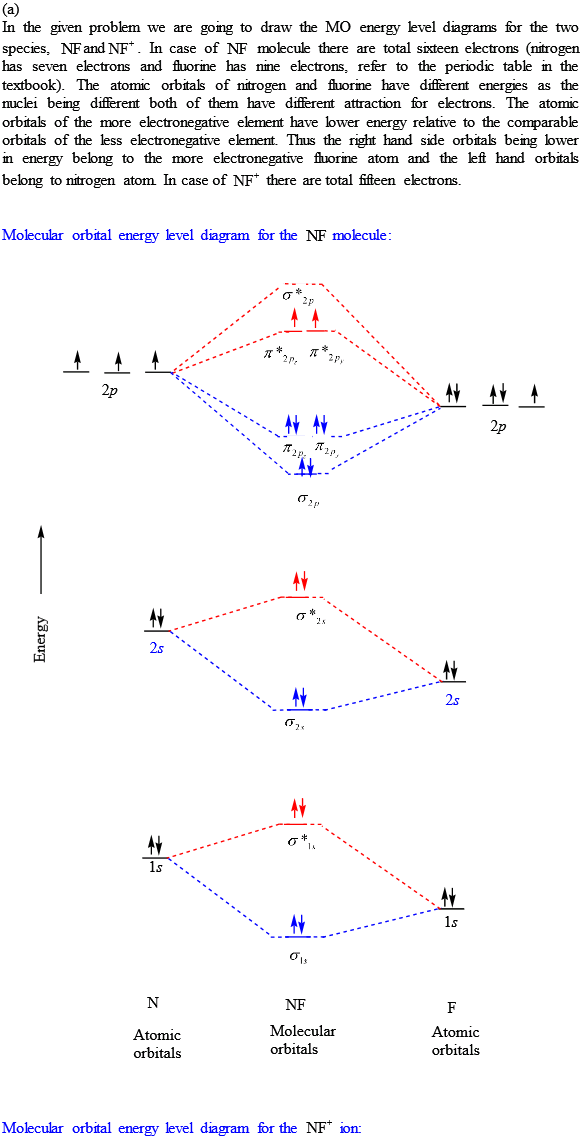
39 nf+ molecular orbital diagram
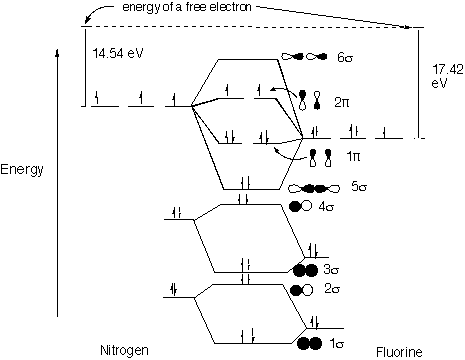
Molecular orbital : A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic. | Online Chemistry tutorial IIT, CBSE Chemistry, ICSE Chemistry, engineering and medical chemistry entrance exams Molecular orbital diagram of Li2 & Be2 : Number of electrons in Li2 molecule =6. Molecular Orbital Diagram for NF - CHEMISTRY COMMUNITY. Draw its molecular orbital energy diagram. A. Using the LCAO-MO scheme, indicate the ground-state MO description for NF, i.e. complete the following: 1(s) 2. . .The LCAO-MO description is: 1s 2 2s 2 3s 2 4s 2 5s 2 1p 4 2p 2. B.
The bonding molecular orbital is fully filled with two electrons .The rest of the electrons remain in their atomic orbitals. Here is a useful MO diagram of HCL found on the internet: The Cl electrons residing up to 3s orbital (1s, 2s, 2px,2py,2pz,3s) are largely stabilized than H electron in 1s orbital and...
Nf+ molecular orbital diagram
The s molecular orbital is a bonding molecular orbital, and has a lower energy than the original atomic orbitals, since this combination of atomic in the schematic sketches on the left of the energy level diagram and in the calculated molecular orbital images on the right.* Because c(1sb) 4 , and. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. • Molecular orbital (MO) diagrams in organic chemistry. Molecular Orbital Diagrams Heteronuclear Diatomic HF. Alicia Rae Welden.
Nf+ molecular orbital diagram. The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. No. 9 Molecular Orbital Diagram for CO. Analysis done by Bond Order. If value of bond order is positive, it indicates a stable molecule and if the value is negative or zero, it means that the molecule is unstable. Molecular orbital theory is a method for determining molecular structure. It describes electrons as moving under the influence of the nucleus and not Molecular Orbital theory starts by assuming that the three atomic p orbitals on the O atoms overlap to form three molecular π orbitals that extend over... molecular orbital diagram. Sapling Self Assessment. University of North Carolina • CHEM 101. State the bond order, the molecular orbital configuration and determine whether each of the following molecules/ions is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. Here we have a molecular orbital diagram for the CO molecule. So when you're drawing on a global diagram like this, you have to draw it, it should be schematically shown lower energy than the carbon.
Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons. Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of MO energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked on the sides by constituent AO energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels ranging from low energy at the bottom to high energy at the top. A molecular orbital is an allowed spatial distribution of electrons in a molecule that is associated with a particular orbital energy. We can therefore use a molecular orbital energy-level diagram and the calculated bond order to predict the relative stability of species such as H2+. Creating molecular orbital diagrams for molecules with more than two atoms relies on the same basic ideas as the diatomic examples presented here. However, with more atoms, computers are required to calculate how the atomic orbitals combine.
To answer the question you have to draw the molecular orbital diagram or electron configuration for OF+ and NO+ (not the lewis For a molecule to be paramagnetic, there has to be at least one unpaired electron in a molecular orbital. This molecular orbital model can be used to explain why He2 molecules don't exist. Combining a pair of helium atoms with 1s2 electron configurations The molecular orbital diagram for an O2 molecule would therefore ignore the 1s electrons on both oxygen atoms and concentrate on the interactions... The molecular orbital diagram for the nitrogen monoxide molecule is shown in Figure 4.6. The orbitals are produced from the same pairs of atomic orbitals as in the cases of the homonuclear diatomic molecules of Section 4.2. Molecular Orbital Theory. Bonding and Antibonding Molecular Orbitals. In molecular orbital theory, bond order is also defined as the difference, divided by two, between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons; this often, but not always, yields the same result.
Download scientific diagram | Molecular orbital diagrams for HBr and HF. from publication: Total energy partitioning within a one-electron formalism: A Hamilton population study of surface-CO interaction in the c(2×2)-CO/ Ni(100)...
element. Accordingly, a molecular orbital diagram such as Figure 9-5 is inappropriate for heteronuclear diatomic molecules. If the two elements are similar (as in NO or CN mole-cules, for example), we can modify the diagram of Figure 9-5 by skewing it slightly.
Molecular Orbital Theory. I'm having a lot of trouble with this stuff. I don't really know how to start these questions (such as how to draw a correlation So here, I basically ask, how do I draw a correlation diagram? Like, how do I know how many electrons to put in the bonding atomic orbital and...

