38 e1 reaction coordinate diagram
Substitution and Elimination Reactions Flashcards - Quizlet Reaction Coordinate Diagram for E1 Types of Products in E2 reactions Zaitsev or major PDT (more substituted & Thermodynamically stable PDT). Hoffman or minor PDT (less substituted & less Thermodynamically stable PDT). How does a base affect regiochemistry? As size of B: increases, the stability of the PDT increases in Hoffman form. Solved Given the general reaction coordinate diagram for an | Chegg.com Given the general reaction coordinate diagram for an E1 reaction, what does the 1st transition state refer to? An activated complex between the base and carbocationic species. An activated complex between the nucleophile and carbocationic species. None of these An activated complex between the leaving group and carbocationic species.
E1 Reaction Coordinate Energy Diagram - YouTube presents: E1 Reaction Coordinate Energy Diagram with step by step mechanism, transition states and intermediates📺Watch Next...

E1 reaction coordinate diagram
PDF Eliminations Instead of substitution reactions, another reaction that can occur - Two ... Reaction Coordinate! S N 1! Potential energy! Reaction Coordinate! E1! S N 1 and E1 Reactions Have Identical Energy Diagrams for Rate Determining Step! Cl H CH3 3C H3C Cl H CH3 3C H3C CH3 H3C CH3 CH3 H3C CH3 OCH3 H CH3 3C H3C H2C CH3 CH3 B CH3OH Rate = k [substrate]! Rate = k [substrate]! Energy Diagram For Sn2 Label the axes, the Ea, the ΔH° and the transition state of the reaction. Assume the reaction is exothermic and ΔH° = kJ/mol and Ea = 50 kJ/mol. Draw the structure of reactants and products on the diagram. You can put the. SN2 reaction coordinate diagram. Answered: Based upon the following energy… | bartleby Solution for Based upon the following energy diagram, is this reaction an E1 or an E2 elimination? reaction coordinate O E1 O E2 free energy, KJ/mol
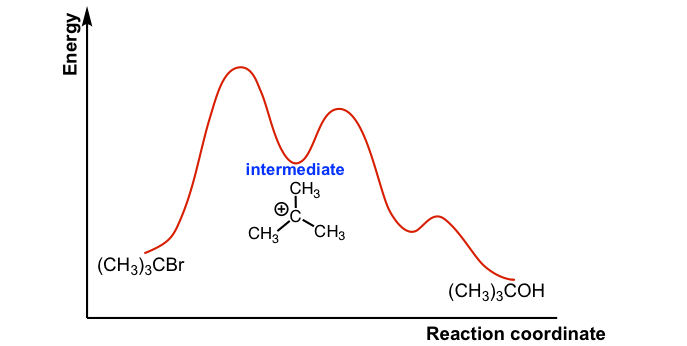
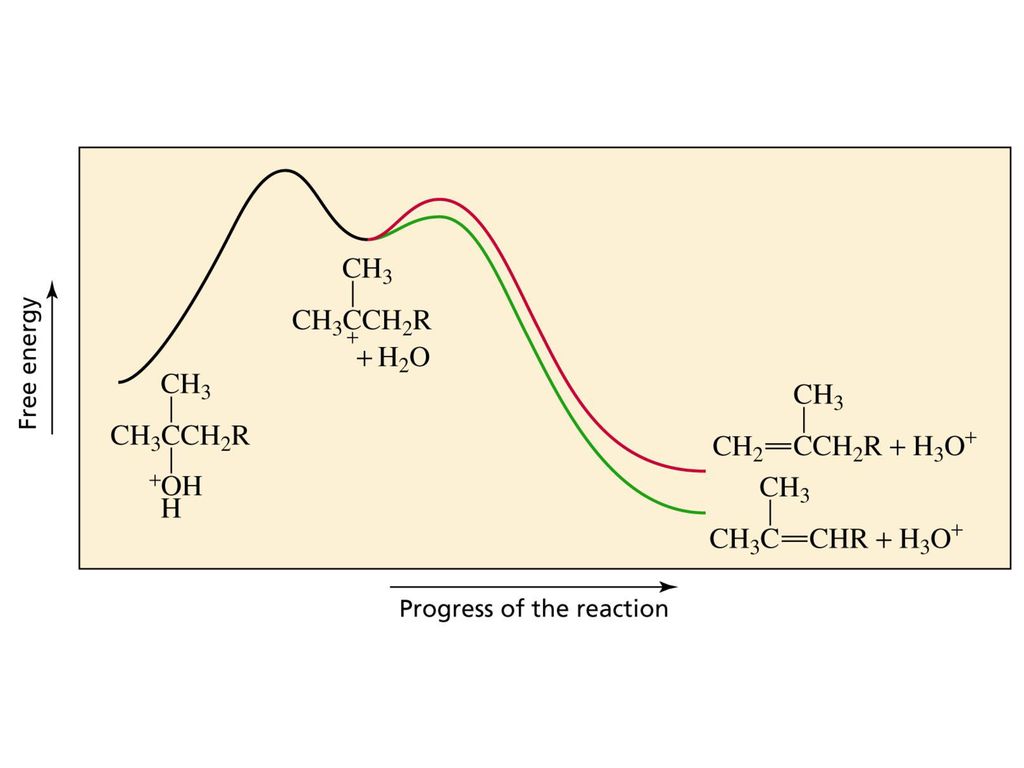
E1 reaction coordinate diagram. Lecture6-7_E1_E2_Pre-slides.pdf - Elimination reaction Functional groups lost from a ... E1 - Reaction Coordinate Diagram "two" steps Rate-Determining Step (RDS) E1 - Regioselectivity • Major product is the more stable alkene (Zaitsev) Stereoselectivity of E1 • Because a carbocation is formed, the stereochemistry of the products can be either cis or trans , with the more configuration being favored PDF Lecture outline A closer look at carbocation stabilities and SN1/E1 reaction rates The Hammond