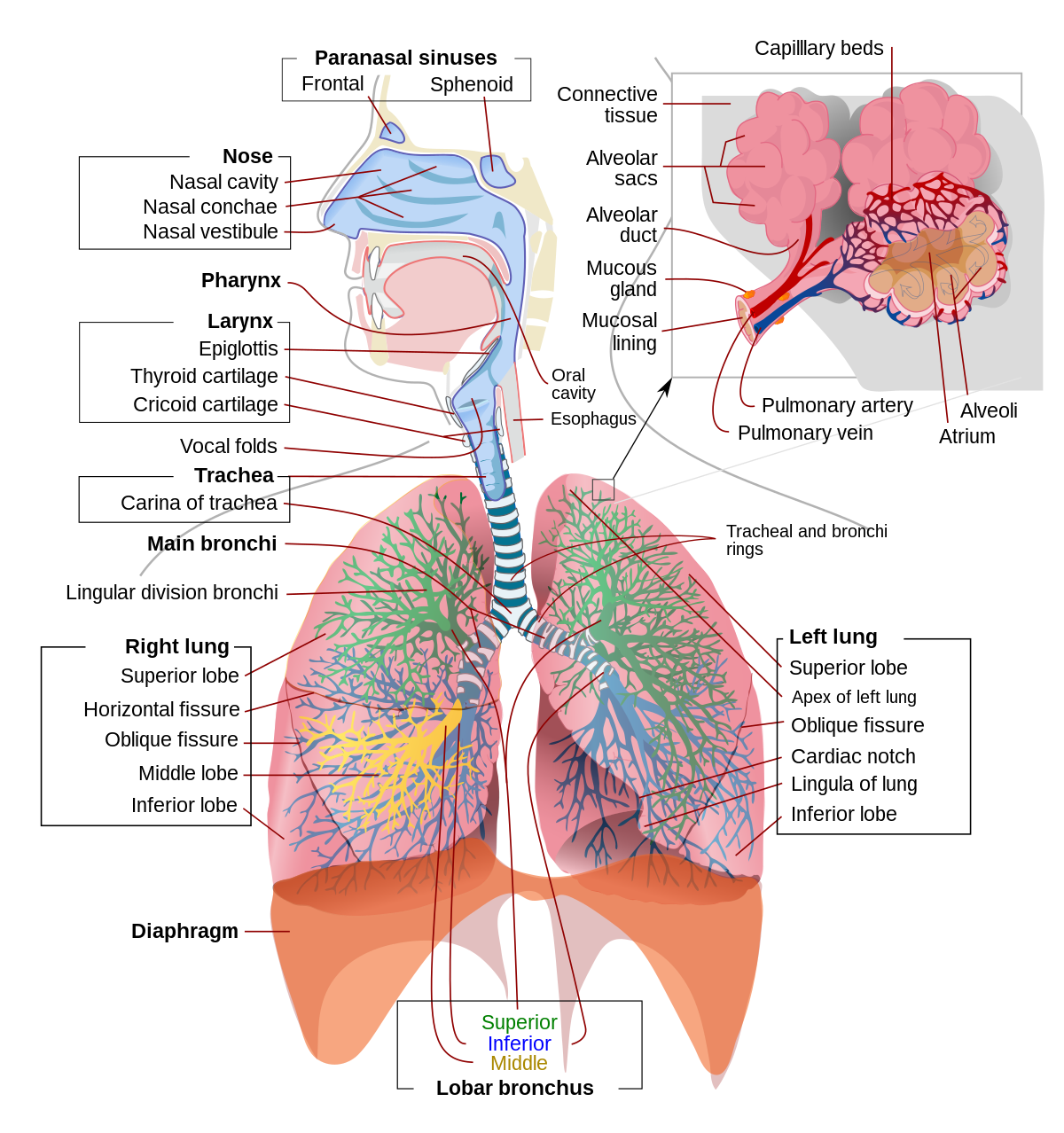
38 on the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium
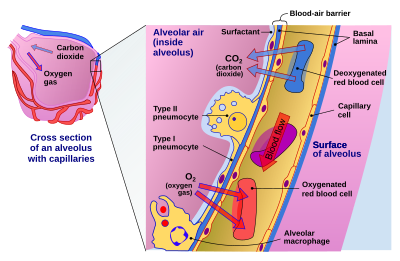
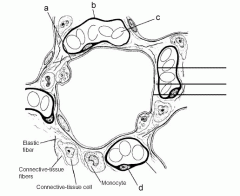
Review Sheet 23 302 14. On the diagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the respiratory membrane. VÉeu É Elastic fiber O st W Connective-tissue fibers I Monocyte Connective-tissue cell 15. Why does oxygen move from the alveoli into the pulmonary capillary blood? CIS 770 16. Page ... epithelial cells. Apical Basal Epithelial cells can also move protein and lipid from one side of the cell to the other by transcytosis. Transcytosis consist of endocytosis from on side of the cell, transport of the vesicles to the other side of the cell and then fusion of the vesicle with the cell membrane. Transcytosis allows cells to capture and
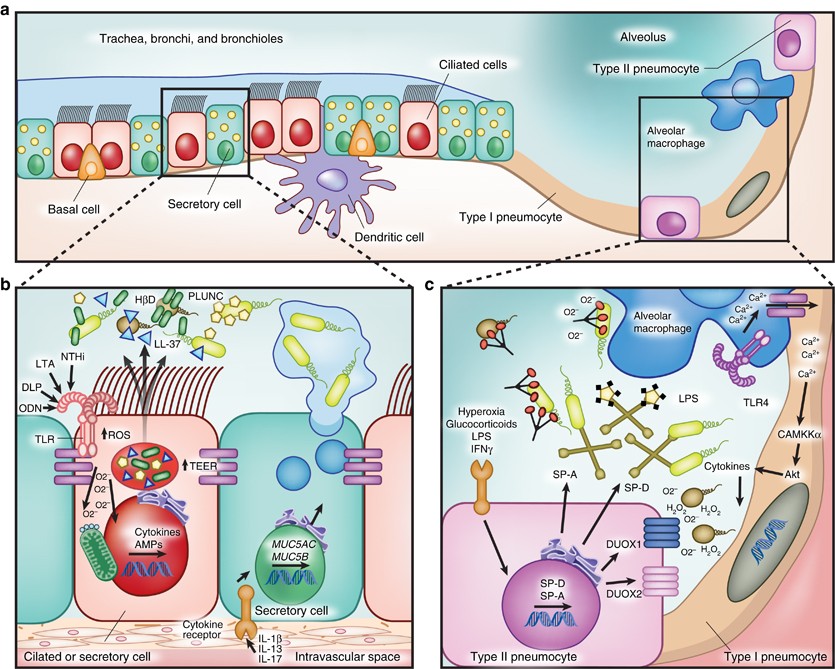
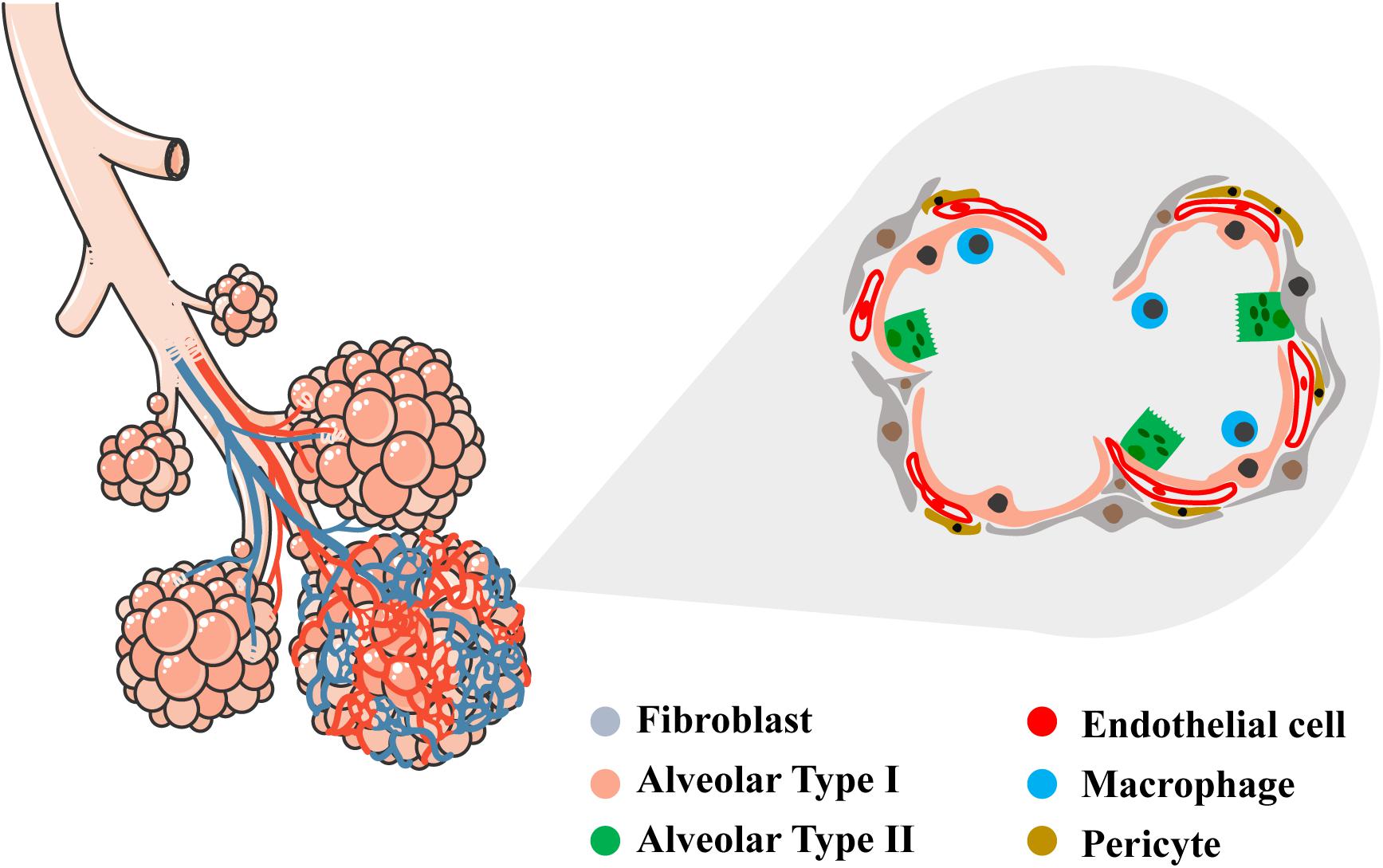
