36 diagram of convection current
Convection Currents Diagram - Quizlet Start studying Convection Currents. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Applications of Convection | Definition, Examples, Diagrams Uses of convection. The following are the uses of convection: Car engines are cooled by convection currents in the water pipes. Water is a very good substance to carry the unwanted heat away from the engine to the radiator. Land and sea breezes are caused due to convection currents. Rising air over the land are convection currents and are used ...
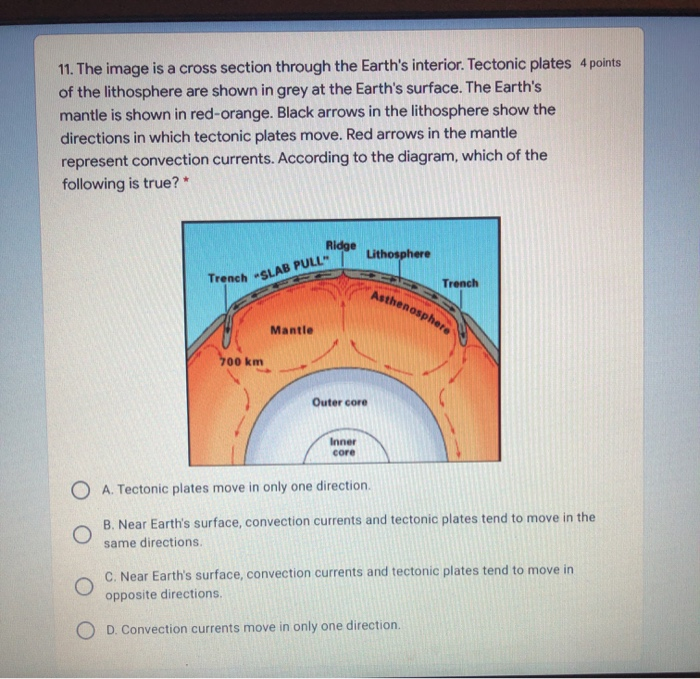
38 diagram of convection current - Wiring Diagrams Manual The diagram represents a convection current in the Earth's ... The diagram represents a convection current in the Earth's mantle. Descriptions of the events at each of the positions are shown. Move each number from the diagram to the blank box that describes the event occurring at the position in the convection current.
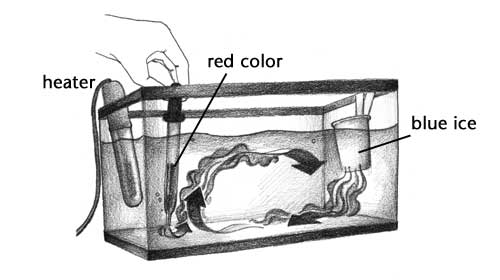
Diagram of convection current
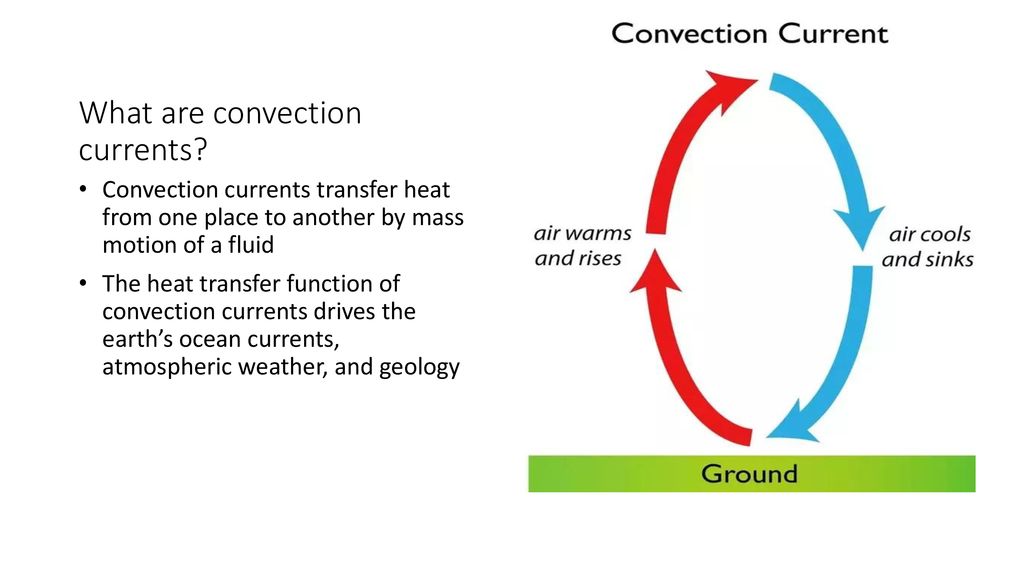
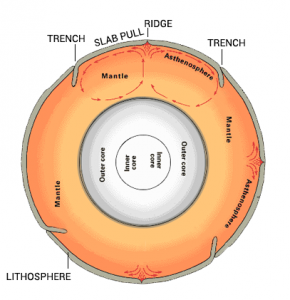
Convection Currents - Utah Education Network Convection currents can occur in any fluid, such as air or a liquid. When a fluid heats up, it expands, making it less dense and therefore lighter than the fluid around it. Warm fluids rise while cold fluids sink, setting up a circular pattern of flow toward and away from a heat source until all of the fluid reaches the same temperature. PDF Mantle convection - Yale University Mantle convection: Thermal convection in the terrestrial planetary mantles, the rocky layer be-tween crust and core, inwhich hotmaterial rises, cold material sinks and the induced flow governs plate tectonic and volcanic activity, as well as chemical segregation and cooling of the entire planet. Mantle convection Introduction and History Convection currents Diagram | Quizlet Theory that the Earth's crust is divided into tectonic plates which move around due to convection currents in the mantle. Convection currents The movement caused within a fluid by hotter and therefore less dense material to rise, and colder, denser material to sink under the influence of gravity.
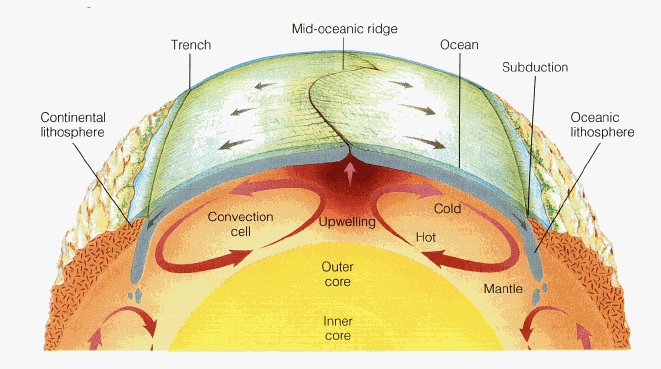
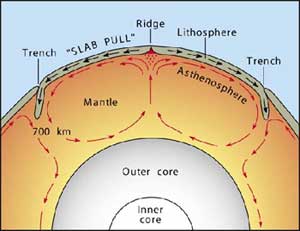
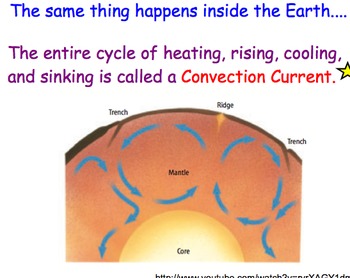
Diagram of convection current. PDF Nitty Gritty Science © 2014 1 - NOTES AND WORKSHEETS Convection Currents Directions: Cut out the descriptions below and paste each statement next to the letter (A-D) that is describing the convection current in the diagram at the corresponding letter. Next complete the graphic organizer by describing the cause and effects of convection currents in the mantle and the result of these actions. The diagram represents a convection current in the Earth's ... The diagram represents a convection current in the Earth's mantle. Descriptions of the events at each of the positions are shown. Move each number from the diagram to the blank box that describes the event occurring at the position in the convection current. Convection Current in Mantle crust 3 Descriptions Movement of loss dense material Convection - schoolphysics ::Welcome:: You should see the colour rise up this side, go across the top and then fall down the other side of the beaker — this is a convection current. You can also use the special piece of apparatus shown in the diagram. It is a "square " glass tube filled with water. Plate Tectonics 6.2 - Radford Convection (Diagram by Phyllis Newbill) Convection currents are powered by the heat deep within the earth. As material heats up, it becomes less dense and rises near mid-ocean ridges. As the heated material moves farther from the heat source, it cools, becomes more dense, and begins to sink. This cycle of heating and cooling is called a ...
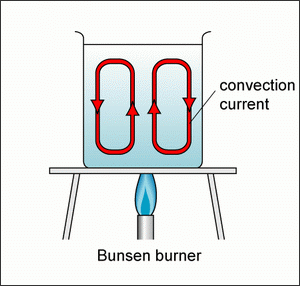
Convection - Conduction, convection and radiation - GCSE ... Convection currents can be seen in lava lamps. The wax inside the lamp warms up, becomes less dense than the liquid and so rises. When it rises, it cools and becomes denser again, so it sinks. What Is Convection? - Heat Definition, Types of Convection ... Convection is the process of heat transfer by the bulk movement of molecules within fluids such as gases and liquids. The initial heat transfer between the object and the fluid takes place through conduction, but the bulk heat transfer happens due to the motion of the fluid. Convection is the process of heat transfer in fluids by the actual ... 10 Common Examples Of Convection (with Pictures) Since a convection current is set, the temperature of the bottle surface is gradually altered and the chilled drink melts. After a long time, it will be at the same temperature with the environment. 6. Convection Oven. Convection oven is quite different from the regular oven. Convection Currents and How They Work - ThoughtCo Convection currents are flowing fluid that is moving because there is a temperature or density difference within the material. Because particles within a solid are fixed in place, convection currents are seen only in gases and liquids. A temperature difference leads to an energy transfer from an area of higher energy to one of lower energy.
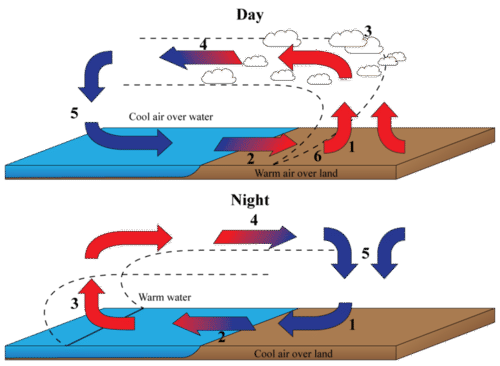
How to draw convection currents in atmosphere - YouTube Learn step by step drawing tutorial. Download a free printable outline of this video and draw along with us. If you don't have a printer just keep this open ... PDF ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS Hot Wired! - Texas A&M College of ... currents. Convection currents are circular patterns that move air and liquids as a result of unequal heating and cooling. Hot air rises because it is less dense and then sinks as it cools. In the investigation, students observe hot water rising and then the cold water sinks. Convection Currents - Definition and Examples | How ... Convection currents are present in the air - A good example of convection current is the warm air that rises towards the ceiling in your house. The process happens as the warm air is said to be less dense than that of the colder air. Another good example of convection current is wind. The wind is mainly caused when the reflected radiation of ... Continental Movement by Plate Tectonics | manoa.hawaii.edu ... Geologists have hypothesized that the movement of tectonic plates is related to convection currents in the earth's mantle. C onvection currents describe the rising, spread, and sinking of gas, liquid, or molten material caused by the application of heat. An example of convection current is shown in Fig. 7.16.
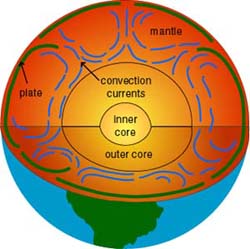
Atmospheric Convection & Convection Cells | What is a ... A diagram of a basic convection cell. ... Convection currents in the atmosphere can be thought of as simply one leg of a convection cell. Imagine a typical sea breeze: warm air rises over the ...
PDF 1008 - 1 - Page 1 Name: A) - Commack Schools C) existence of rising mantle convection currents D) existence of ancestral mountains 23) According to the diagram, what is the approximate rate of seafloor spreading? A) 40 km/million years B) 2 km/million years C) 1 km/million years D) 50 km/million years 1008 - 1 - Page 5
Fresh Diagram Of Convection Currents - Best printable ... Diagram of convection currents. Convection currents occur when temperature differences cause fluid material to move. The direction of movement and type of plate margin is determined by which way the convection currents are flowing. You can observe convection currents in water boiling in a pot.