postulate says that if two consecutive structures on a reaction coordinate are similar in energy, they are also similar in structure. For example, in the SN1/E1 reactions, we know that the carbocation intermediate is much higher in energy than the alkyl halide reactant, so the transition state for the ionization step must Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram - schematron.org Figure 2: Reaction coordinate diagram for an SN1 reaction1. 1. Identify the . Figure 2 identifies these species in a reaction coordinate diagram like the one in the right-hand panel of Figure 1. Here the nucleophile is hydroxide ion. The SN1 Mechanism. 4. Determining Draw a reaction coordinate diagram that illustrates your equilibrium prediction. PDF 9.6 THE SN1 AND E1 REACTIONS - Macmillan Learning reaction coordinate Br Figure 9.11 Reaction free-energy diagram for the S N1-E1 solvolysis reaction of (CH 3) 3CBr with ethanol.The rate-limiting step,ionization of the alkyl halide (red curve),has the transition state of highest standard free energy.The
Survey in Substitution Reactions and Elimination Reactions E1 indicates aelimination, unimolecularreaction, where rate = k [R-LG]. This implies that the rate determining step of the mechanism depends on the decomposition of a single molecular species. Overall, this pathway is a multi-step process with the following two critical steps: Answered: The following reaction coordinate… | bartleby The following reaction coordinate diagram charts the energy of a substrate molecule (S) as it passes through a transition state (X‡) on its way to becoming a stable product (P) alone or in the presence of one of two different enzymes (E1 and E2). PDF Elimination Reactions - University of Minnesota reaction coordinate E1 and SN1 Frequently Occur Together (because they pass through a common intermediate) (as base) CH3OH Ratio of E1/SN1 products depends on the relative basicity/ l hili it f th Br _ nucleophilicity of the electron donor. (as nucleophile) Nucleophilicity and basicity are often correlated. So, difficult to control. 8.5. Elimination reactions | Organic Chemistry 1: An open textbook - Lumen Learning E1 Reactions Unimolecular elimination (E1) is a reaction in which the removal of an HX substituent results in the formation of a double bond. It is similar to a unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN1) in particular because the rate determining step involves heterolysis (losing the leaving group) to form a carbocation intermediate.
