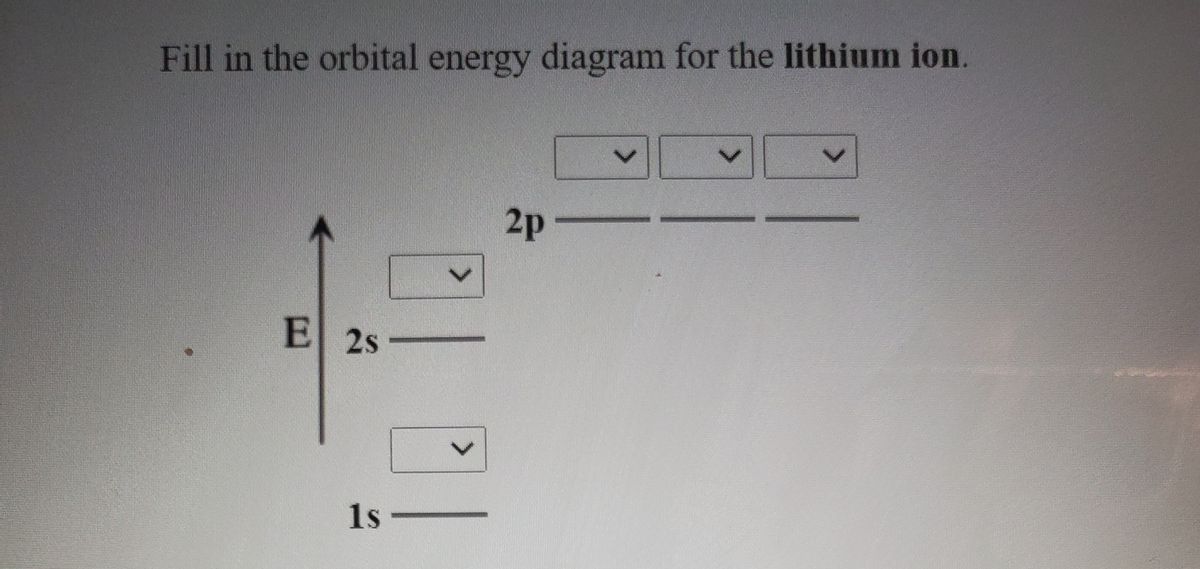
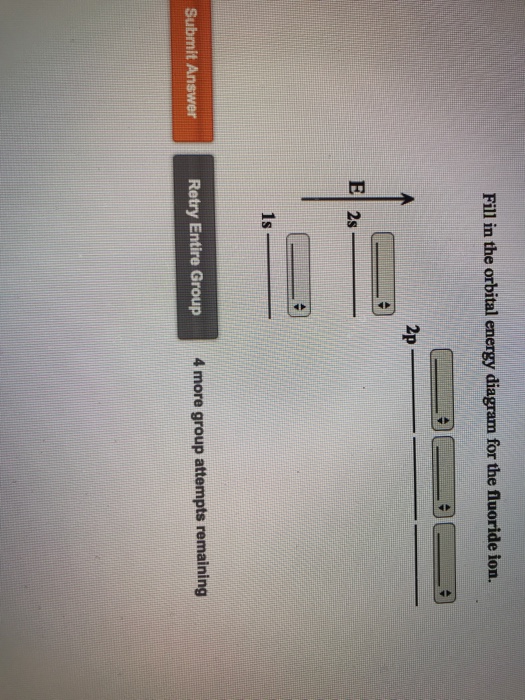
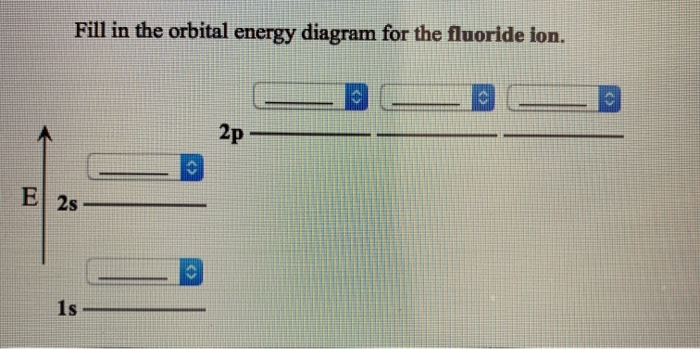
38 fill in the orbital energy diagram for the fluoride ion.
