38 draw and label an energy level diagram for hydrogen
What are the highest level consumers in this food web? Bear, wolf, red fox. Create an energy pyramid from the food chain: leaves → insects → birds → red fox → bear . Where is the most energy in this pyramid? Where is the least energy? At the bottom – leaves. At the top - bear. What happens to energy as it moves through the food chain/web? Bohr Diagrams 1) Draw a nucleus with the number of protons and neutrons inside. 2) Carbon is in the 2nd period, so it has two energy levels, or shells. 3) Draw the shells around the nucleus. 6p 6n. Bohr Diagrams 1) Add the electrons. 2) Carbon has 6 electrons. 3) The first shell can only hold 2 electrons. 6p 6n.
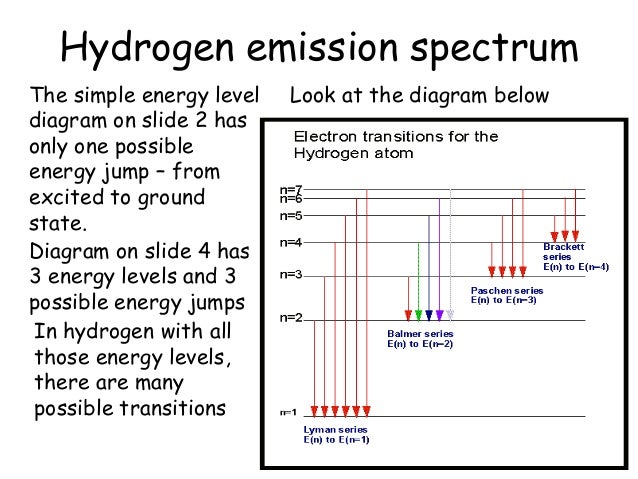
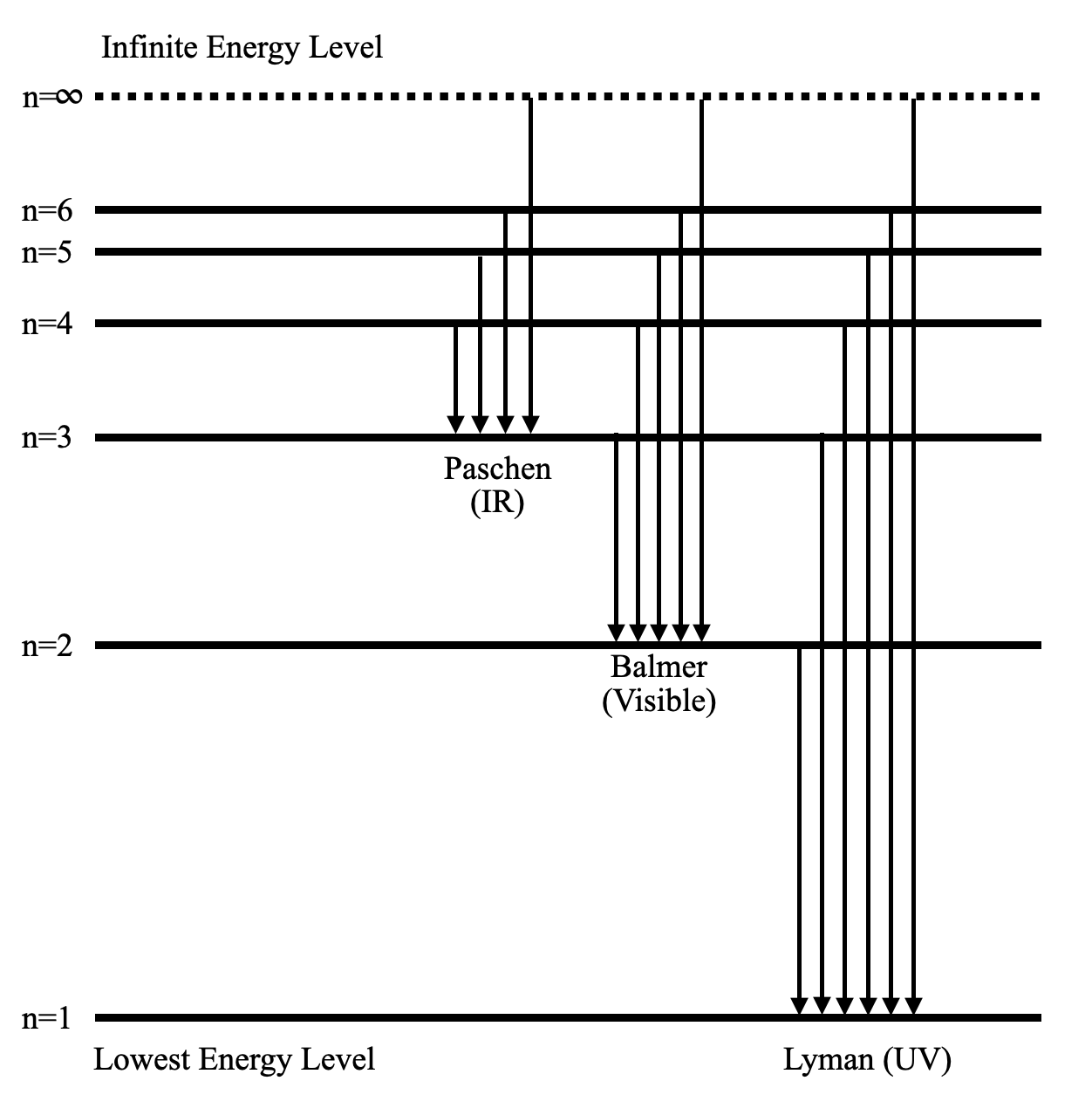
Draw a Neat, Labelled Energy Level Diagram for H Atom Showing the Transitions. Explain the Series of Spectral Lines for H Atom, Whose Fixed Inner Orbit Numbers Are 3 and 4 Respectively.

Draw and label an energy level diagram for hydrogen
Draw a Neat and Labelled Energy Level Diagram and Explain Balmer Series and Brackett Series of Spectral Lines for Hydrogen Atom. Maharashtra State Board HSC Science (Computer Science) 12th Board Exam. Question Papers 181. Textbook Solutions 11950. MCQ Online Tests 60. ... Draw and label an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. In your diagram show how the series of lines in the ultraviolet and visible regions of its emission spectrum are produced, clearly labelling each series. showing y-axis labelled as energy/E / labelling at least two energy levels; showing a minimum of four energy levels/lines with convergence; showing jumps to n = 1 for ultraviolet ... Energy level diagrams and the hydrogen atom. It's often helpful to draw a diagram showing the energy levels for the particular element you're interested in. The diagram for hydrogen is shown above. The n = 1 state is known as the ground state, while higher n states are known as excited states. If the electron in the atom makes a transition from a particular state to a lower state, it is losing energy.
Draw and label an energy level diagram for hydrogen. Hydrogen Spectrum - Wavelength, Diagram, Hydrogen Emission Spectrum. Hydrogen Spectrum introduction. We all know that electrons in an atom or a molecule absorb energy and get excited, they jump from a lower energy level to a higher energy level, and they emit radiation when they come back to their original states. Atomic Physics 1. Draw and label an energy level diagram for hydrogen using the Bohr Model. On it, show all the transitions by which an electron in the n 4 state could emit a photon. Question: Atomic Physics 1. Draw and label an energy level diagram for hydrogen using the Bohr Model. 2. Draw and label an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. In your diagram show how the series of lines in the ultraviolet and visible regions of its emission spectrum are produced, clearly labelling each series. (Total 4 marks) 3. Describe the emission spectrum of hydrogen. Outline how this spectrum is related to the energy levels in the ... Answer. Step 1: The chemical equation for the complete combustion of methane is: CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) Step 2: Combustion reactions are always exothermic (Δ H is negative) so the reactants should be drawn higher in energy than the products. Step 3: Draw the curve in the energy level diagram clearly showing the transition state.
Spacecraft propulsion is any method used to accelerate spacecraft and artificial satellites. In-space propulsion exclusively deals with propulsion systems used in the vacuum of space and should not be confused with space launch or atmospheric entry.. Several methods of pragmatic spacecraft propulsion have been developed each having its own drawbacks and advantages. Question: Sketch and label an energy level diagram for hydrogen, and draw the transitions corresponding to the first four lines in the Balmer series (nf = 2).1 answer · Top answer: The energy of the nthnth orbit of the hydrogen atom is given as, En=−13.6n2eVEn=−13.6n2eV The energy associated with the ground state (n=1)(n=1) ... the fine structure constant and the rest energy of the electron. The fine structure constant is given by α ≡ e2 ~c ≃ 1 137, (2.1.4) and the rest energy of the electron is mc2. Then, e2 a 0 = me4 ~2 = mα2~2c2 ~2 = α2 mc2. (2.1.5) This states that the energy scale of hydrogen bound states is a factor of α2 smaller than It is very easy. Click on the order now tab. You will be directed to another page. Here there is a form to fill. Filling the forms involves giving instructions to your assignment. The information needed include: topic, subject area, number of pages, spacing, urgency, academic level, number of sources, style, and preferred language style.
