38 oceanic food web diagram
An example of this kind of network analysis is shown in the diagram, based on data from a marine food web. It shows relationships between the topological positions of web nodes and the mobility values of the organism's involved. The web nodes are shape-coded according to their mobility, and colour-coded using indices which emphasise (A) bottom ... Diagram of marine food web 3. Producers, Consumers and Decomposers teacher answer sheet 4. Pencils PROCEDURE: 1. Introduce or review the concepts and vocabulary for food chains and food webs. 2. Pass out the sheets for students to complete. 3. Discuss the answers. Connections to the Massachusetts Curriculum Frameworks in Science and ...
Feb 05, 2022 · Three cut-away diagrams show the relationship and movement between the asthenosphere, lithosphere and continental crust, as well as oceans. ocean food web. Collection by Jenifer Hollingsworth. I made a food web building kit which sequentially builds the creation of food webs from food chains.

Oceanic food web diagram
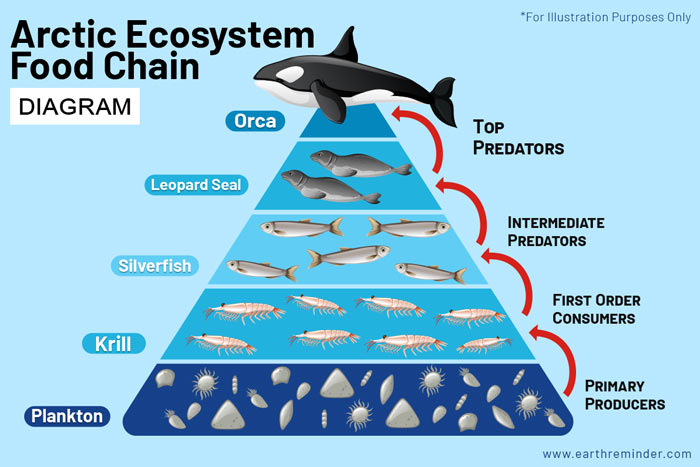
Which of the following organism provides energy for more than one organism in the food web? answer choices . Mouse. Hawk. Snake. Lizard. Tags: Question 15 . SURVEY . 60 seconds . Q. Use the diagram to answer the question. The Mayfly is a food source for which 3 organisms? answer choices . Frog, Dragon Fly and snake. Frog, trout and dragon fly. August 1, 2019 - Most of these aquatic species are tied together through the food web. ... The foundation of the sea's food chain is largely invisible. Countless billions of one-celled organisms, called phytoplankton, saturate sunlit upper-ocean waters