Write The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of N2 And Calculate Their Bond Order Chemistry Topperlearning Com Qbqjy
Bonding and antibonding orbitals. Simple molecular orbital diagrams. Dihydrogen and its ion H2+. Dihelium He2. The molecular orbital model is by far the most productive of the various models of chemical bonding, and serves as the basis for most quantiative calculations, including those that lead...
• Molecule orbital theory (Robert Mullikan). • Electrons are delocalised - Different to Lewis and hybridisation (these are not MO). • Energy level diagram represents this interaction. - Two s orbitals interaction to create a low energy bonding and high energy anti-bonding molecular orbital.
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular Orbital Theory. Valence Bond Theory proposes that electrons are localized between two atoms.
Figure 9. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that H2 will be a stable molecule with lower energy than the separated atoms. Creating molecular orbital diagrams for molecules with more than two atoms relies on the same basic ideas as the diatomic examples presented here.
Molecular orbital theory was put forward by Hund and Mullikan in 1932. This theory is modern and more rational. This theory assume that in molecules, atomic orbitals lose their identity and the electrons in molecules are present in new orbitals called molecular orbitals.
Molecular Orbital Theory: Detailed information on the molecular orbital theory class 11 and more in this article above. Stay tuned to Embibe. Molecular Orbital Theory- To simplify things, we will consider the interaction of the orbitals containing valence electrons to create molecular orbitals.

