39 monty hall tree diagram
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Monty_Hall_problemMonty Hall problem - Wikipedia The Monty Hall problem is a brain teaser, in the form of a probability puzzle, loosely based on the American television game show Let's Make a Deal and named after its original host, Monty Hall.The problem was originally posed (and solved) in a letter by Steve Selvin to the American Statistician in 1975. It became famous as a question from reader Craig F. Whitaker's letter quoted in Marilyn ... The Monty Hall Problem — Solved! - William M. Briggs The Monty Hall Problem — Solved! In honor of Monty Hall, who passed away this past weekend (in October 2017), this classic article (which ran long ago, the date lost due to the hacking, solving his namesake probability problem. Because of comments about adjusting the rules (see below), I have made some additions.
The Monty Hall Problem, Simplified - The Update The Monty Hall Problem, Simplified. You're on a game show. The prize for winning is a brand new car. The way the game show works is that the game show host (in this case it'll be me) is standing in front of you, with three doors. Behind one of those doors is the car you've always wanted.

Monty hall tree diagram
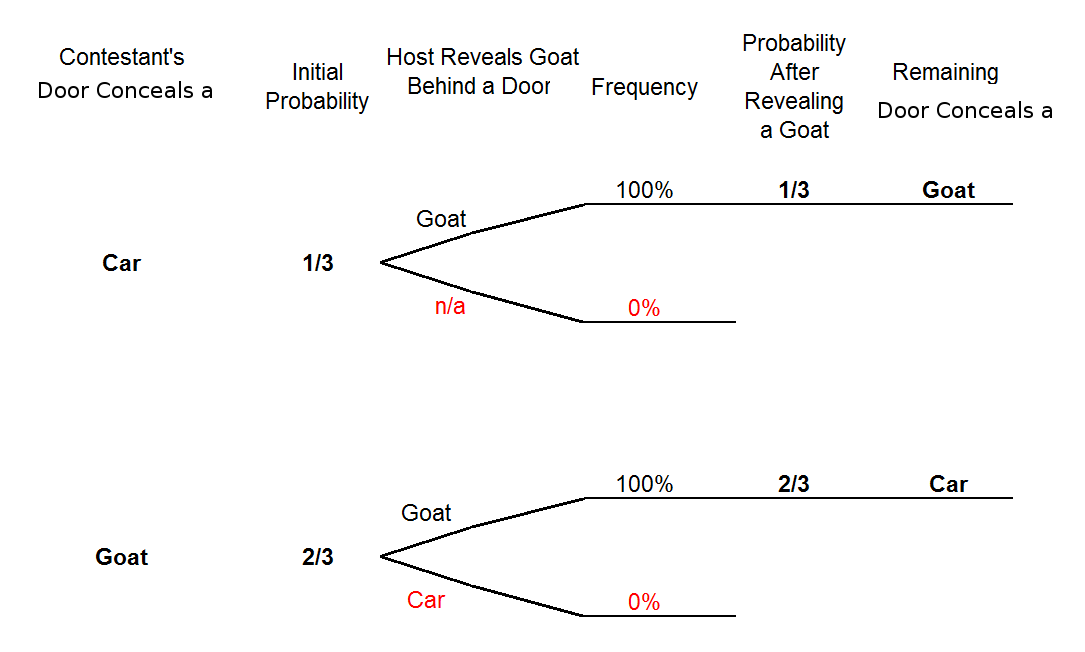
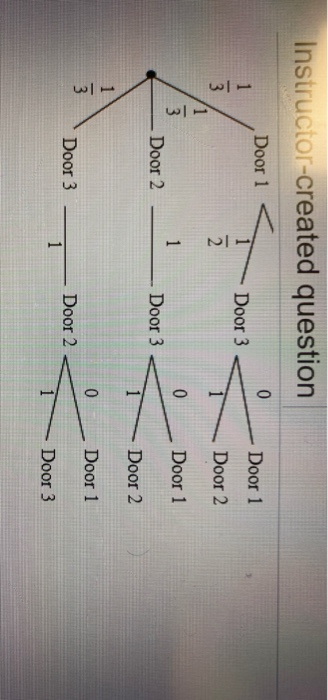
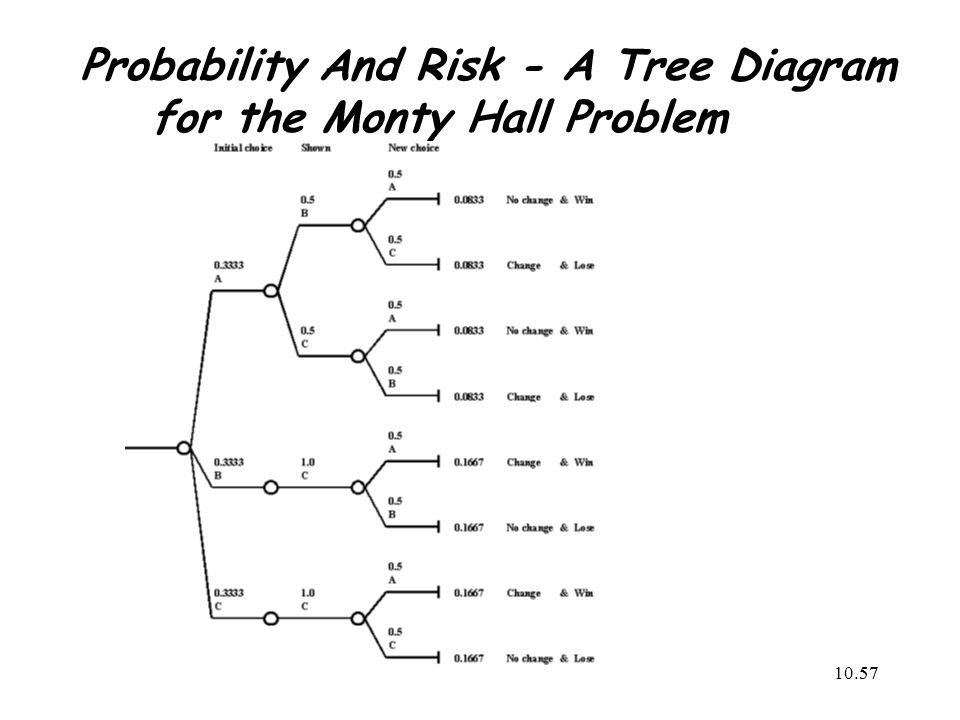