worldwide. These tiny plants and bacteria capture the sun's ... Each step of the food web or chain is called a trophic level. Primary producers are always the first trophic level and are represented at the bottom of an ecological pyramid. The diagram below shows an example of an ecological pyramid for the ocean. These pyramids can also show how much energy is available at each trophic level of a food web.
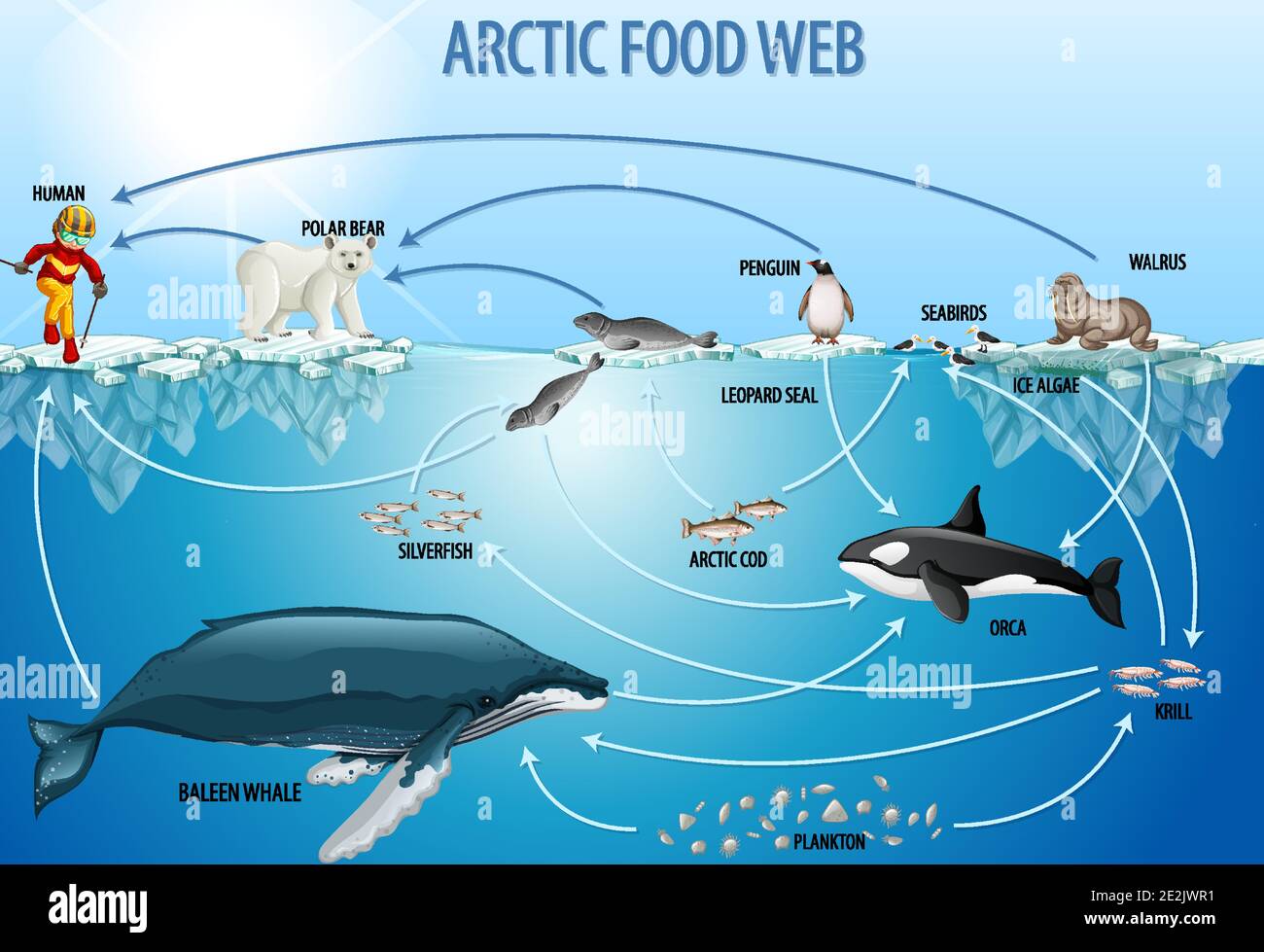
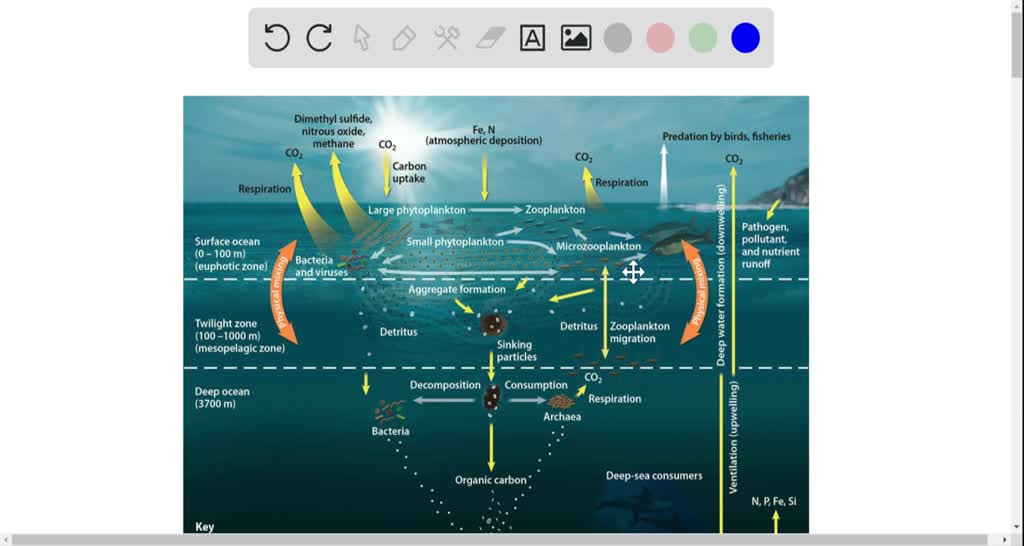
Oceanic food web diagram. Microscopic plants and other photosynthetic organisms that drift with ocean currents lie at the heart of the marine carbon cycle. Sunlit surface waters teem with phytoplankton that convert inorganic carbon dissolved in surface waters to organic carbon, which forms the basis of the marine food web, ... A food chain in the ocean begins with tiny one-celled organisms called diatoms, which make their own food from sunlight. Shrimplike creatures eat the diatoms. Small fish eat the shrimplike creatures, and bigger fish eat the small fish. The ocean food web is very complex and many top predators can be prey for something else. As on land, there are even detritivores such as crabs, giant isopods, bacteria, and other scavengers. North Carolina Aquariums Education Section Page 4 of 8 Included in this food web are the following organisms: ers in a food web. • Describe food web interac-tions specific to the arctic sea ice. • Illustrate an arctic marine food web. Arctic Food Webs In this activity students work in groups to develop an arctic marine food web. Groups then move through the classroom viewing each others' food webs and adding their own information. FLOW 1.