Sodium(Na) is the 11th element in the periodic table and its symbol is 'Na'. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of sodium and orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of sodium, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles.Hopefully, after reading this article you will know in detail about this. Fluoride ion ranks low in the spectrochemical series and produces a weak crystal field in complex ions. Based on this information, predict the number of unpaired electrons in CoF63-. a) 0 b) 1 c) 2 d) 3 e) 4
Fill in the orbital energy diagram for the fluoride ion. 2p El 2s 1s 4 more group attempts remaining Submit Answer Retry Entire Group ; Question: Fill in the orbital energy diagram for the fluoride ion. 2p El 2s 1s 4 more group attempts remaining Submit Answer Retry Entire Group

Fill in the orbital energy diagram for the fluoride ion.
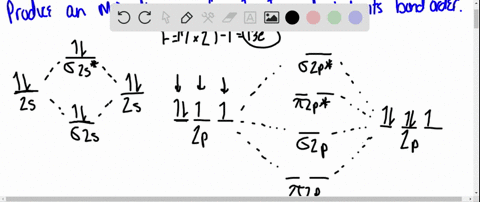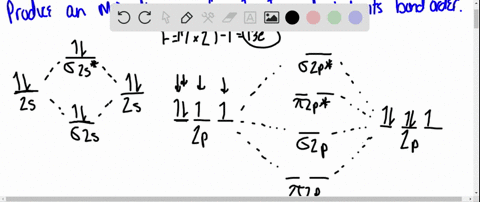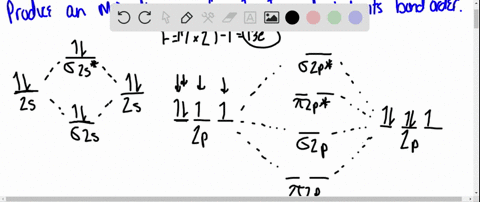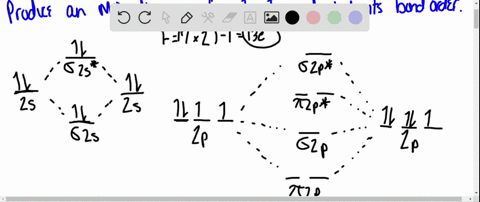
Using Molecular Orbital Theory, draw the molecular orbital energy diagram for B22+. To earn full credit, you must: (a) draw the atomic orbital diagram for each boron atom, (b) draw and label the molecular orbital diagram in the middle, using dashed lines to show which atomic orbitals combine, (c) fill in all electrons. This element is in group 6A ....It will gain 2 electron (s) to obtain the nearest noble gas configuration and form an anion with a charge of -2 Fill in the orbital energy diagram for the fluoride ion using the following key: u= electron with spin "up" d= electron with spin "down" Always start with spin up.. ., Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. Hydrogen | Fluorine | Nitrogen | Hydrogen Fluoride | Carbon Monoxide | Methane | Ammonia | Ethylene | Acetylene | Allene | Formaldehyde | Benzene
Fill in the orbital energy diagram for the fluoride ion.. Science Chemistry Q&A Library Fill in the orbital energy diagram for the lithium ion. 2p- E 2s- 1s-. MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine Fluoride Ion is considered a trace element, fluoride is any combination of elements containing the fluorine atom in the -1 oxidation state (fluoride ion). Due to its reactivity, fluorine is found in nature as fluorine compounds or fluorides. Fluoride inhibits various enzyme systems, erythrocyte glycolysis and binds Ca++, causing anticoagulation and other toxic effects. 2.[4] (A) Sketch the ground-state orbital energy diagram for the fluoride ion (F-)—clearly show every electron and label the orbitals. (B) Give the electron configuration for the fluoride ion. │ │ │ │ Energy │ │ │ │ │ Electron configuration for the fluoride ion: _____ 3.[2] Give the Lewis Symbol for H2S.