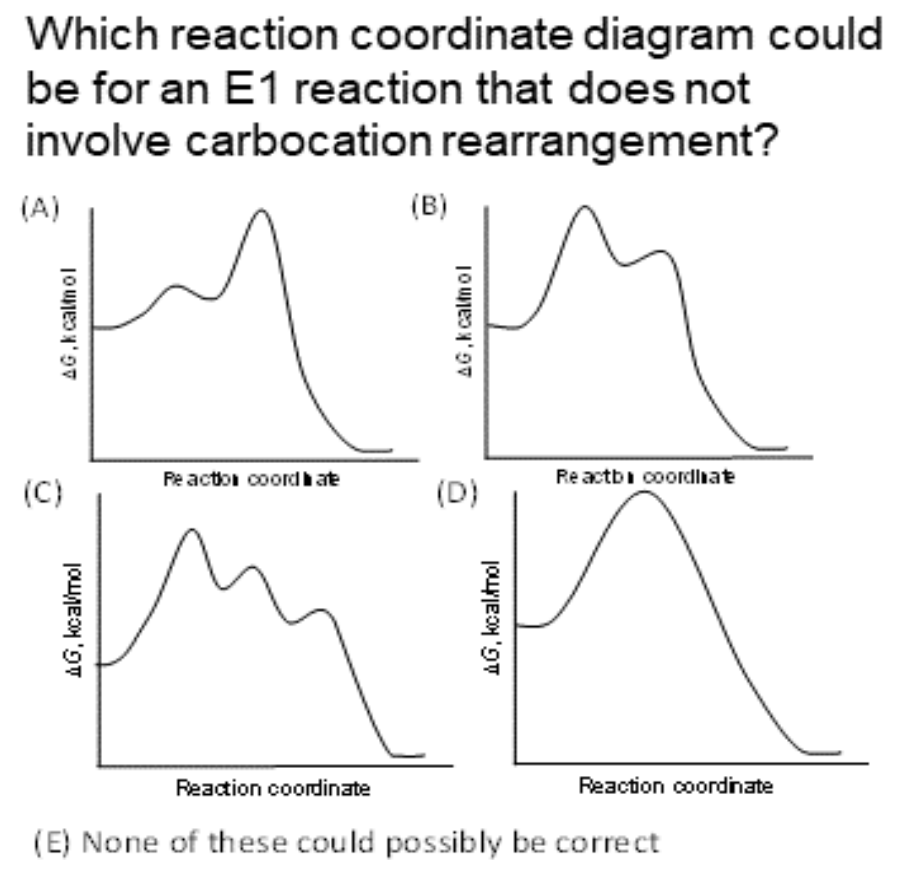
PDF Chem 14D - Spring 2010 - Garg Midterm 1 Review / Practice Problems Reaction coordinate diagram Inter and intramolecular examples Solvent trends / solvation S N1 Mechanism / solvolysis Stereochemistry Transition state Reaction coordinate diagram Solvent trends E1 and E2 Mechanisms Stereochemistry Solvent/reaction condition trends Alcohol Synthesis Nucleophilic additions to carbonyls NaH vs. NaBH 4 / LiAlH 4 PDF Ch11MR elimination reaction2 - staff.du.edu.eg Reaction coordinate diagram for the E1 reaction of 2-chloro-2-methylbutane E1 reactions can be regioselective . The role of the leaving group Since the leaving group is involved in the rate-determining step of both E1 and E2, in general, any good leaving group will lead to a fast Reaction Coordinate Diagrams The diagram below is called a reaction coordinate diagram. It shows how the energy of the system changes during a chemical reaction. In this example, B is at a lower total energy than A. This is an exothermic reaction(heat is given off) and should be favorable from an energy standpoint. The energy difference between A and B is E in the diagram. Organic Chap 8 Flashcards | Quizlet The reaction coordinate vs. energy diagram has two energy barriers. E1 reactions are ________ -selective, favoring formation of the more substituted, more stable alkene. regio
PDF Elimination Reactions - IIT Kanpur Factors Affectin g the Rate of an E1 Reaction The rate of an E1 reaction increases as the number of R groups on the carbon with the leaving group increases. Increasing rate of E1 reaction RCH 2 XR 2CH XR 3C X 1° 2° 3° + + + I i bili f b i RCH 2 R 2CH R 3C 1° 2° 3° ncreas ng sta ty o car ocat ons The strength of the base usually determines ...