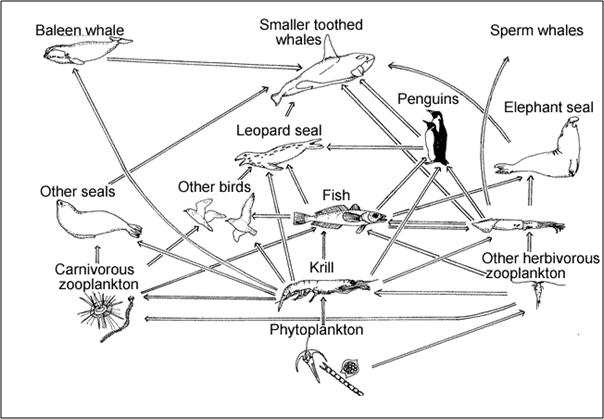
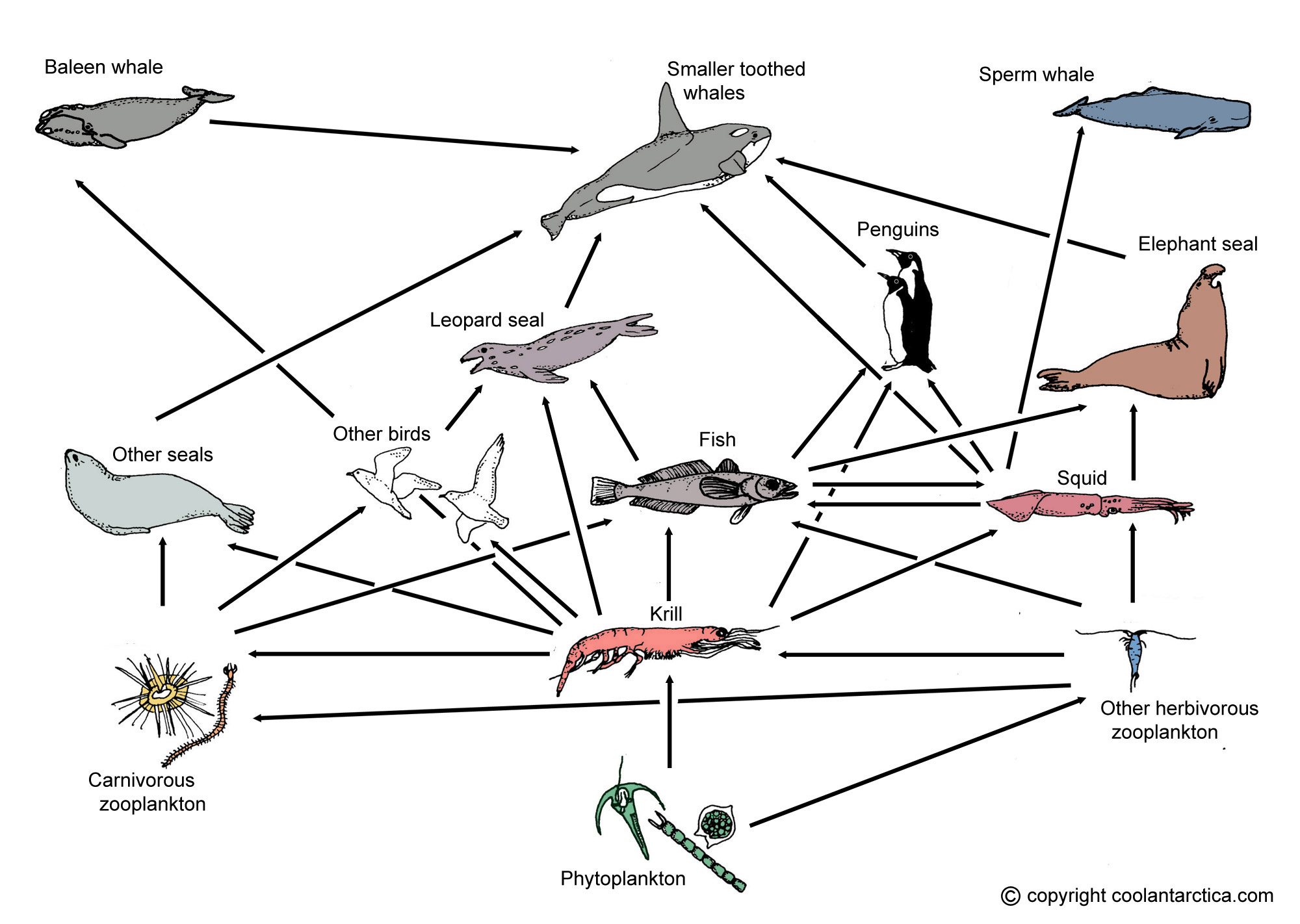
ocean ocean E continent A C B D (a) (i) Complete the table using letters A to E from the diagram. feature letter ... 2 The diagram shows part of a food web in the Southern Ocean. baleen whale killer whale elephant seal squid penguin bird fish phytoplankton krill leopard seal not to scale Organisms in a community are linked through what they eat and what eats them. A food chain is a single pathway connecting a producer with several levels of consumers. In a typical marine food chain, dinoflagellates convert energy from sunlight into food through photosynthesis and store it in ... Q: What is a food web and how is it different from a food chain? A food web is an assemblage of organisms that eat and are eaten by each other. Food webs are usually described within the boundaries of a particular location (e.g. a pond, an island, a meadow). A geographical boundary keeps the scope of the food web manageable; otherwise, Marine Food Web Information Phytoplankton, which are microscopic photosynthetic organisms (single-celled algae, including diatoms) that drift in the water, are the foundation of the oceanic food chain. Phytoplankton are also known as the primary producers of the oceanic food chain because they are able to produce their own food through photosynthesis using sunlight.