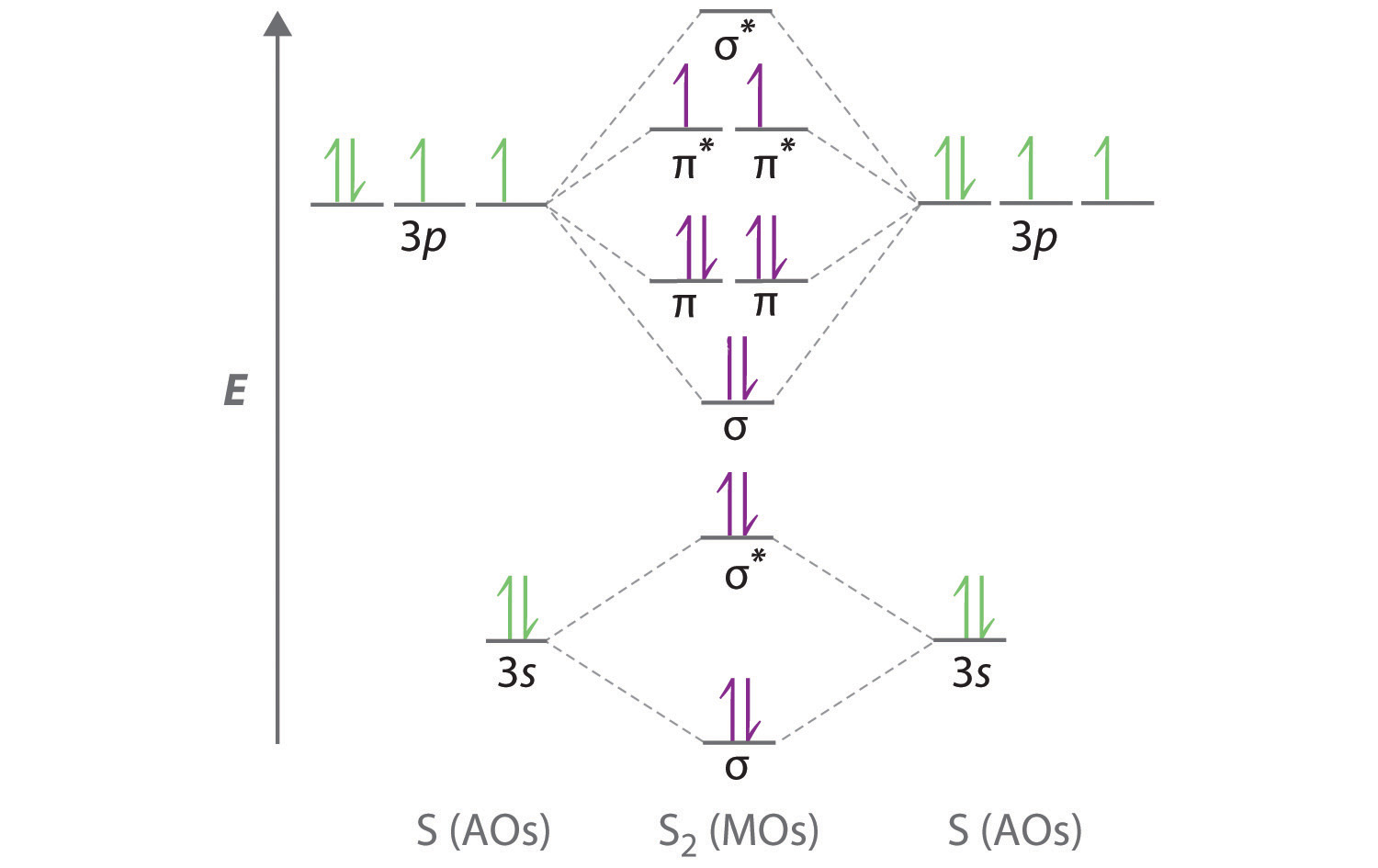
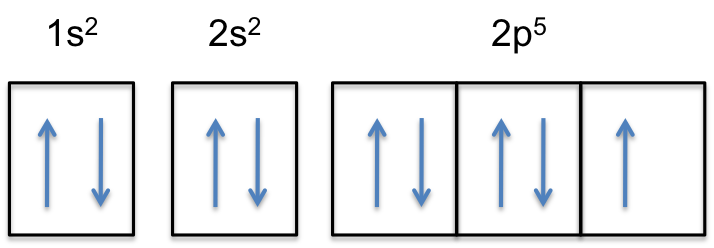
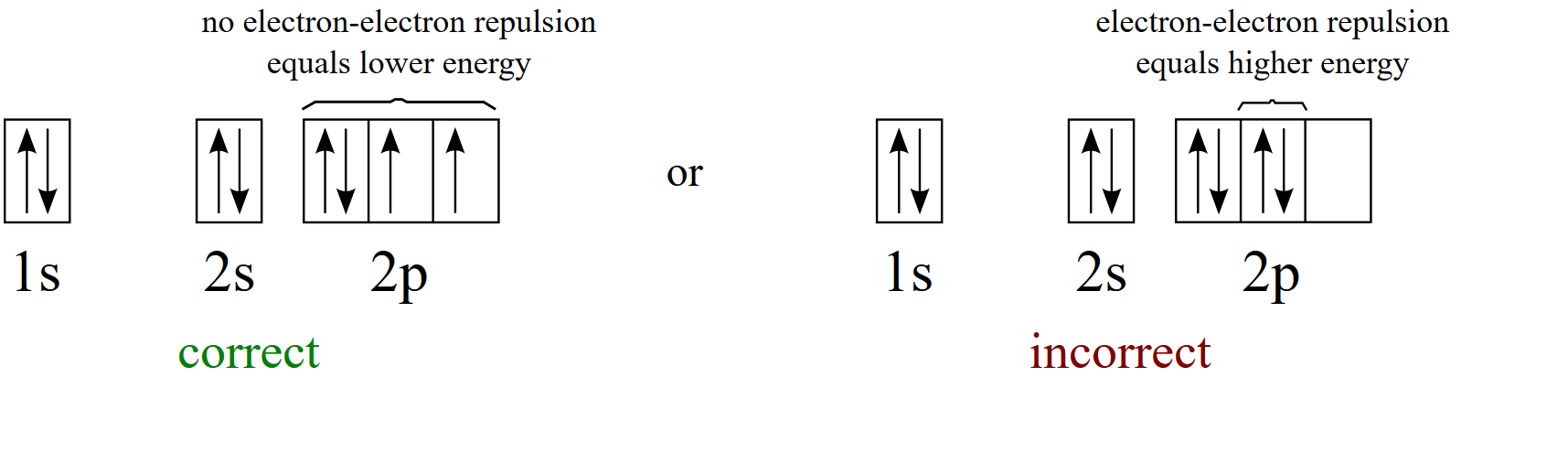
Electron Configurations The Pauli exclusion principle says that all electrons in an atom have to have a unique set of quantum numbers. NO duplicates! It's like a serial number for electrons, except we use n, ℓ, m ℓ, and m s.. The aufbau principle tells us to "build up" from the bottom of the energy well to the top. Pour water in a bucket and it fills from the bottom up - same idea. Dec 05, 2016 · F^- : 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 alternatively: F^- : [Ne] Elemental Fluorine has an electron configuration of 1s^2 2s^2 2p^5 and needs 1 more electron to complete its 2p orbital which it will acquire in formation of the fluoride ion. Thus it gains an electron when forming the fluoride ion, and becomes isoelectronic to neon. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... Answer: This just shows energy levels so let's take this a step further. Atomic Electron Configurations And I'm not having any luck but if you go to this site, you should be about to see what the 1s, 2s, 2px, 2py, 2pz, and 3s orbitals look like together. Jmol orbital structures If not, see what...
