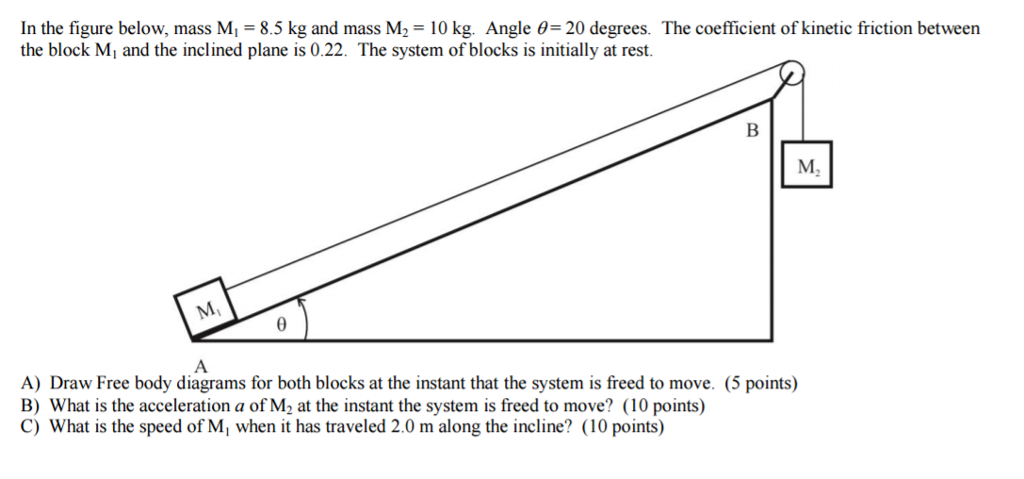
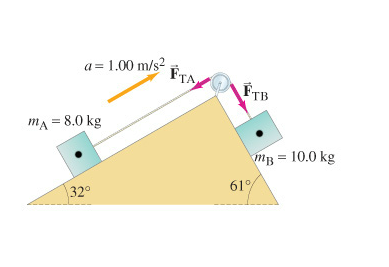
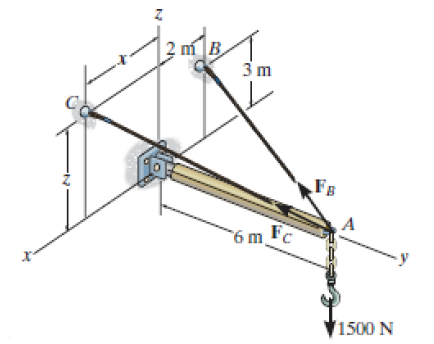
40 draw a free body diagram for the block a
› freebody-diagramWhat is a Free-Body Diagram and How to Draw it (with Examples ... Examples of drawing free-body diagrams. To better understand how to draw free-body diagrams using the 3 steps, let's go through several examples. Example 1. A box is pushed up an incline with friction which makes an angle of 20 ° with the horizontal. Let's draw the free-body diagram of the box. The first step is to sketch what is happening: › homework-help › questions-andSolved 1. Draw a free body diagram of the wood block - Chegg Draw a free body diagram of the wood block floating in the water, or any of the fluids because they will be identical, then write the force summation equation from that free body diagram (10 points) 2. Calculate the weight of fluid displaced by the wood block for all three fluids. (5 points) 3.
courses.lumenlearning.com › suny-osuniversity5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams | University Physics Volume 1 Draw a free-body diagram for each block. Be sure to consider Newton’s third law at the interface where the two blocks touch. Solution Significance →A 21 A → 21 is the action force of block 2 on block 1. →A 12 A → 12 is the reaction force of block 1 on block 2. We use these free-body diagrams in Applications of Newton’s Laws. Example

Draw a free body diagram for the block a
› homework-help › questions-andSolved Draw the free-body diagram for the block sliding up a ... Draw the free-body diagram for the block sliding up a rough slope after having been given a quick push. Draw the force vectors such that their tails align with the center of the block (indicated by the black dot). The orientations of your vectors will be graded but not the lengths. Show transcribed image text Expert Answer › homework-help › questions-andSolved Part A: Draw free-body diagram for the block A. Draw ... This problem has been solved! See the answer Part A: Draw free-body diagram for the block A. Draw the force vectors with their tails at the dot. The orientation of your vectors will be graded. The exact length of your vectors will not be graded but the relative length of one to the other will be graded. opentextbc.ca › 5-7-drawing-free-body-diagrams5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams – University Physics Volume 1 Draw a free-body diagram for each block. Be sure to consider Newton’s third law at the interface where the two blocks touch. Solution. Significance . is the action force of block 2 on block 1. is the reaction force of block 1 on block 2. We use these free-body diagrams in Applications of Newton’s Laws.