A food web is a system of interconnected food chains. A food chain is a top-to-bottom set of animals and plants. They are linked to each other because those on top eat those below. The bottom level of the ocean's food chain is made up of one-celled organisms called phytoplankton. These tiny organisms are microscopic. Tuna’s Carbon Ratios Indicate Changes in Oceanic Food Web Seafood News II. Food Chains and Food Webs A. Show students the An Ocean of Food Chains and Food Webs PowerPoint (Slides 1-8 only, the remaining slides will be used in Lesson 2). Have them use page two of their Student Worksheet Marine Organisms Vocabulary to take notes as they view the presentation. Then, conduct a discussion to complete their Nov 17, 2021 · The ocean's food chains build webs which are the sum of the possible interactions of those food chains (Figure 1). Figure 1: Food web diagram showing the complexity of several food chains in an ...
Food chain is a linear sequence of organisms which starts from producer organisms and ends with decomposer species. Food web is a connection of multiple food chains. Food chain follows a single path whereas food web follows multiple paths. From the food chain, we get to know how organisms are connected with each other.
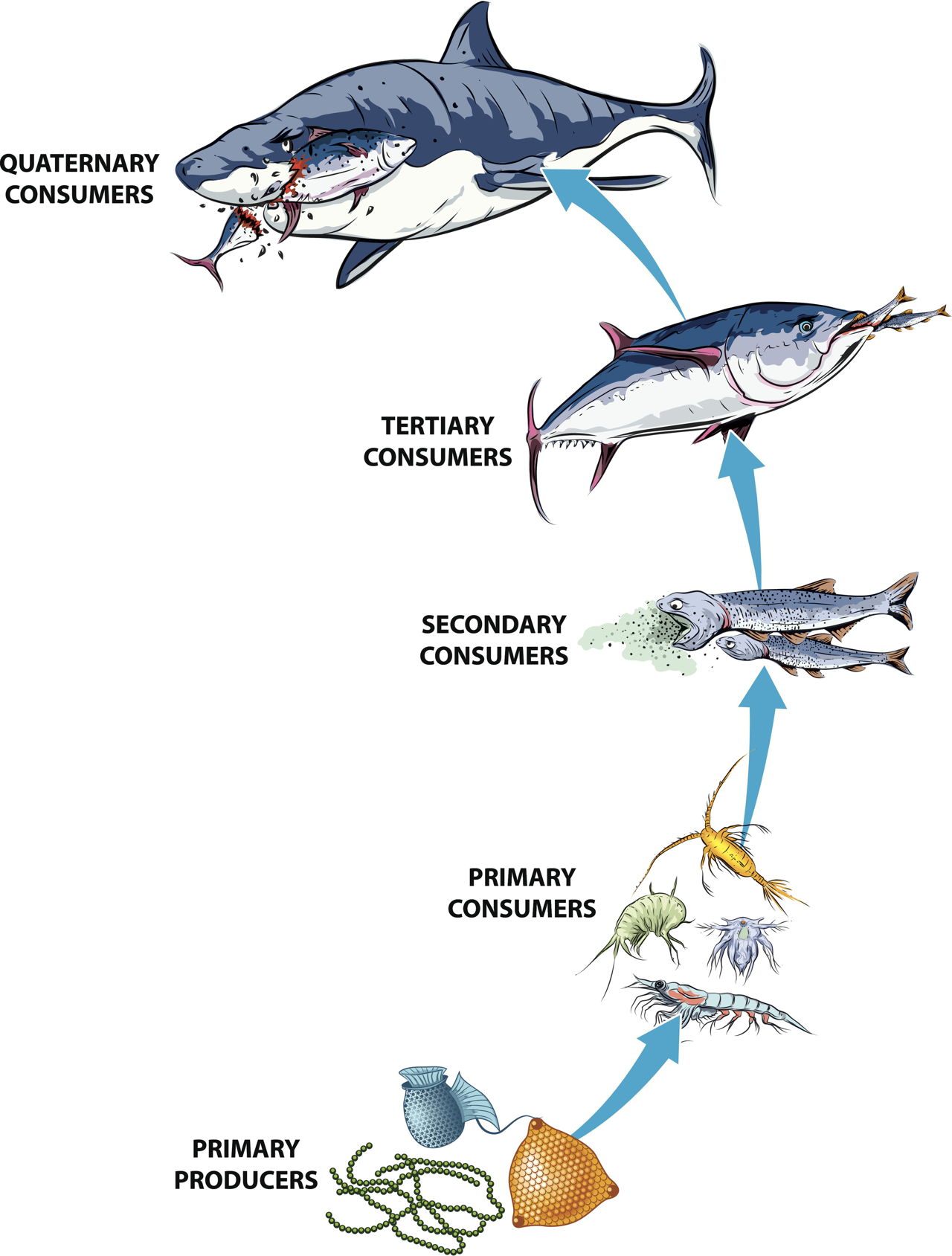
Note: In this diagram, we start at the bottom-most level of the food chain with the preys, and the arrows point towards the predators at each level. The lowest trophic level of an ocean food chain will consist of the primary producers, which in the case of a marine biome would be phytoplanktons. These are single-celled marine plants that live in the surface layers of the ocean, and use the energy from the sun to produce carbohydrates.