- The epithelial lining of alveoli consists mainly of type I alveolar cells (also known as type I pneumocytes). - These are large, flat, squamous cells with few organelles and thin cytoplasm. - They cover about 93% of alveolar surface area. - Their primary purpose is air-blood gas exchange. - The junctions between these cells are narrow (1nm).

On the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium
Label the structures of the upper respiratory system. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures of the upper respiratory system. drag the labels onto the diagram to identify respiratory system structures reset help one of 80 million alveolar air space muscles of expiration alveolus branch of pulmonary vein bl muscles used for ve tilation alveci (e) branching of airways n ... 14. On the diagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the respiratory membrane. VÉeu É Elastic fiber O st W Connective-tissue fibers I Monocyte Connective-tissue cell 15. Why does oxygen move from the alveoli into the pulmonary capillary blood? CIS 770 16. alveolar sac. middle lobe. terminal bronchiole. respiratory bronchioles. inferior lobe alveolar duct. alveolar duct alveoli ##### 13. On the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the ##### respiratory membrane. Demonstrating Lung Inflation in a Sheep Pluck ##### 14.
On the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium. On the diagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red bloo... A: Lungs provide the respiratory surface for the exchange of gases. Alveoli are very small sacs present... Diagram of an alveolar epithelial cell typical of the lactating bovine mammary gland illustrating an extensive rough endoplasmic reticulum (R), secretory vesicles (S) and numerous casein ... Solution for 14. On the diagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the respiratory membrane.… On the diagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red bloo... A: Lungs provide the respiratory surface for the exchange of gases. Alveoli are very small sacs present...