Draw a free body diagram for the block a. opentextbc.ca › 5-7-drawing-free-body-diagrams5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams – University Physics Volume 1 Draw a free-body diagram for each block. Be sure to consider Newton’s third law at the interface where the two blocks touch. Solution. Significance . is the action force of block 2 on block 1. is the reaction force of block 1 on block 2. We use these free-body diagrams in Applications of Newton’s Laws. › homework-help › questions-andSolved Part A: Draw free-body diagram for the block A. Draw ... This problem has been solved! See the answer Part A: Draw free-body diagram for the block A. Draw the force vectors with their tails at the dot. The orientation of your vectors will be graded. The exact length of your vectors will not be graded but the relative length of one to the other will be graded. › homework-help › questions-andSolved Draw the free-body diagram for the block sliding up a ... Draw the free-body diagram for the block sliding up a rough slope after having been given a quick push. Draw the force vectors such that their tails align with the center of the block (indicated by the black dot). The orientations of your vectors will be graded but not the lengths. Show transcribed image text Expert Answer
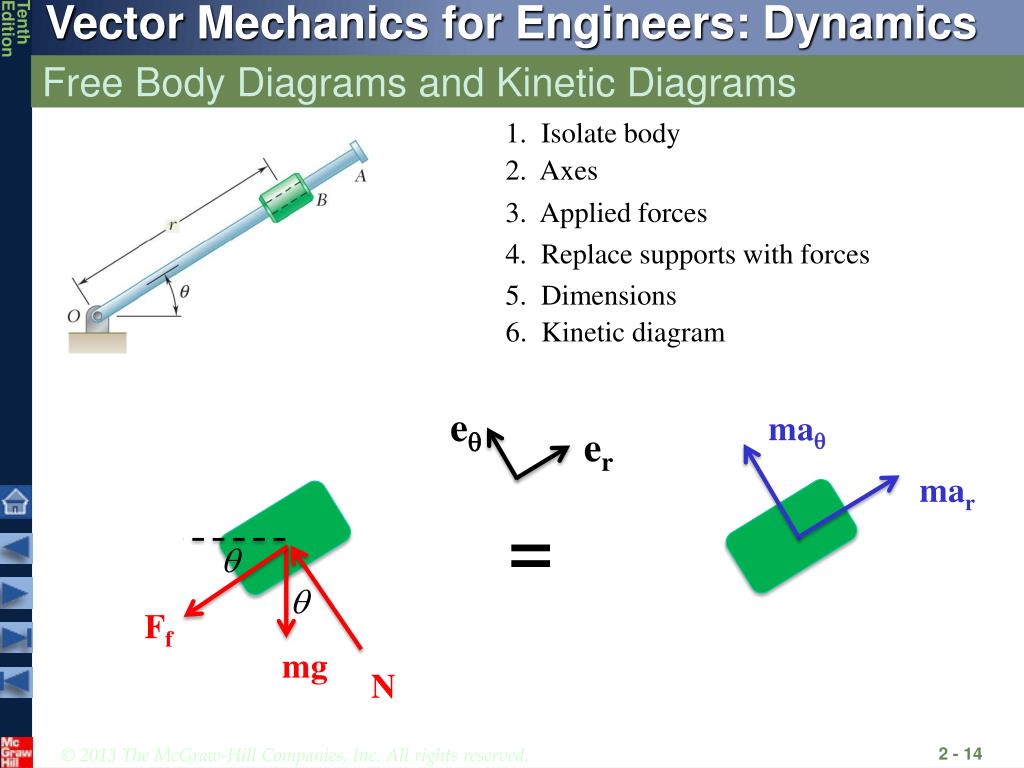
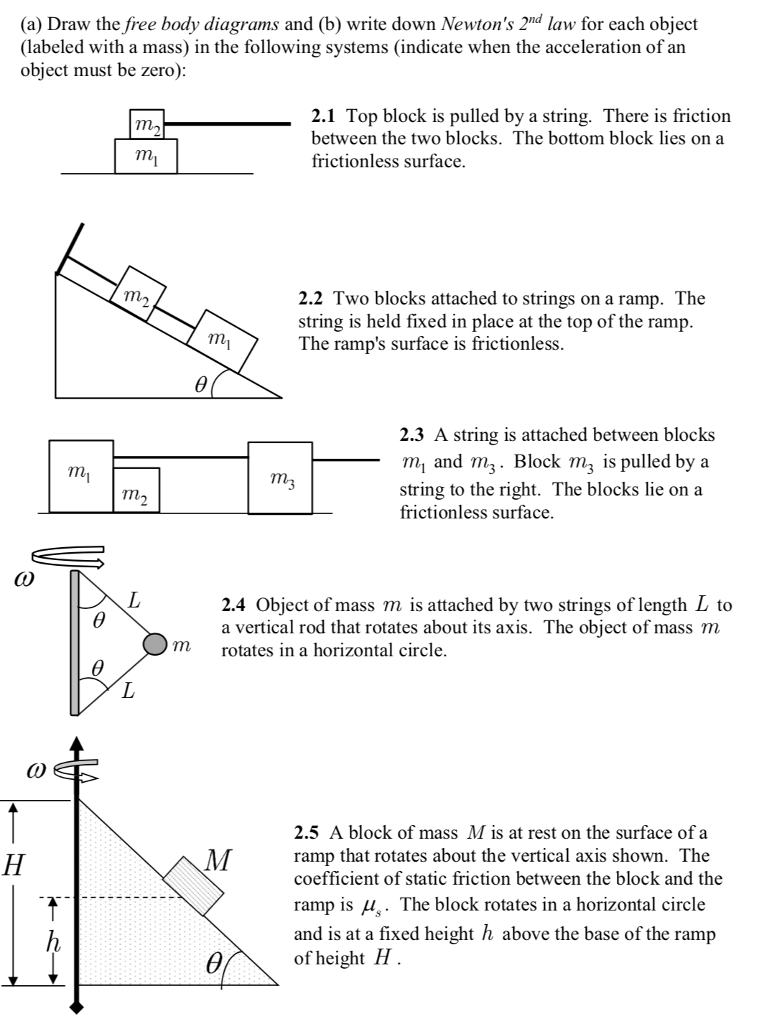


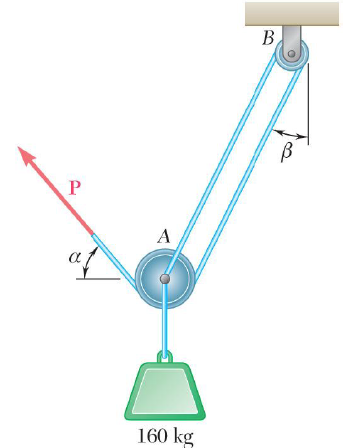


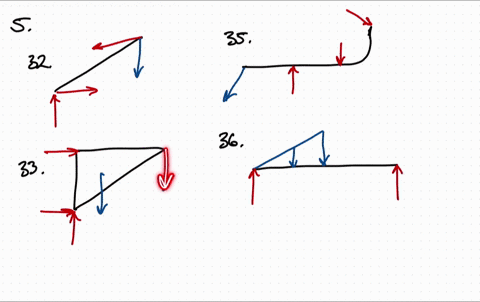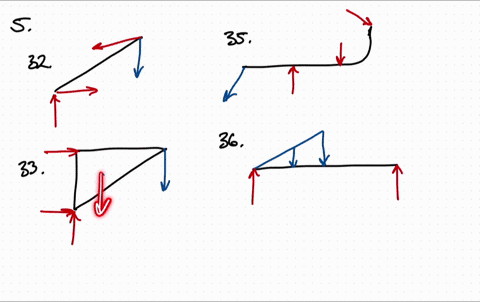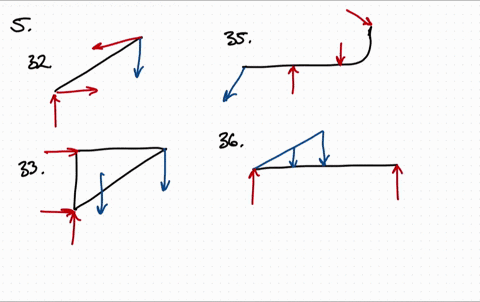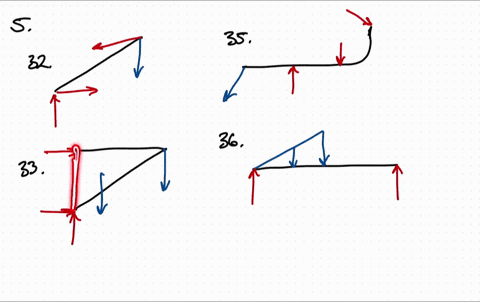


0 Response to "40 draw a free body diagram for the block a"
Post a Comment