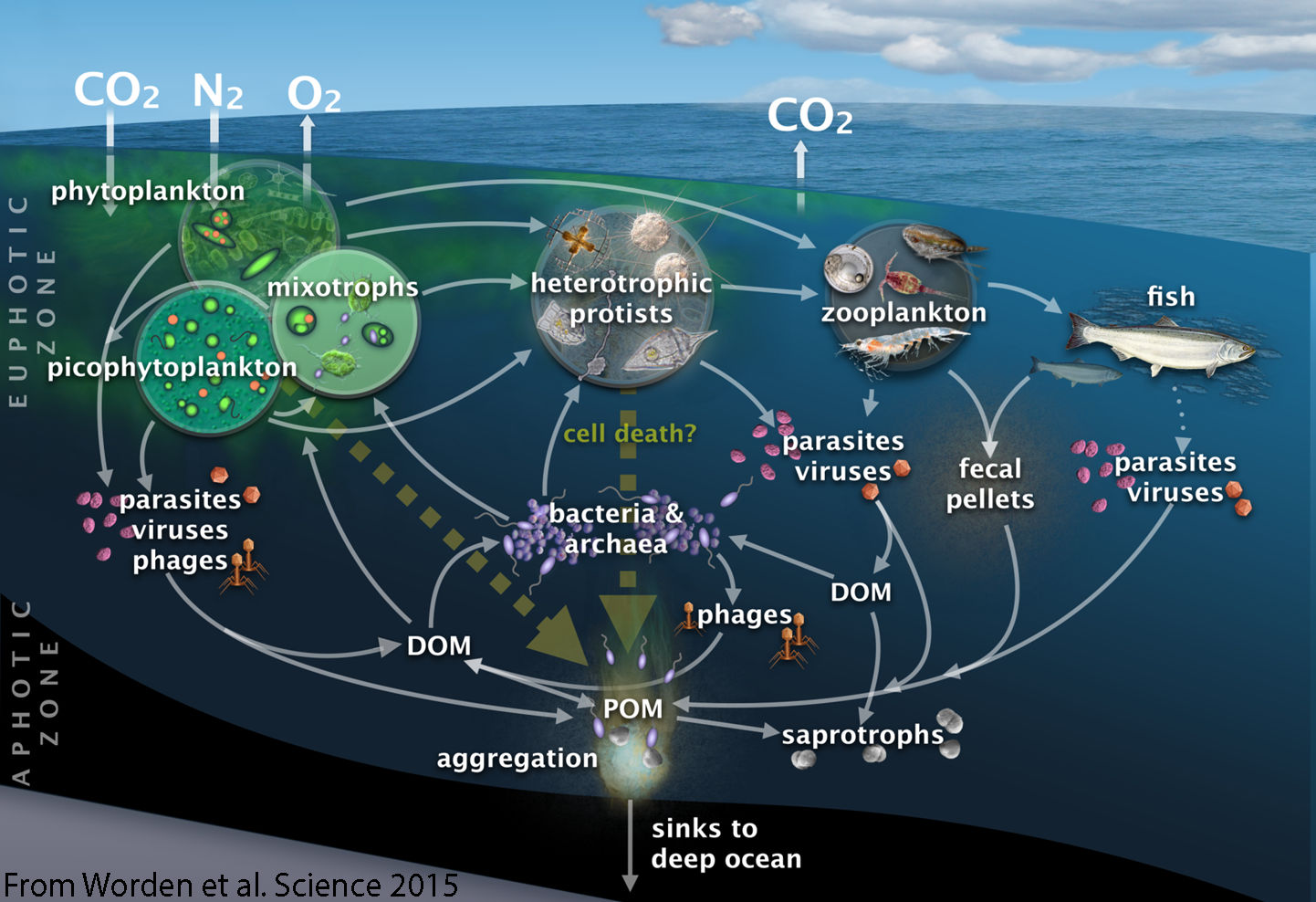
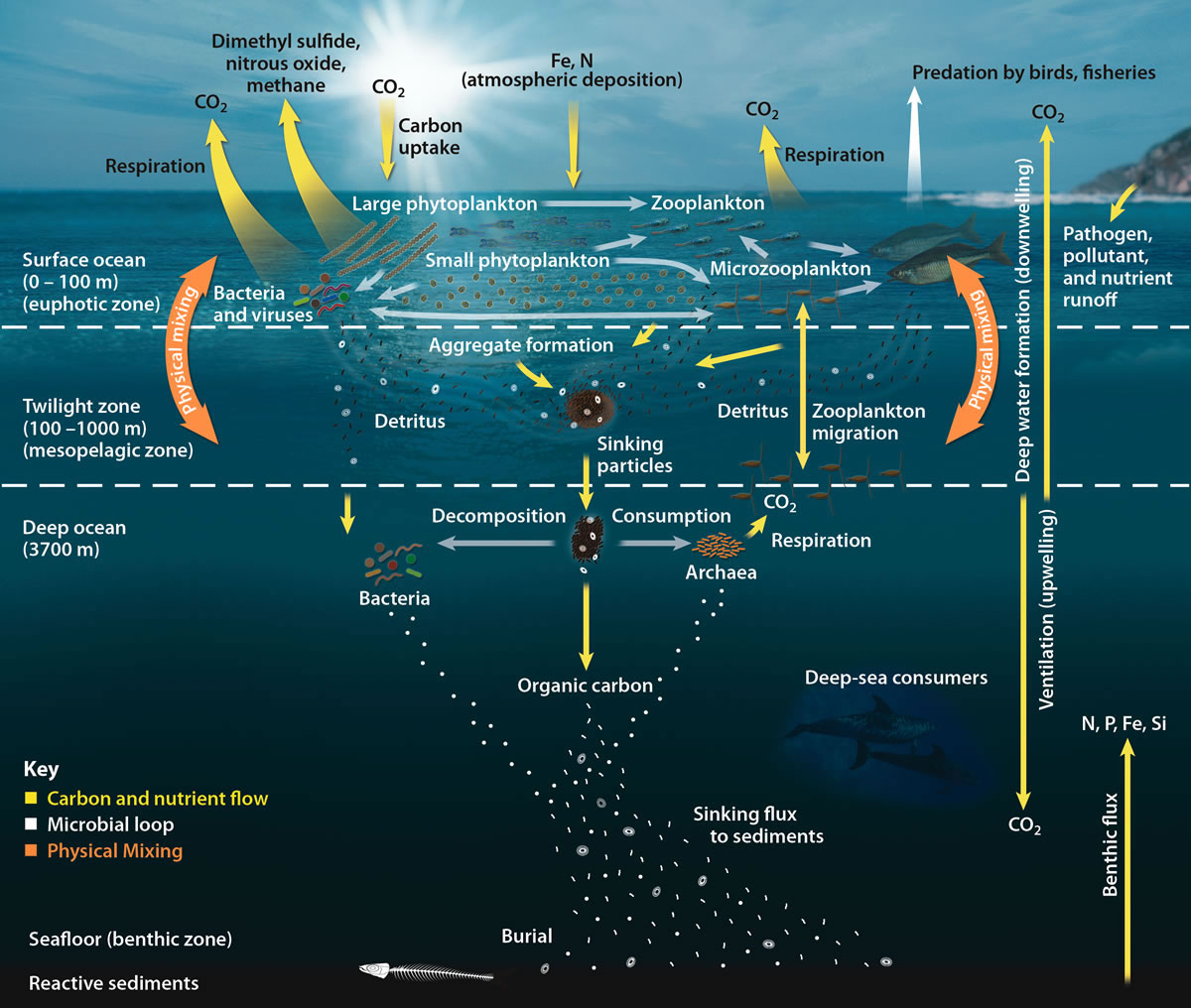
Food webs describe who eats whom in an ecological community. Made of interconnected food chains, food webs help us understand how changes to ecosystems — say, removing a top predator or adding nutrients — affect many different species, both directly and indirectly. Phytoplankton and algae form the bases of aquatic food webs. They are eaten by primary consumers lik
In general, food webs with low biodiversity are more vulnerable to changes than food webs with high biodiversity. In some food webs, the removal of a plant species can negatively affect the entire food web, but the loss of one plant species that makes up only part of the diet of a herbivorous consumer may have little or no effect.
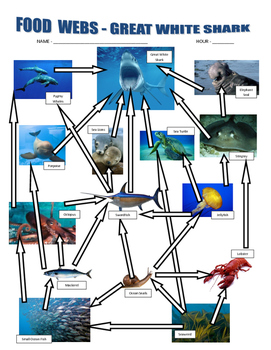
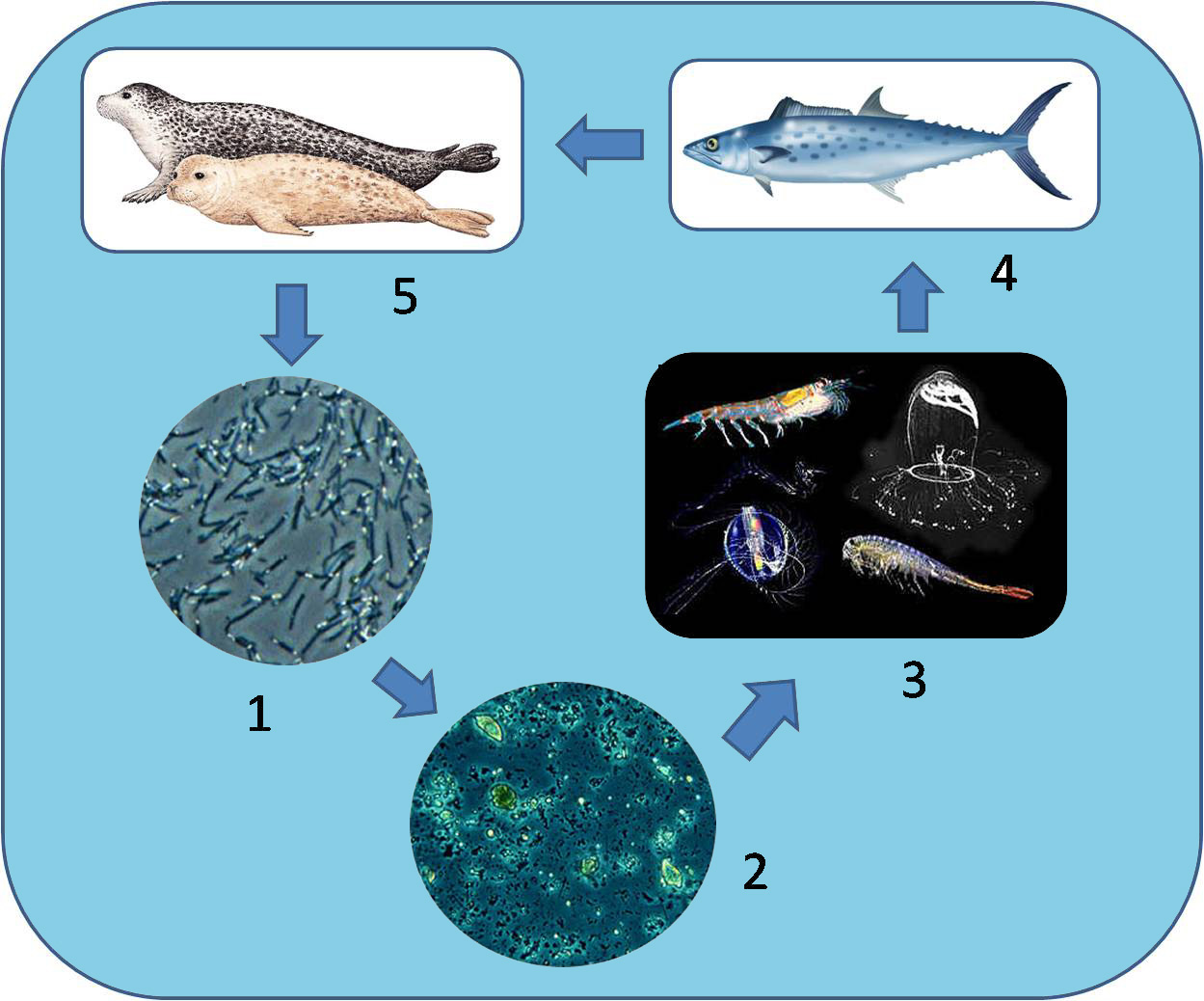
The killer whales primarily feed on the secondary consumers in the oceanic food web. Explanation: Killer whales are the tertiary consumers and occupy the highest position in the ocean food web. They are predating carnivores and feed on secondary consumers like other fishes, marine animals like ...
Ocean food web primary consumers. Primary consumers are the second level in the food chain, feeding off of producers like phytoplankton. The marine biome is the largest in the world, and therefore contributes to intricate food webs. This is evident in the diagram complementing this article.