Given N22 Using Molecular Orbital And Valence Bond Theory A Write The Molecular Orbital Configuration B Determine The Bond Order C Determine The Stability D Is It Paramagnetic Or Diamagnetic Study Com
In a molecular orbital diagram, which of the following is listed down the center of the diagram? Select the correct answer below: atomic orbitals atomic or a diatomic molecule, how many molecular orbitals will have an n value of 1? 2 [For a diatomic molecule there will be a σ1s bonding orbital and...
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available: Molecules of the First Row
• Molecular orbital (MO) diagrams in organic chemistry. Molecular Orbital Diagrams Heteronuclear Diatomic HF. Alicia Rae Welden.
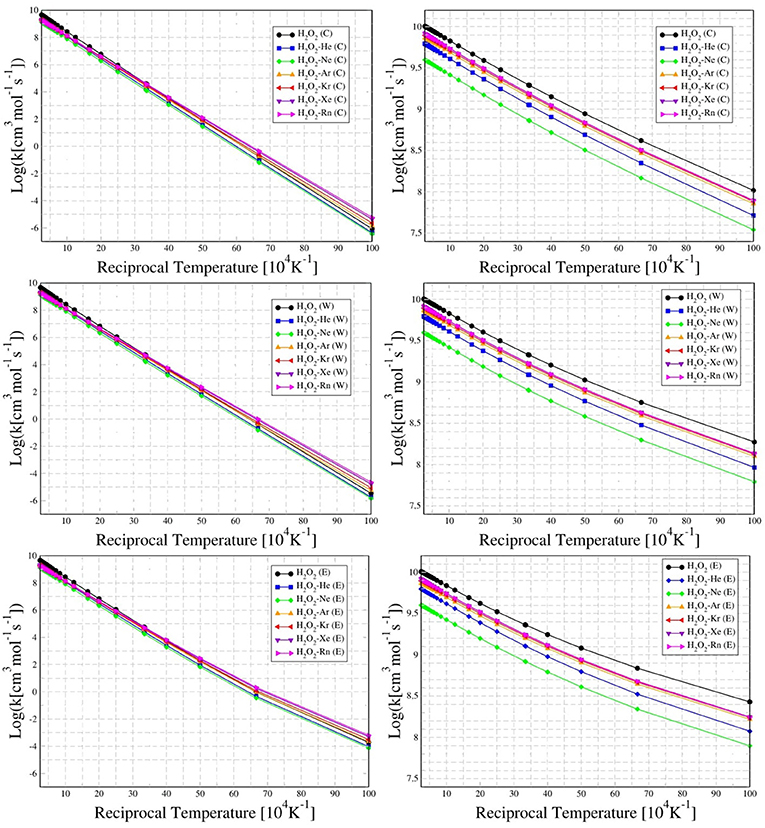
Frontiers Theoretical Investigation On H2o2 Ng He Ne Ar Kr Xe And Rn Complexes Suitable For Stereodynamics Interactions And Thermal Chiral Rate Consequences Chemistry
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
The s molecular orbital is a bonding molecular orbital, and has a lower energy than the original atomic orbitals, since this combination of atomic in the schematic sketches on the left of the energy level diagram and in the calculated molecular orbital images on the right.* Because c(1sb) 4 , and.
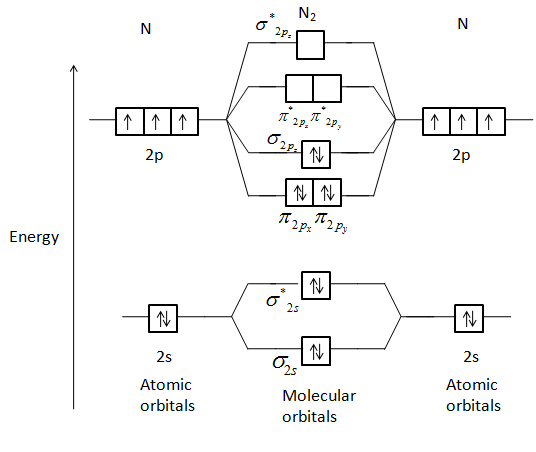
Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of N2 Also Find Its Bond Order And Magnetic Character Chemistry Topperlearning Com 4s4p942zz

4 15 Points Use Frontier Molecular Orbital Theory Fmo To Rationalize The Lack Of Reactivity Between Homeworklib

From Elementary Molecular Orbital Theory We Can Deduce The Electronic Configuration Of The Singly Positive Nitrogen Molecular Ion N 2 As


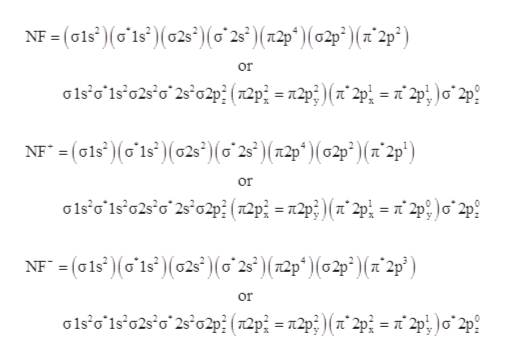














0 Response to "39 nf+ molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment