38 Orbital Diagram For Silicon
Carbon(C) electron configuration and orbital diagram This is clearly shown in the figure of the orbital diagram of carbon. Carbon(C) excited state electron configuration. Atoms can jump from one orbital to another by excited state. This is called quantum jump. Ground state electron configuration of carbon is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2. The p-orbital has three sub-orbitals. The sub-orbitals are p x, p y, and p z. Each sub-orbital can have a … your-online.ru › en › electronic-formulasElectron configuration for Molybdenum (element 42). Orbital ... The order of filling the orbitals with electrons in the Mo atom is an exception to the rule. Expected electronic configuration 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 10 4p 6 5s 2 4d 4 But in reality, one electron moves from the 5s orbital to the 4d orbital:
topblogtenz.com › nitrogen-bohr-modelNitrogen Bohr Model - How to draw Bohr diagram for Nitrogen(N ... Electron dot diagram of a Nitrogen atom. Electron dot diagram also called lewis structure which represents the valence electrons of atoms. As, from the Bohr diagram of Nitrogen, we got to know, it has 5 valence electrons. So, just represent these 5 valence electrons around the Nitrogen atom as a dot.
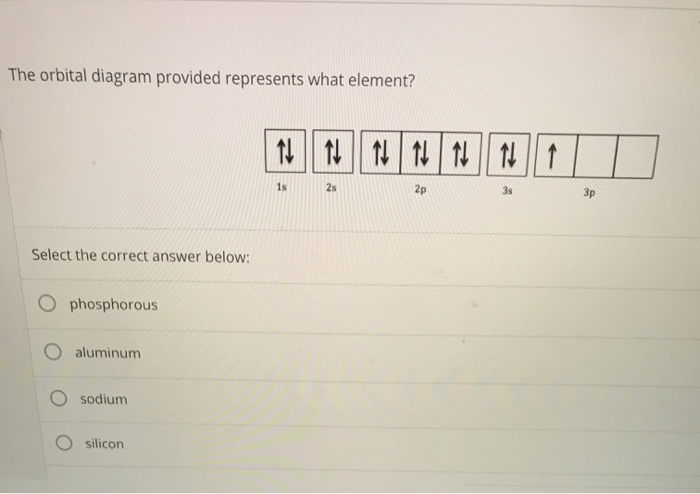
Orbital diagram for silicon
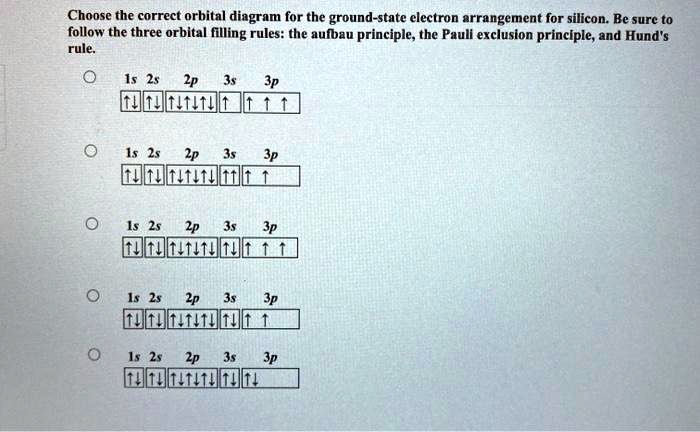
8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory – Chemistry Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. Figure 11. This shows the MO diagrams for each homonuclear diatomic molecule in the second period. The orbital energies decrease across the period as the effective nuclear charge increases and atomic radius decreases. Between N … topblogtenz.com › bohr-model-of-carbonCarbon Bohr Model - How to draw Bohr diagram for Carbon(C) atom Electron dot diagram of Carbon atom. Electron dot diagram also called lewis structure which represents the valence electrons of atoms. As, from the Bohr diagram of Carbon, we got to know, it has 4 valence electrons. So, just represent these 4 valence electrons around the Carbon atom as a dot. Orbital Diagram of All Elements (Diagrams given Inside) 10.04.2021 · Orbital diagram of Silicon (Si) 15: Orbital diagram of Phosphorus (P) 16: Orbital diagram of Sulfur (S) 17: Orbital diagram of Chlorine (Cl) 18: Orbital diagram of Argon (Ar) 19: Orbital diagram of Potassium (K) 20: Orbital diagram of Calcium (Ca) 21: Orbital diagram of Scandium (Sc) 22: Orbital diagram of Titanium (Ti) 23: Orbital diagram of Vanadium (V) 24: …
Orbital diagram for silicon. Orbital Diagram For Nitrogen (N) | Nitrogen Electron ... 15.02.2021 · What is the Orbital Diagram For Nitrogen? When we talk about the orbital diagram, we first need to understand what exactly it means. Therefore, during exams, the student can expect questions related to this topic so it is important that the students must go through it. If you are new to such a subject and looking for periodic tables and their other information, then … Catenation - Definition, Occurrence, Examples, and FAQs Orbital 4 separating the symbols s and p is called an sp3 hybrid orbital because orbitals 1s and 3p are used. The shape and orientation of this orbit should have been explained in the lecture, but here we need a diagram. The diamond bond is perfectly explained by the sp3 hybrid orbital. Benzene and Graphite Bonds Choose the Right Azure Region for You | Microsoft Azure Securely connect embedded MCU-powered devices from silicon to cloud. Azure Defender for IoT Monitor and detect security threats to both managed and unmanaged IoT assets. Windows IoT Enterprise Build intelligent edge solutions with world-class developer tools, long-term support and enterprise-grade security. Azure RTOS Making embedded IoT development and connectivity … sciencing.com › calculate-valency-2790How to Calculate Valency - Sciencing Feb 10, 2020 · Valency is a measure of the ability of an atom to bond with other atoms. The higher the number of valent electrons, the more reactive the atom or molecule is. Electrons will occupy the most stable position first. The inner orbital holds up to 2 electrons. The next orbital holds up to 8 electrons.
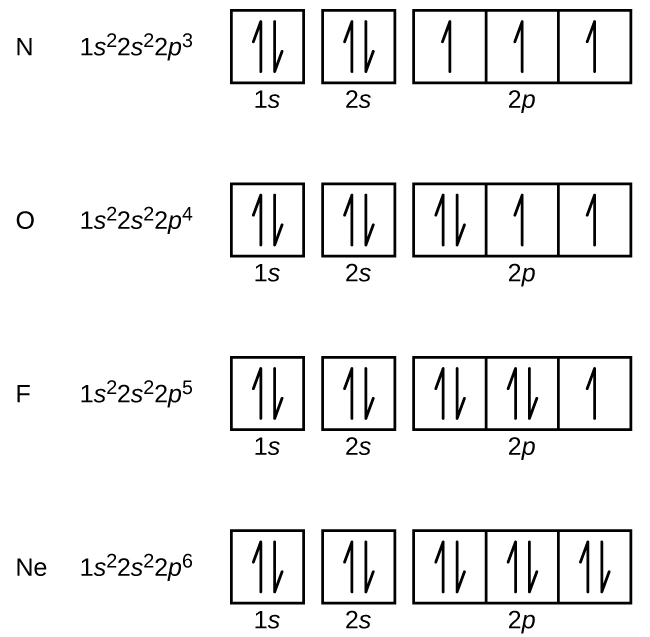
› files › quiaAP Chemistry- Practice Bonding Questions for Exam - Quia The following molecular orbital diagram may be used for the following problems. For oxygen and fluorine, the σ 2p orbital should be lower in energy than the π 2p. However, the diagram will still yield correct bond order and magnetic behavior for these molecules. valenceelectrons.com › nitrogen-electron-configurationNitrogen(N) electron configuration and orbital diagram Orbital Diagram for Nitrogen (N) Nitrogen(N) excited state electron configuration. Atoms can jump from one orbital to another by excited state. This is called quantum jump. Ground state electron configuration of nitrogen is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3. The p-orbital has three sub-orbitals. The sub-orbitals are p x, p y, and p z. Each sub-orbital can have a ... Labeled Periodic Table of Elements with Name [PDF & PNG] 04.05.2021 · Are you searching for the Labeled Periodic Table of elements with the name? We have searched for the periodic table or P table on the internet but do you know; we did not get complete information related to the table. You did not need to worry as you will get every piece of information about Orbital Diagram of All Elements (Diagrams given Inside) 10.04.2021 · Orbital diagram of Silicon (Si) 15: Orbital diagram of Phosphorus (P) 16: Orbital diagram of Sulfur (S) 17: Orbital diagram of Chlorine (Cl) 18: Orbital diagram of Argon (Ar) 19: Orbital diagram of Potassium (K) 20: Orbital diagram of Calcium (Ca) 21: Orbital diagram of Scandium (Sc) 22: Orbital diagram of Titanium (Ti) 23: Orbital diagram of Vanadium (V) 24: …
topblogtenz.com › bohr-model-of-carbonCarbon Bohr Model - How to draw Bohr diagram for Carbon(C) atom Electron dot diagram of Carbon atom. Electron dot diagram also called lewis structure which represents the valence electrons of atoms. As, from the Bohr diagram of Carbon, we got to know, it has 4 valence electrons. So, just represent these 4 valence electrons around the Carbon atom as a dot. 8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory – Chemistry Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. Figure 11. This shows the MO diagrams for each homonuclear diatomic molecule in the second period. The orbital energies decrease across the period as the effective nuclear charge increases and atomic radius decreases. Between N …

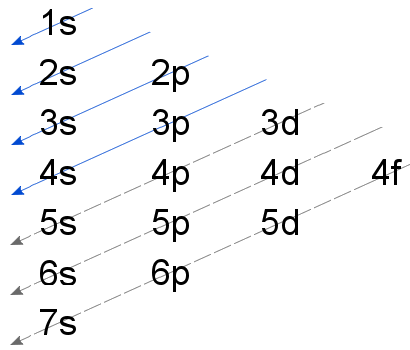
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/aufbauexample-56a129555f9b58b7d0bc9f48.jpg)























0 Response to "38 Orbital Diagram For Silicon"
Post a Comment