The food webs INB template will diagram the flow of energy that takes place in a terrestrial, freshwater, and marine ecosystem. Estimated Class Time for the Exploration: 2-3, 45 minute class periods ELABORATION The elaboration section of the 5E method of instruction is intended to give students choice on how they can prove mastery of the concept.
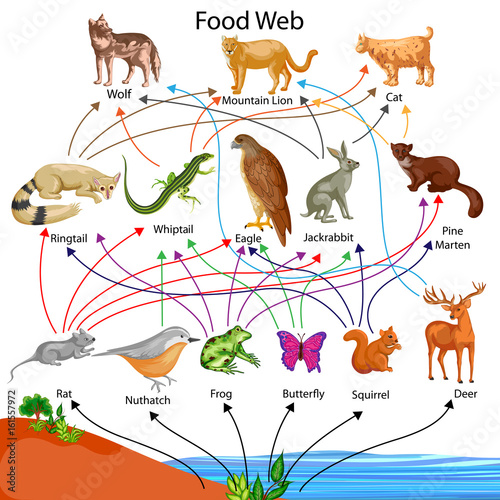
A food web diagram illustrates 'what eats what' in a particular habitat. Pictures represent the organisms that make up the food web, and their feeding relationships are typically shown with arrows. The arrows represent the transfer of energy and always point from the organism being eaten to the one that is doing the eating. Trophic levels
Food Web Diagram Template. Check this fully designed food web science diagram template to show your kids the fierce competition between wild animals. Replace or move around any of the pre-made animal symbol based on your preference. Get started with a free trial right now. Lab Apparatus List.
The diagram shows an oceanic food web. At what trophic level do the killer whales primarily feed? Choose the correct answer. the third and fourth trophic levels. When a giraffe eats leaves from a tree, it incorporates the leaves into its own _____. Choose the correct answer.
Download scientific diagram | Oceanic food web supporting all species of tuna and other large pelagic fish (source: Le Borgne et al. (2011) and the Pacific Community, New Caledonia). from ...