Convection currents and plate movement - Plate tectonics ... Where convection currents converge, plates move towards each other. The movement of the plates, and the activity inside the Earth, is called plate tectonics.
What are Convection Currents? - Definition & Examples ... Convection currents are the result of a type of heat transfer that only happens in fluids, liquids and gases, when a significant difference in temperature between two parts of a fluid exists.
Convection Currents Vector Illustration Labeled Diagram ... iStock Convection Currents Vector Illustration Labeled Diagram Stock Illustration - Download Image Now Download this Convection Currents Vector Illustration Labeled Diagram vector illustration now. And search more of iStock's library of royalty-free vector art that features Tide graphics available for quick and easy download. Product #: gm1204215150 $ 12.00 iStock In stock
Science Diagram for Radiation, Convection and Conduction ... Science Diagram for Radiation, Convection and Conduction [classic] Use Creately's easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. You can edit this template and create your own diagram. Creately diagrams can be exported and added to Word, PPT (powerpoint), Excel, Visio or ...
Convection Currents | A Level Geography Convection currents, that occur within the molten rock in the mantle, act like a conveyor belt for the plates. Tectonic plates move in different directions. The direction of movement and type of plate margin is determined by which way the convection currents are flowing. Convection currents. The heat from the core is transferred to the mantle.
PDF Convection Questions CONVECTION (teacher answers) I. Define: a) convection Convection is the transfer of heat energy which occurs when heated liquid or gas particles travel from one place to another. b) convection current Convection current is the circular pattern created when heat energy is transferred between particles. 2.
PDF These diagrams illustrates how Conduction, Convection and ... Convection Currents, and these are very important for studying weather. 3. Radiation: Heat transfer by IR radiation. How heat is transferred through space; also works well in gases. Example: the heat from the sun. > A hot object will give off IR radiation; the hotter it is, the more intense the radiation (e.g., a bonfire vs. a match). We can ...
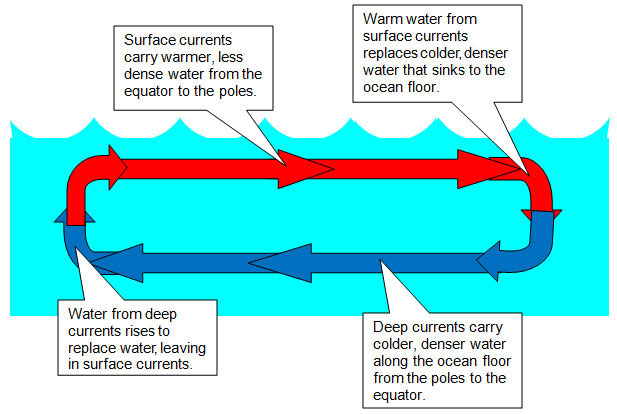
PDF Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection, and Radiation convection current. The convection current helped spread the heat around, until all of the soup was heated up. Convection currents explain why the air is hotter at the top of a room and cooler at the bottom. Convection currents also explain why water is warm at the top of the ocean, but gets colder as you swim deeper.
Convection currents Diagram | Quizlet Theory that the Earth's crust is divided into tectonic plates which move around due to convection currents in the mantle. Convection currents The movement caused within a fluid by hotter and therefore less dense material to rise, and colder, denser material to sink under the influence of gravity.
PDF Mantle convection - Yale University Mantle convection: Thermal convection in the terrestrial planetary mantles, the rocky layer be-tween crust and core, inwhich hotmaterial rises, cold material sinks and the induced flow governs plate tectonic and volcanic activity, as well as chemical segregation and cooling of the entire planet. Mantle convection Introduction and History
Convection Currents - Utah Education Network Convection currents can occur in any fluid, such as air or a liquid. When a fluid heats up, it expands, making it less dense and therefore lighter than the fluid around it. Warm fluids rise while cold fluids sink, setting up a circular pattern of flow toward and away from a heat source until all of the fluid reaches the same temperature.














0 Response to "36 diagram of convection current"
Post a Comment