› chapter1 › 1_5_0_chapterProblems Basic Concepts - probabilitycourse.com Complete the following tree diagram: ... Problem * (The Monty Hall Problem) You are in a game show, and the host gives you the choice of three doors. Behind one door ... Solution To Monty Hall Problem - University of Notre Dame The probabilities can best be calculated with a tree diagram. Game Rules: 1. Pick a door. The diagram below shows the chances that you will pick the door with the car or either of the goats, Goat A or Goat B. 2. The host then reveals a goat behind one of the remaining doors. Solving the Monty Hall Problem with Bayes Theorem | by ... Now let's calculate the components of Bayes Theorem in the context of the Monty Hall problem. Let's assume we pick door A, then Monty opens door B. Monty wouldn't open C if the car was behind C so we only need to calculate 2 posteriors: P (door=A|opens=B), the probability A is correct if Monty opened B,
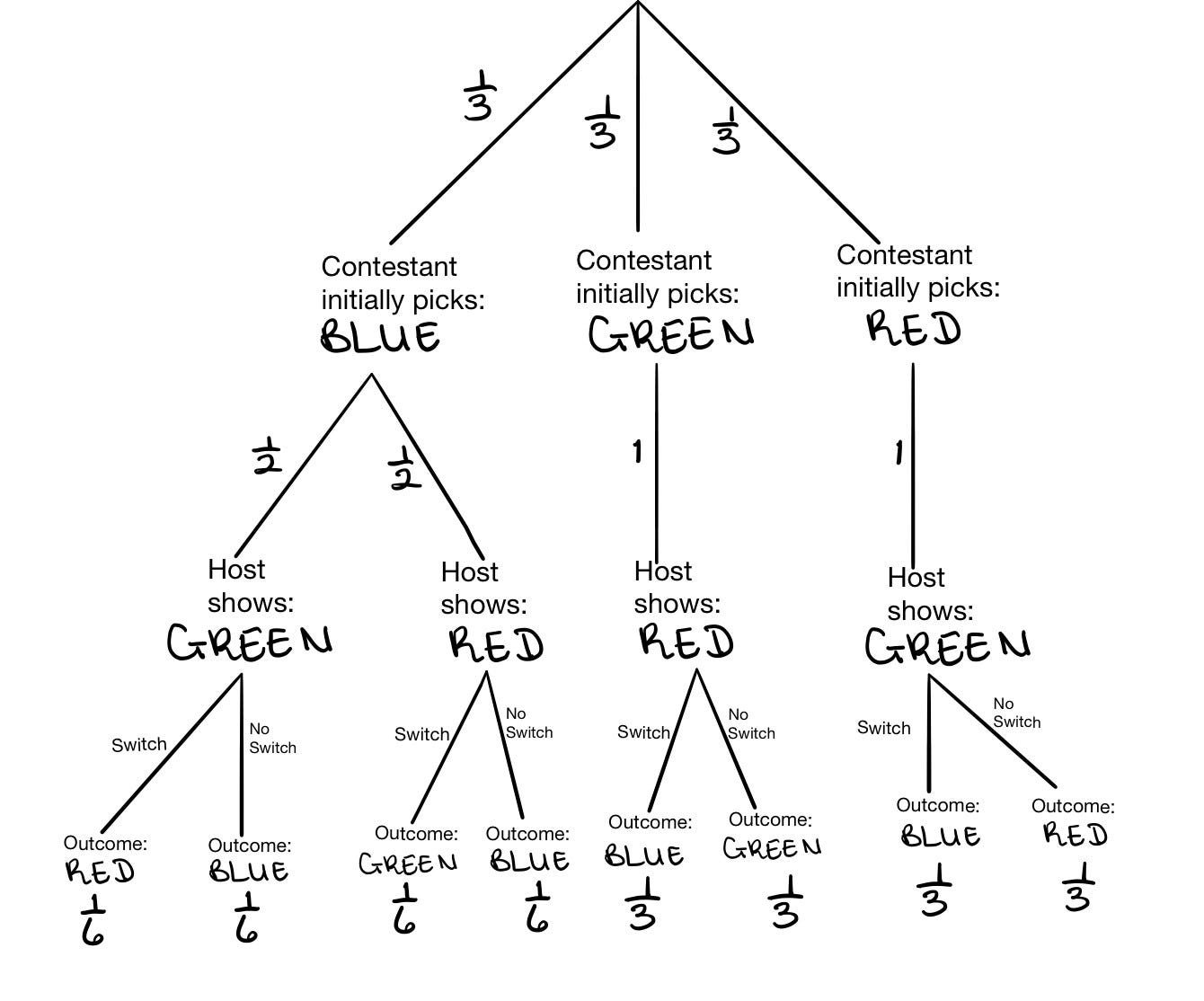
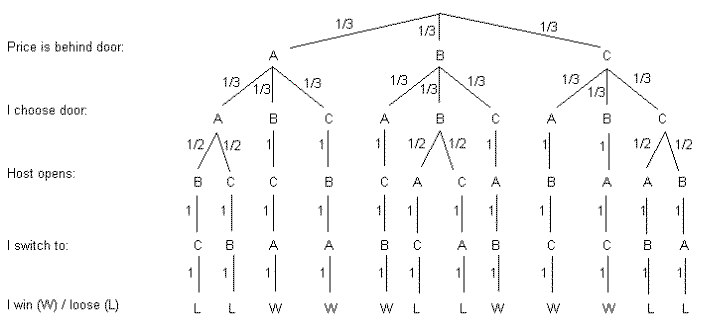
Monty hall tree diagram. Conditional Probability, The Monty Hall Problem Just as in the Monty Hall problem, we think that the probability of preferring blue to green is 1/2 due to symmetry, but the probability is 1/3. This time however conditioning on red being preferred to green reduced the original probability of 1/2 to 1/3, whereas in the Monty Hall problem the probability was initially 1/3 and did not change. Monte Hall Problem - Question on Decision Tree ... I read about the Monte Hall problem and understand the principle behind it: The door you choose is random, but the door Monte chooses is NOT. This is why switching doors gives you a higher probability. What I really had a question on is the construction of the decision tree for part (b). (a): I understand this solution is 1/3. Monty Hall Problem | Brilliant Math & Science Wiki The Monty Hall problem is a famous, seemingly paradoxical problem in conditional probability and reasoning using Bayes' theorem. Information affects your decision that at first glance seems as though it shouldn't. In the problem, you are on a game show, being asked to choose between three doors. Behind each door, there is either a car or a goat. You choose a door. The host, Monty Hall ... Understanding the Monty Hall Problem - BetterExplained The Monty Hall problem is a counter-intuitive statistics puzzle: There are 3 doors, behind which are two goats and a car. You pick a door (call it door A). You're hoping for the car of course. Monty Hall, the game show host, examines the other doors (B & C) and opens one with a goat. (If both doors have goats, he picks randomly.)
The Monty Hall Problem (21) - Math in Popular Media Introducing the Monty Hall Problem is also an excellent way to introduce the concept of conditional probabilities and multi-step tree diagrams in a Secondary V high school math class. Click here to try playing the game yourself! Additional resources Easy and informal explanation of the Monty Hall Problem PDF The Monty Hall Problem - University of Kentucky Play the Monty Hall Game. Record your results in the table below. Be sure to play 50 times WITH switching doors and 50 times WITHOUT switching doors. STRATEGY Switch Doors Don't Switch Doors WINS LOSSES WINNING PERCENTAGE 3. Do your results display a difference in your chance of winning based on whether or not you switched doors? Explain. 