28.The diagram below represents a marine food web. The organisms represented by X are A)consumer B)producer C)autotroph D)carnivore 29.The diagram below represents an energy pyramid. Which type of organism could occupy levels B, C, and D of this energy pyramid? A)an increase in the variety of genetic material available
Workflow layout with linear icons. Sea, ocean and lake fishing, sport Fishing, aquaculture and fisher license infographic with world map. Vector graphs, charts of fish catch in sea, ocean and lake, fisherman tackles and baits, squid and crab, tuna and salmon ocean food web diagram stock illustrations.
A food web is a diagram showing the transfer of energy between species. Since the energy is transferred as food, the food web basically shows what eats what in an ecosystem. Food webs are complex and are made of many food chains, which focus on individual species.The food web is organized into layers called trophic levels.
page 14 with diagrams showing the diets of other ocean species ranging in size from microorganisms to whales. The result is a food web, which is much more complex than a food chain. The diagram on this page gives you a basic idea of an ocean food web, but the page is not large enough to include all the details. 15 16 Energy Pyramid
Q. Use the diagram to answer the question. The Mayfly is a food source for which 3 organisms? Q. What part of the food chain is missing? Q. Which of the following organisms provides energy for more than one organism in the food web? Q. Based on the food web, which shows correctly the one way that energy flows? Q.