A) draw a molecular orbital (mo) diagram for co and show the filling of electrons. Let's take [co(nh3)6]3+ as an example. For the homonuclear diatomic #o_2#, we simply have two copies of this atomic orbital diagram far apart at first. Electronic configuration of co molecule is: Draw the orbital diagram for the ion co2+. Feb 23, 2016 · The orbital filling diagram for helium. The electron configuration for helium is 1s². This means that we have two electrons in the 1s orbital, which looks like this: This diagram is exactly the same as the one for hydrogen, except that there’s a second arrow added to the 1s orbital. This represents the second electron in the 1s orbital, and ... Problems 1 and 2: orbital energy diagram - ions Problem3: Electron Configurations for Main Group Ions Problem 4: Electron Configurations of Ions Problem1 Fill in the orbital energy diagram for the nitride ion using the following key: The electron configuration of all the elements can be done through orbital diagrams. Electron configuration of fluorine(F) atom through orbital. Atomic energy levels are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are called orbital. The sub energy levels are expressed by ‘l’. The value of ‘l’ is from 0 to (n – 1).
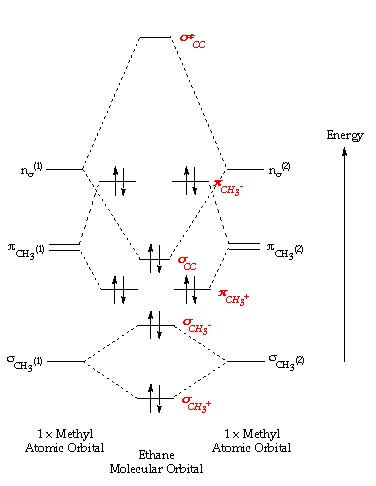
electrons to fill into these orbitals, so the lower energy molecular orbital (σ) will be filled and the higher energy molecular orbital (σ*) will be empty (recall the Aufbau Principle). While there are only two molecular orbitals in this example, in a more general example there may be many molecular orbitals. Of
So the electron configuration of potassium will involve 19 electrons. The full electron configuration of potassium is "1s"^2"2s"^2"2p"^6"3s"^2"3p"^6"4s"^1". The noble gas notation is "[Ar]4s"^1". The following orbital diagram shows the increase in energy from one energy sublevel to the next, but you can write them on the same level horizontally,
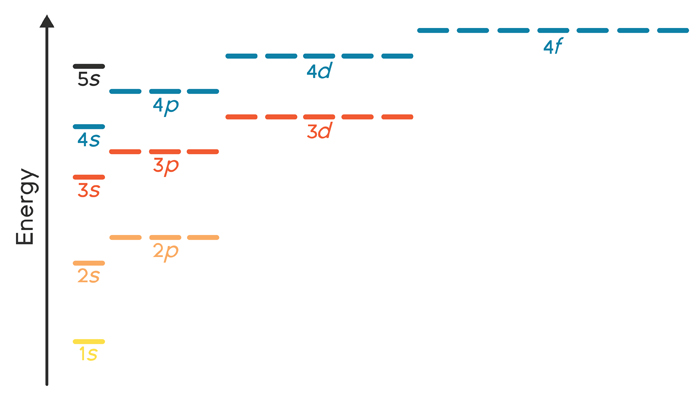
A 4s orbital is higher in energy than a 3s orbital. As increases, orbital energy increases. In the n = 3 shell, 3s < 3p < 3d. As n increases, the subshell energies become more closely spaced and overlapping occurs. The 4f orbital is higher in energy than the 5s orbital, despite its lower n value. 7.3 Electron Configuration of Elements
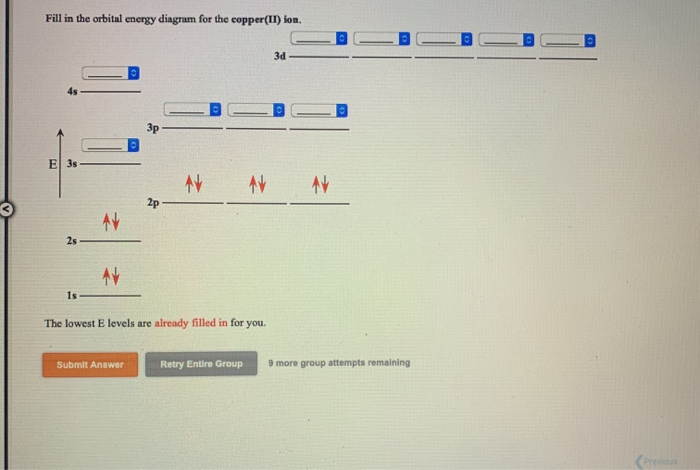
Example 2: Draw and fill the orbitals for carbon. Example 3: Draw and fill the energy level orbital diagram for the fluoride ion Example 4: Draw and fill the energy level orbital diagram for the for cations, draw the full zinc ion. set of e-s of the neutral atom first, then remove the required electrons from the highest energy level ...
Okay let's do the orbital diagram for iron, iron we know is on its ground state of 26 electrons, so we know the first electrons are going to go into the 1s orbital and we said 2 electrons can fall into the 1s orbital. The orbital filling diagram of lithium. The electron configuration of lithium is 1s²2s¹.
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics.
Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal -each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for "build up" •Electrons are notated with an arrow -Up arrow goes first then, down arrow -Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom
Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. Hydrogen | Fluorine | Nitrogen | Hydrogen Fluoride | Carbon Monoxide | Methane | Ammonia | Ethylene | Acetylene | Allene | Formaldehyde | Benzene
This element is in group 6A ....It will gain 2 electron (s) to obtain the nearest noble gas configuration and form an anion with a charge of -2 Fill in the orbital energy diagram for the fluoride ion using the following key: u= electron with spin "up" d= electron with spin "down" Always start with spin up.. .,
Using Molecular Orbital Theory, draw the molecular orbital energy diagram for B22+. To earn full credit, you must: (a) draw the atomic orbital diagram for each boron atom, (b) draw and label the molecular orbital diagram in the middle, using dashed lines to show which atomic orbitals combine, (c) fill in all electrons.











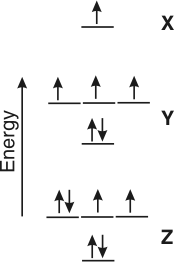


![Electron Configuration | Chemistry [Master]](https://textimgs.s3.amazonaws.com/boundless-chemistry/gram-four-2p-hund-27s-rule.svg)


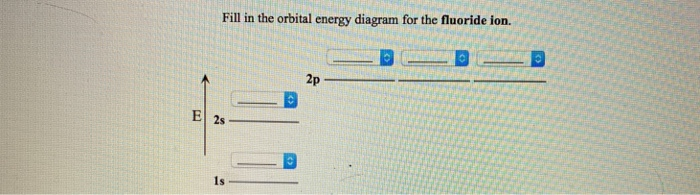


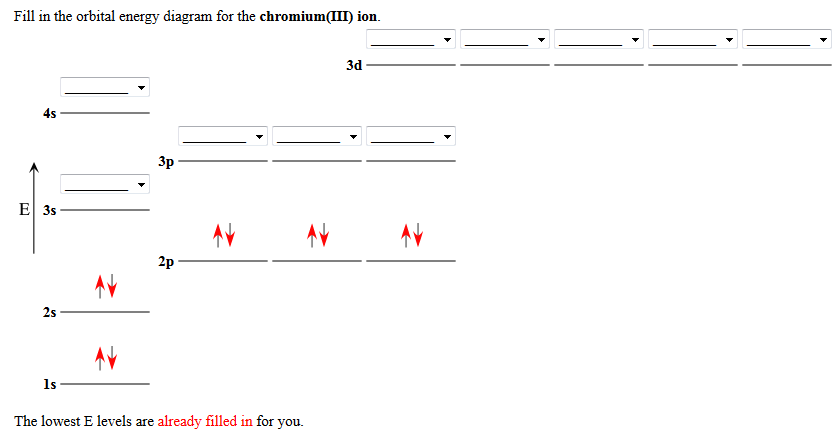

0 Response to "38 fill in the orbital energy diagram for the fluoride ion."
Post a Comment