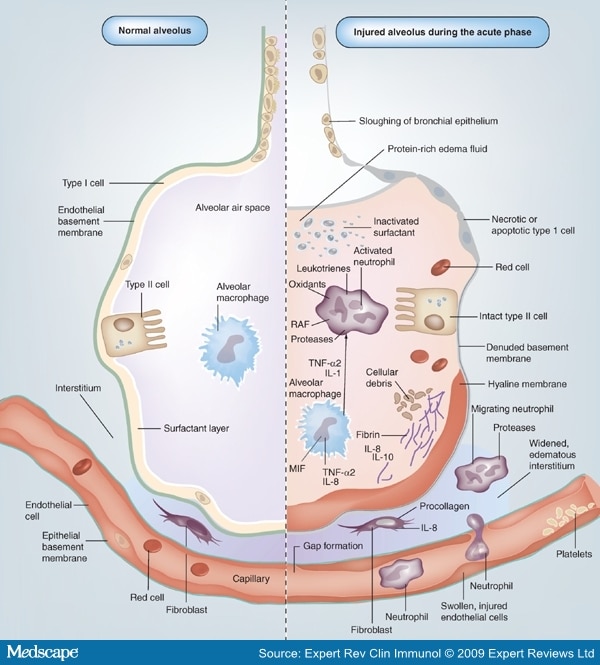
B. Alveolar ducts The walls of alveolar ducts View Image are lined by alveoli and alveolar sacs (clusters of alveoli). C. Alveolus The walls of these structures are covered on both sides by squamous epithelium (too thin to see) of Type I cells lining adjacent alveolar lumens. Within the walls is an extensive capillary network. Alveolar Epithelium. The one-cell thick walls of the alveoli are composed of two distal airway epithelium cell types (pneumocytes) [7]. Type-1 squamous alveolar epithelial cells: Constituting 95% of the alveolar surface area [8], the type 1 cells are extremely thin and flexible to help in the process of gas diffusion so the oxygen-carbon dioxide exchange can occur between the alveoli and the ... On the diagram below, identify the alveolar duet, respiratory bronchioles, terminal bronchiole, alveoli, and alveolar sa. Examining Prepared Slides of Tracheal and Lung Tissue 14. The tracheal epithelium is ciliated and has goblet cells. What is the function of each of these modifications? cilia: goblet cells: 15. Lines the inner layer of alveolar epithelium. Synthesized by SER of type II pneumocytes. Function - 1. To reduce the surface tension of alveoli mainly during expiration, thus reduces the work of lung inflation. 2. Waterproofing. Surfactant synthesis starts after 26 weeks of fetal life. Therefore premature infants,with
Identify the tissue type and its function. Simple Squamous Epithelium •Diffusion and Filtration •Secretes lubricating substances in serosae. Identify the structure indicated. Skeletal Muscle. MultiplePeripherally Located Nuclei. Identify the structure indicated. Neuron Cell Body . The epithelium of the alveoli, contains two main types of cells: type I pneumocytes: large flattened cells - (95% of the total alveolar area) which present a very thin diffusion barrier for gases. type II pneumocytes (making up 5% of the total alveolar area, but 60% of cells). These cells secrete 'surfactant' which decreases the surface tension ... Ans. 1- Alveolar epithelium 2- Capil …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: iagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the brane respira Elastic fiber Connective tissue fibers Monocyte. Previous question Next question. On the diagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the respiratory membrane. VÉeu É Elastic fiber O st W Page 1/6. Acces PDF Review Sheet 23 Anatomy Respiratory System Diagram Connective-tissue fibers I Monocyte Connective-tissue cell 15. Why does oxygen move from the
R.J. Mason, in Encyclopedia of Respiratory Medicine, 2006 The alveolar epithelium is composed of two types of epithelial cells, named alveolar type I and type II cells. Type I cells are large flat cells that comprise about 95% of the alveolar surface. Type II cells are small cuboidal cells with characteristic lamellar inclusions and apical microvilli and cover about 5% of the alveolar surface.
The epithelium here remains low cuboidal. Each respiratory bronchiole branches into between 2 and 11 alveolar ducts that still contain smooth muscle fibers in their walls. Along these walls, the alveolar ducts give rise to single alveoli and to numerous alveolar sacs, which are associated with 2 to 4 alveoli.