Marine Food Webs. 1. Build background about marine trophic pyramids and food webs. Review with students that food chains show only one path of food and energy through an ecosystem. In most ecosystems, organisms can get food and energy from more than one source, and may have more than one predator. Healthy, well-balanced ecosystems are made up ...
Build a marine food web. Add to collection. + Create new collection. In this activity, students build their own food web using images of organisms from the marine ecosystem. This activity can be done indoors on paper or outdoors on a tarmac surface using chalk. By the end of this activity, students should be able to:
Creating a Food Web. Of course, the menu in the ocean is a lot larger than what your food chain shows! Individual animals can eat many other types of plants and animals, not just one. For example, a seal likes to eat other fish like salmon, and seals in turn can be eaten by larger animals such as orca whales.
A food chain is a network of links in a food web. Here, the producers are consumed by the predators-primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. When many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as Food Web. A food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms.
Below is a visual diagram style representation of the food web of the Great Barrier reef featuring some of the core marine animals that can be found in its waters that provides a basic overview, with the arrows pointing in the direction of one animal that eats another.
• A food web is made of several interconnected food chains. • A food web shows the flow of energy from one organism to another. 1. List out all of the individual food chains that are present in this food web. (Example: tree Î deer Î mountain lion) 2. Identify the following using the colors indicated: Green: producers Blue: primary consumers
Diagram a food web and identify producers and consumers in this food web. Concepts: input/output, text handling, simple events, layers
Food Web Diagram Example To see how a food web works, it can be easiest to look at an example. For instance, plants are eaten by grasshoppers and squirrels. The grasshopper is eaten by the lizard, which is then eaten by the fox. The squirrel can be eaten by a fox or a golden eagle.
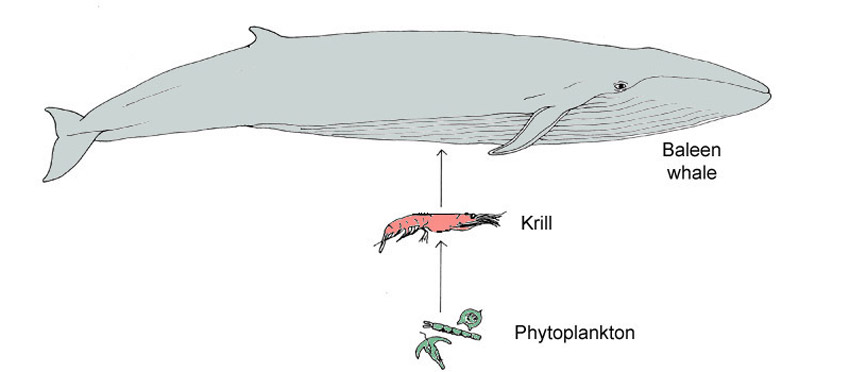
Simple marine food web. The diagram shows the relationships among organisms living in an ocean. producers and consumers. Whales, and other marine mammals are at ...
This 28 piece set features a marine life food web diagram (includes primary producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer and tertiary consumer). Two food web diagrams are included - complex and simple. All animals and algae in the food web are also included as separate illustrations. The set incl. Subjects:
Oct 11, 2017 - Explore Jenifer Hollingsworth's board "ocean food web" on Pinterest. See more ideas about ocean food web, food web, ocean food.
Afood web is an ecological concept based on food and energy transfer. It shows the relationship of animals present in a particular habitat or ecosystem. A food web is a combination of several food chains. This food flow also depicts the flow of energy from the producers to the consumers. The terrestrial food web is different from an aquatic food web. The structure of the food web is dependent on the species of animals present in the particular ecosystem. The basic idea of the food web is the transfer of food and energy from autotrophs to carnivorous or omnivorous animals. There are mainly two ways of food webs. They are: 1. The grazing food web 2. The detrital food webs In the grazing food web, the nutrients get circulated from plants to carnivorous or omnivorous animals. The green plants are the primary producers or autotrophs. The nutrients from them are passed on to the primary consumers or herbivores. Rabbits, grasshoppers, ground squirrels belong to this category. These herbivo...
Science.gov is a gateway to government science information provided by U.S. Government science agencies, including research and development results.
Each step of the food web or chain is called a trophic level. Primary producers are always the first trophic level and are represented at the bottom of an ecological pyramid. The diagram below shows an example of an ecological pyramid for the ocean. These pyramids can also show how much energy is available at each trophic level of a food web.
August 1, 2019 - Most of these aquatic species are tied together through the food web. ... The foundation of the sea's food chain is largely invisible. Countless billions of one-celled organisms, called phytoplankton, saturate sunlit upper-ocean waters worldwide. These tiny plants and bacteria capture the sun's ...
Which of the following organism provides energy for more than one organism in the food web? answer choices . Mouse. Hawk. Snake. Lizard. Tags: Question 15 . SURVEY . 60 seconds . Q. Use the diagram to answer the question. The Mayfly is a food source for which 3 organisms? answer choices . Frog, Dragon Fly and snake. Frog, trout and dragon fly.




















0 Response to "38 oceanic food web diagram"
Post a Comment