4. PDF Πιθανότητες - Πανεπιστήμιο Πατρών The Monty Hall problem • Υπάρχουν3 πόρτες • Πίσωαπό1 απόαυτέςυπάρχειένααυτοκίνητο ... Tree Diagram for Monty Hall Problem - YouTube In this video I have drawn the tree diagram for Monty Hall problem. In this video I have drawn the tree diagram for Monty Hall problem.
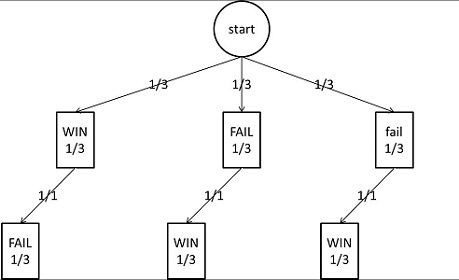
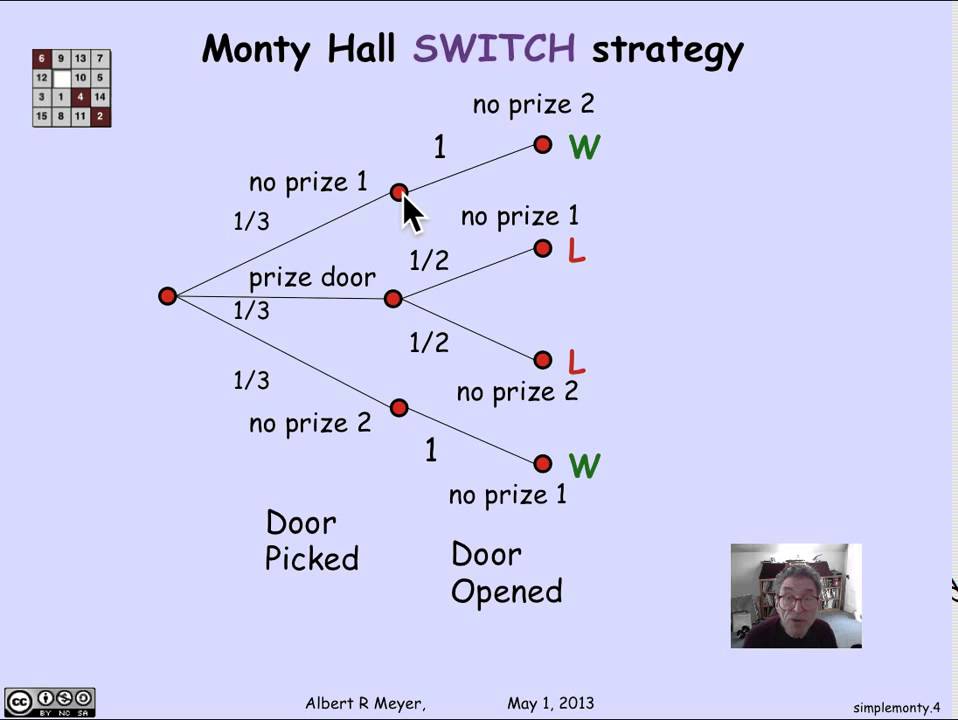
2 ways to look at The Monty Hall Problem | by Shen Huang ... Venn Diagram of Bayes' Theorem We can describe the Monty Hall Problem with a set of conditions. The probability of the car behind any of the door is 1/3. The probability of the host eliminating one... Monty Hall Problem Explained With Tree Diagram - YouTube Monty Hall Problem explained with a tree diagram. Original tree diagram obtained from an accompaniment to this vid... Monty Hall Problem — An empirical proof | by Madhushan ... Figure 1 — Tree diagram showing the probabilities associated with the Monty Hall Problem (Diagram by the Author) When you are asked to make your first choice, there is an equal probability that the car is behind any one of the three doors. So you have a 1/3 chance of guessing it correctly. This implies that 2/3 of the times your guesses are wrong. PDF 17 Conditional Probability Figure 17.1 The tree diagram for computing the probability that the local team wins two out of three games given that they won the first game. Step 1: Find the Sample Space Each internal vertex in the tree diagram has two children, one corresponding to a win for the local team (labeled W) and one corresponding to a loss (labeled L).