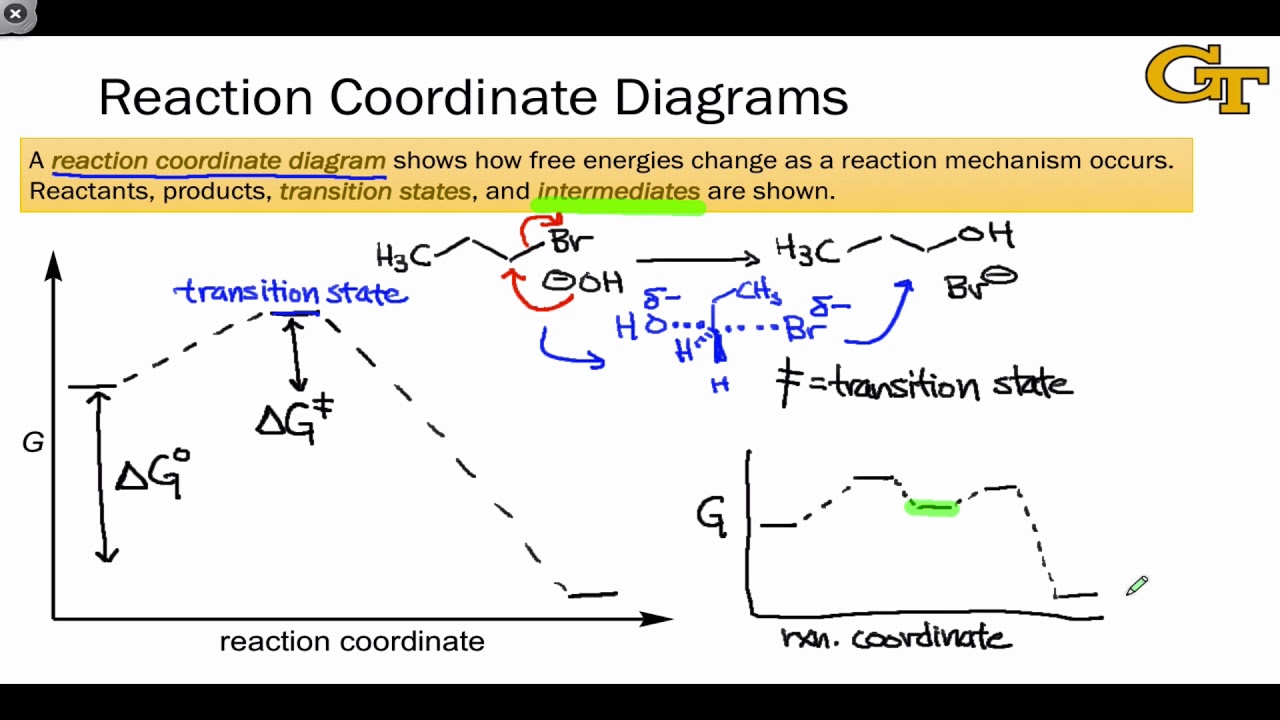
5.3. Reaction coordinate diagrams | Organic Chemistry 1: An open textbook In an energy diagram, the vertical axis represents the overall energy of the reactants, while the horizontal axis is the ' reaction coordinate ', tracing from left to right the progress of the reaction from starting compounds to final products.
PDF Lecture Handouts | Organic Chemistry I | Chemistry | MIT OpenCourseWare Free Radical Reactions: Thermo/Kinetics Sarah Tabacco Ch. 4 12 Free Radical Reactions: Thermo/Kinetics Sarah Tabacco Ch. 4 13 Alkyl Halides/SN2 Sarah Tabacco Ch. 6 14 SN2/SN1 Sarah Tabacco Ch. 6 15 SN1/E1 Sarah Tabacco Ch. 6 16 E1/E2 Sarah Tabacco Ch. 6 17 E2 Sarah Tabacco Ch. 6 18 Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes
Solved Based upon the energy diagram shown, is this reaction | Chegg.com Based upon the energy diagram shown, is this reaction an E1 or an E2 elimination? free energy, kJ/mol reaction coordinate O E1 elimination O E2 elimination O It is impossible to determine from the diagram alone. The diagram suggests that it is not an elimination reaction. What substitution reaction mechanism is most likely for the conversion shown?
Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram SN1 reaction The S1 reaction is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry. or process an energy profile (or reaction coordinate diagram) is a theoretical. SN1 reaction is a two step reaction as mentioned below: 1. Leaving group leaves first being solvolysed by solvent creating a carbocation intermediate. This is.
Nucleophilic Substitution and Beta Elimination - SN1 SN2 E1 E2 Reactions - Leah4sci This video walks you through the energy of the SN2 reaction mechanism from starting reactant to final product by reviewing, in detail, the SN2 Reaction Energy Diagram. Comparing Between SN1 and SN2 Reactions E1 - Unimolecular Beta Elimination E2 - Bimolecular Beta Elimination Think you understand the four mechanisms?
PDF SN2 S 1 - ocw.mit.edu E2 E1. 2 reaction coordinate (S N2) ... Generic Reaction-Energy Diagrams Predicting the Products: Substitution versus Elimination Is Nuc/Base strong? no Unimolecular Reaction Bimolecular yes Reaction
PDF Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides E2 and E1 Reactions in Detail - bingol.edu.tr Reaction coordinate diagram for the E1 reaction of 2-chloro-2-methylbutane. Must consider possible carbocation rearrangement. Stereochemistry of the E1 Reaction. E1 Elimination from Cyclic Compounds E1 mechanism involves both syn and anti elimination. Summary & Applications (Synthesis) S N 1 / E1 vs. S N
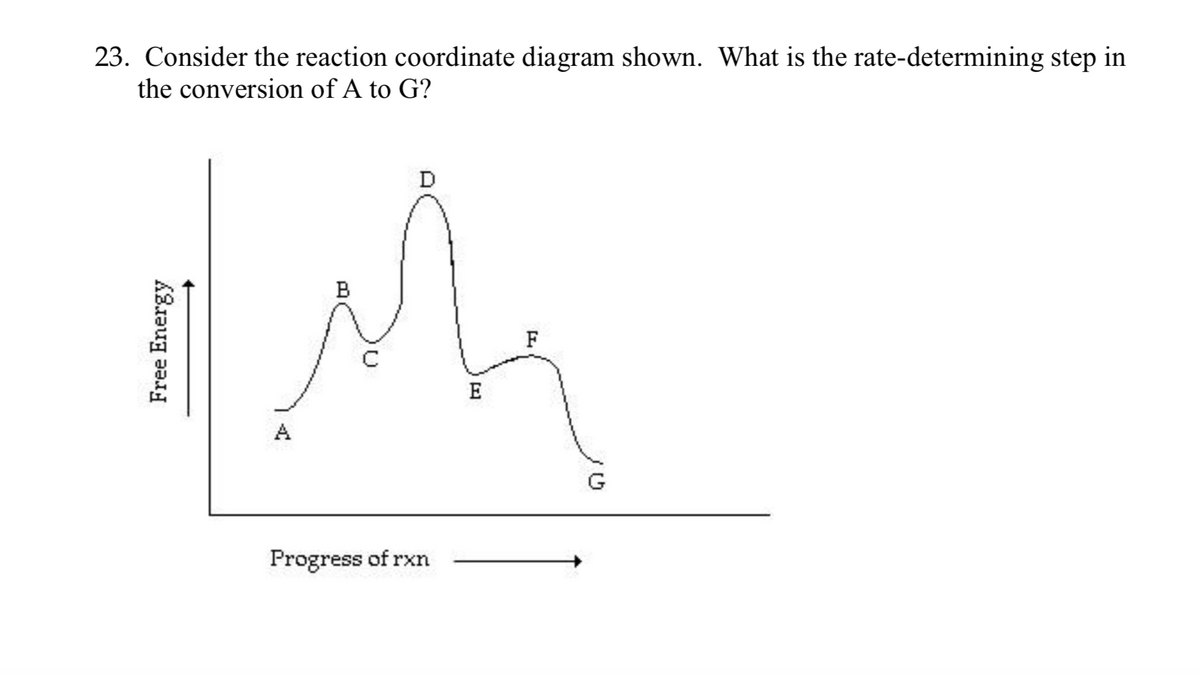
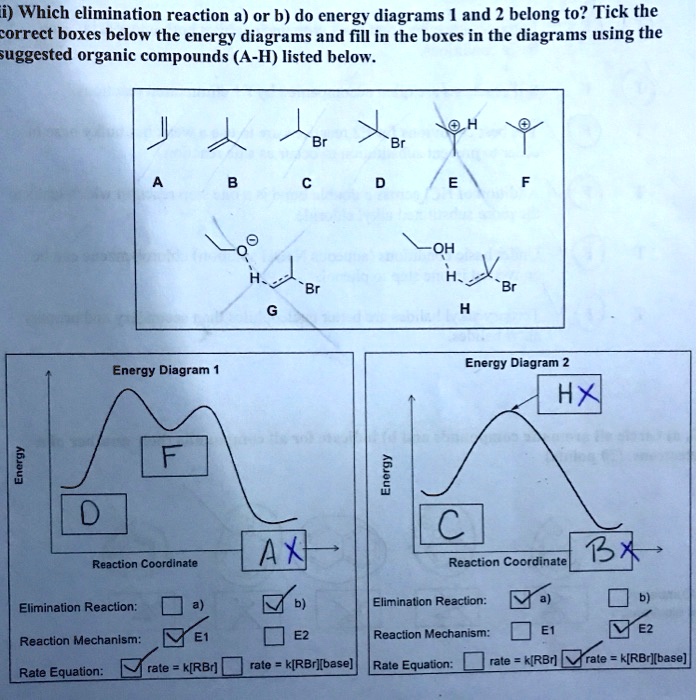
CHEM 233 Spring 2022 E1 Reactions and Fractional Distillation Lecture Slides.pdf - 4/7 ... 4/7/2022 7 Identify the rate-determining step in the following reaction coordinate diagrams. 13 E1 reactions Using Montmorillonite K10 clay instead of H 3 PO 4 H"Acid": Montmorillonite K10 clay Montmorillonite K10 clay is quite susceptible to static electricity 14 13 14