Energy level diagram . The energy of the electron in the n th orbit of the hydrogen atom is given by, En = -13.6 /n 2 eV. Energy associated with the first orbit of the hydrogen atom is, E 1 = -13.6 /1 2 = -13.6 eV. It is called ground state energy of the hydrogen atom. Energy associated with the second orbit is given by, E 2 = -13.6 /2 2 = -3.4 eV 4. Construct an energy level diagram to scale for the allowed energies of the electron in the hydrogen atom. Use the results from question 1 above. On the energy level diagram: a. Draw and label the n = 1 and n = 6 energy levels. Give the value of n 3:03 calculate the heat energy change from a measured temperature change using the expression Q = mcΔT; 3:04 calculate the molar enthalpy change (ΔH) from the heat energy change, Q; 3:05 (Triple only) draw and explain energy level diagrams to represent exothermic and endothermic reactions which are, oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, calcium, and phosphorous. Of these, carbon is the best at joining with other elements to form compounds necessary for life, such as sugars, starches, fats, and proteins. Together, all these forms of carbon account for approximately half of the total dry mass of living things.
So, those are electrons falling from the higher energy levels down to the 2nd energy level. So, let's go ahead and draw them on our diagram here. So, let's say an electron fell from the 4th energy level down to the 2nd. Alright, so, that energy difference, if you do the calculations, that turns out to be the blue-green line in your line spectrum.
Below is a blank energy level diagram which helps you depict electrons for any specific atom. At energy level 2, there are both s and p orbitals. The 2s has lower energy when compared to 2p. The three dashes in 2p subshells represent the same energy. 4s has lower energy when compared to 3d. Therefore, the order of energy level is as follows: s ...
3.3.1a - Bohr Diagram. Let's take a look at how to draw Bohr diagrams: For a hydrogen atom, H, the one electron goes into the first energy level. Draw a circle and label it with the symbol of the nucleus, H. Write the number of protons for the nucleus, 1p +. Draw an arc to represent the first energy level.
1. Drawing the Simplest Atoms: Hydrogen and Helium. The most common element in the universe is hydrogen, a gas which makes up about 99% of the universe's known mass 1. Hydrogen is the main component of stars, and a star is, by far the most massive thing in any solar system. 1 That's not including "dark matter," which is beyond the scope ...
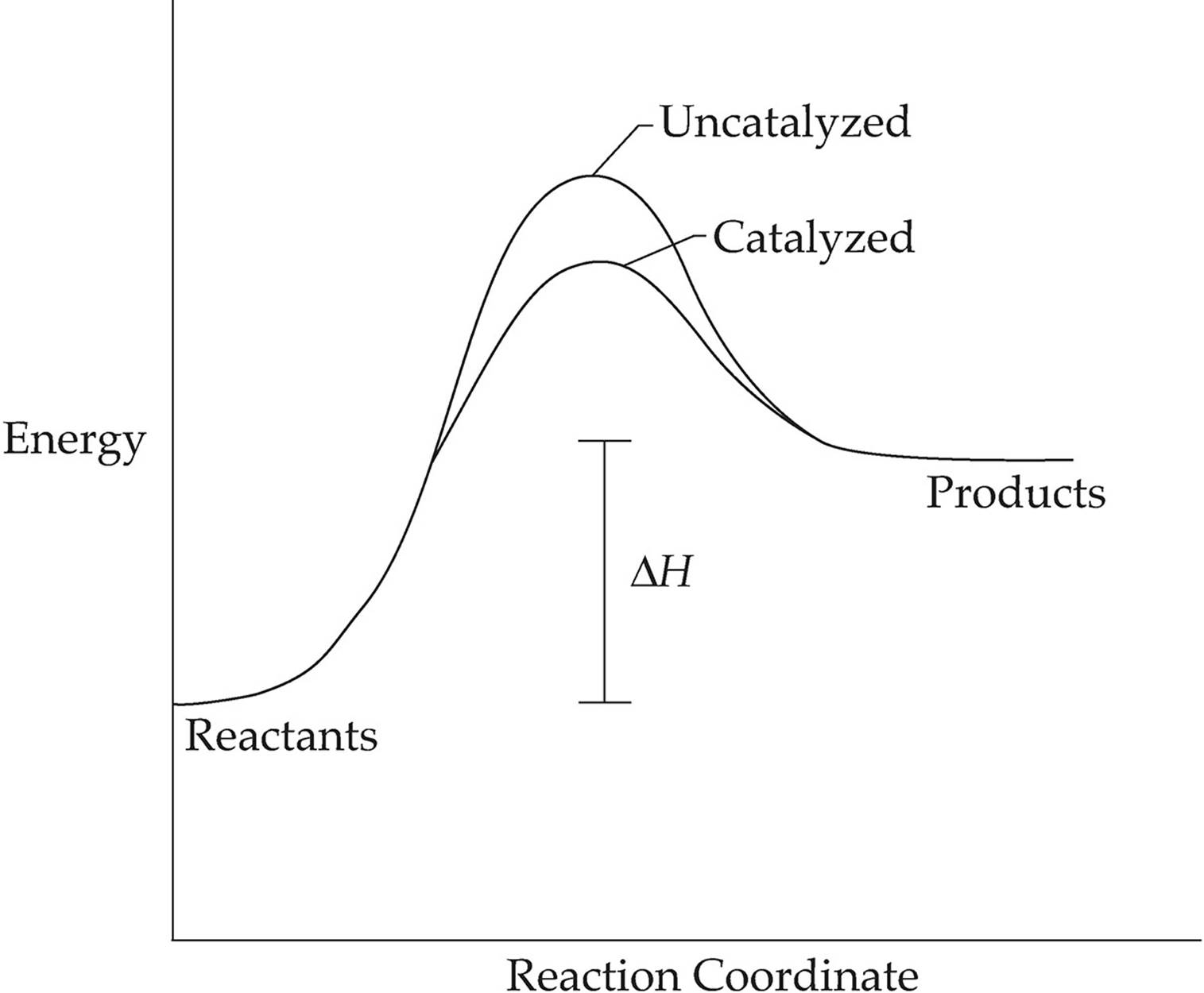
An energy level diagram. shows whether a reaction is exothermic. or endothermic. It shows the energy in the reactants. and products, and the difference in energy between them.