Python Diagram - 8 images - python editors, st louis mo ... monty hall problem explained with tree diagram youtube. Python Diagram. Here are a number of highest rated Python Diagram pictures on internet. We identified it from obedient source. Its submitted by giving out in the best field. We undertake this nice of Python Diagram graphic could possibly be the most trending topic later we part it in ...
1 The Monty Hall Problem | Odds & Ends - Jonathan Weisberg Tree diagrams are a handy tool for solving probability problems. They also illustrate some central concepts of probability. Probabilities are numbers assigned to possibilities. In the Monty Hall problem, there are three possibilities for where the prize is: door A, door B, and door C.
The Monty Hall Problem - Mathematical Mysteries Definition Monty Hall problem is a mathematical brain teaser dealing with probabilistic decision making. It originated from a TV show hosted by Monty Hall in 1963. It is a very good example of how probabilistic scenarios may seem simple but yet at times can be difficult to wrap our minds around them. 1 Who
site/monty-hall-problem-generalized-with-tree-diagram.html ... static website for lubian.info. Contribute to lubian/site development by creating an account on GitHub.
Monty Hall Problem | Understand Monty Hall Problem in Detail Monty Hall Problem is one of the most perplexing mathematics puzzle problems based on probability. It was introduced by Marilyn Savant in 1990. It is named after the host of a famous television game show 'Let's Make A Deal'. In this game, the guest has to choose among three closed doors, only one of which has the surprise car behind it ...