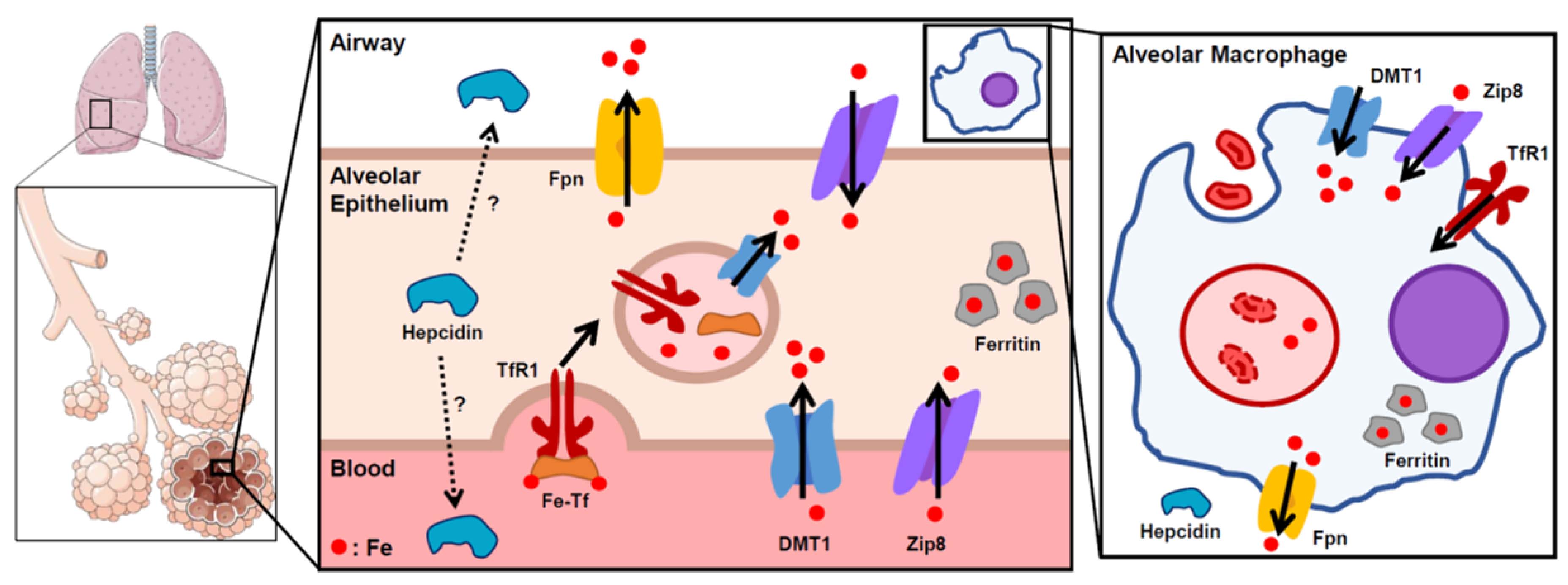
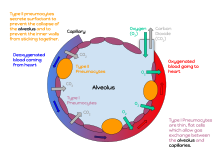
alveolar epithelium The respiratory membrane is a composite structure consisting of three layers: (1) the endothelial cells lining an adjacent capillary (capillary endothelium) (2) the fused basal laminae that lie between the alveolar and endothelial cells(basement membrane - fused basal lamiae)
the alveolar epithelium is a mosaic of type i alveolar epithelial cells which cover around 95% of the total alveolar surface with their thin squamous cell extensions interspersed with single cuboidal type ii alveolar epithelial cells which are easily recognized by their characteristic secretory organelles, the surfactant-storing lamellar bodies …
Underneath the thin skin of the nose are its skeletal features. ... An olfactory epithelium used to detect odors is found deeper in the nasal cavity.
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions. -Identify the letter that indicates structures that assist in filtering, heating, and humidifying inspired air. ... -Identify the letter that indicates the ciliated pseudostratified epithelium of the trachea. Free. Unlocked . Multiple Choice . Unlock to view answer.
A cross section through an alveolus is shown on Figure 13-4B and a blow-up of the respiratory membrane is shown in Figure 13-4C. On these illustrations color the alveolar epithelium yellow, the capillary endothelium pink, and the red blood cells in the capillary red. Also, label the alveolar chamber and color it pale blue.
The principal functions of Type I pneumocytes are gas exchange and fluid transport. Type II Pneumocytes secrete surfactant, which decreases the surface area between thin alveolar walls, and stops alveoli from collapsing during exhalation. These cells connect to the epithelium and other constituent cells by tight junctions.
alveolar sac. middle lobe. terminal bronchiole. respiratory bronchioles. inferior lobe alveolar duct. alveolar duct alveoli ##### 13. On the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the ##### respiratory membrane. Demonstrating Lung Inflation in a Sheep Pluck ##### 14.
14. On the diagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endothelium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the respiratory membrane. VÉeu É Elastic fiber O st W Connective-tissue fibers I Monocyte Connective-tissue cell 15. Why does oxygen move from the alveoli into the pulmonary capillary blood? CIS 770 16.
Label the structures of the upper respiratory system. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the structures of the upper respiratory system. drag the labels onto the diagram to identify respiratory system structures reset help one of 80 million alveolar air space muscles of expiration alveolus branch of pulmonary vein bl muscles used for ve tilation alveci (e) branching of airways n ...





_AdultLung_x16_001.jpg)










:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/194/btmPfjc39HYDMLuj8cL4Q_bronchioles-alveoli-anatomy_english.jpg)


0 Response to "38 on the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium"
Post a Comment