Organic Chemistry: E1 Reaction with Alkyl Halides & Reaction Coordinate - YouTube This reaction is good but check out our new improved animation of the E1 reaction!The E1 reaction with an alkyl halide occurs in two steps. In the first ste...
Ch 8 : SN2 mechanism - Faculty of Science two species, the nucleophile and the organic substrate. This pathway is a concerted process (single step) as shown by the following reaction coordinate diagrams, where there is simultaneous attack of the nucleophile and displacement of the leaving group. Let's look at how the various components of the reaction
Answered: Based upon the following energy… | bartleby Solution for Based upon the following energy diagram, is this reaction an E1 or an E2 elimination? reaction coordinate O E1 O E2 free energy, KJ/mol
Energy Diagram For Sn2 Label the axes, the Ea, the ΔH° and the transition state of the reaction. Assume the reaction is exothermic and ΔH° = kJ/mol and Ea = 50 kJ/mol. Draw the structure of reactants and products on the diagram. You can put the. SN2 reaction coordinate diagram.
PDF Eliminations Instead of substitution reactions, another reaction that can occur - Two ... Reaction Coordinate! S N 1! Potential energy! Reaction Coordinate! E1! S N 1 and E1 Reactions Have Identical Energy Diagrams for Rate Determining Step! Cl H CH3 3C H3C Cl H CH3 3C H3C CH3 H3C CH3 CH3 H3C CH3 OCH3 H CH3 3C H3C H2C CH3 CH3 B CH3OH Rate = k [substrate]! Rate = k [substrate]!






















0 Response to "38 e1 reaction coordinate diagram"
Post a Comment