Monty Hall problem decision tree according to conditional ... Download scientific diagram | Monty Hall problem decision tree according to conditional probability According to Figure 5, in case the host opens door 3 and the contestant changes his/her choice ...
xkcd.com › archivexkcd - A webcomic of romance, sarcasm, math, and language ... I'm a Car Carnot Cycle Barnard's Star Tectonics Game Hygrometer Modified Bayes' Theorem Rock Wall Internal Monologues Horror Movies Bluetooth Data Pipeline Incoming Calls Stanislav Petrov Day Bad Opinions 6/6 Time Unfulfilling Toys Curve-Fitting Beverages Trum-Social Media Announcement Sandboxing Cycle Boathouses and Houseboats Rolle's Theorem ...
The Monty Hall Problem - Probability - Mathigon The Monty Hall Problem - Probability - Mathigon The Monty Hall Problem Welcome to the most spectacular game show on the planet! You now have a once-in-a-lifetime chance of winning a fantastic sports car which is hidden behind one of these three doors. Unfortunately, there are only goats behind the other two doors. Select one to make your choice!
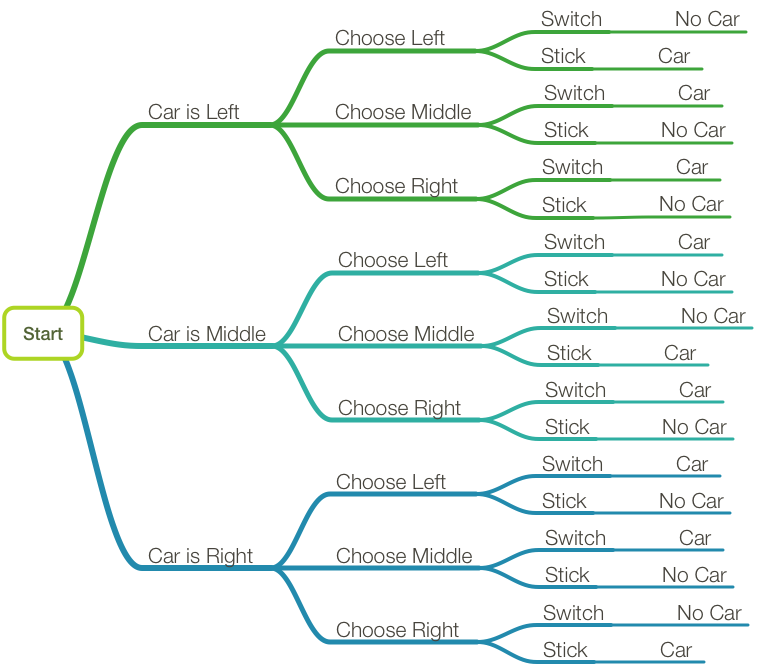
Outcome tree for the Monty Hall problem. From the left ... Download scientific diagram | Outcome tree for the Monty Hall problem. From the left: first the car is assigned to one of from publication: Probability, problems, and paradoxes pictured by ...
› types-of-neural-networksTypes of Neural Networks | Top 6 Different Types of ... - EDUCBA In the above diagram, the data moves in the forward direction with 3 nodes in Layer 1 having a distinct function to process within itself. These have found useful usage in face recognition modeling and computer vision. 2. Radial Basis Function (RBF) Neural Network
Solving the Monty Hall Problem with Bayes Theorem | by ... Now let's calculate the components of Bayes Theorem in the context of the Monty Hall problem. Let's assume we pick door A, then Monty opens door B. Monty wouldn't open C if the car was behind C so we only need to calculate 2 posteriors: P (door=A|opens=B), the probability A is correct if Monty opened B,
Solution To Monty Hall Problem - University of Notre Dame The probabilities can best be calculated with a tree diagram. Game Rules: 1. Pick a door. The diagram below shows the chances that you will pick the door with the car or either of the goats, Goat A or Goat B. 2. The host then reveals a goat behind one of the remaining doors.
› chapter1 › 1_5_0_chapterProblems Basic Concepts - probabilitycourse.com Complete the following tree diagram: ... Problem * (The Monty Hall Problem) You are in a game show, and the host gives you the choice of three doors. Behind one door ...
























0 Response to "39 monty hall tree diagram"
Post a Comment