Metabolism (/ m ə ˈ t æ b ə l ɪ z ə m /, from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms.The three main purposes of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the ...
energy of isolated atoms bond order (H2 molecule) = (2) - (0) 2 = 1 bond 1sb H H H H σ∗ = 1s H H a - 1sb = antibonding MO = LCAO = linear combination of atomic orbitals node = zero electron density because of opposite phases ∆E = bond energy There is a big energy advantage for a hydrogen molecule over two hydrogen atoms.
Nov 21, 2010 · The ionization energy of an atom is the energy required to remove the electron completely from the atom.(transition from ground state n = 0 to infinity n = ∞). For hydrogen, the ionization energy = 13.6eV; When an excited electron returns to a lower level, it loses an exact amount of energy by emitting a photon. The Lyman(ultraviolet) series of spectral lines corresponds to electron transitions from higher energy levels to level n = 1.
Seven electrons are trapped in a one-dimensional infinite potential well of width L.What multiple of 8 m L 2 h 2 gives the energy of (a) the first excited state, (b) the second excited state, and (c) the third excited state of the system of seven elec-trons? (d) Construct an energy-level diagram for the lowest four energy levels of the system.
c) Draw an energy level diagram for the reaction. 5. Draw an energy level diagram for a reaction in which the total energy of the reactants is 50 kJ mol-1, the total energy of products is 120 kJ mol-1 and the activation energy for the forward reaction is 120 kJ mol-1. Label the diagram clearly. Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic?
Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. ... Bond order value of 1 means that two hydrogen atoms are connected by a single bond. Greater value of bond order for H 2 molecule than H 2 + ion shows that two H 2 molecule is more stable than H 2 +. Bond length of H 2 is smaller than that of H 2 + ion.
Hydrogen molecules are first broken up into hydrogen atoms (hence the atomic hydrogen emission spectrum) and electrons are then promoted into higher energy levels. Suppose a particular electron was excited into the third energy level. This would tend to lose energy again by falling back down to a lower level. It could do this in two different ways.
The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H 2 molecule is shown in Figure 13. On either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms A and B, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding ...
Draw a neat labelled energy level diagram of the Hydrogen atom. · A rectangular corral of widths Lx=L and Ly=2L contains seven electrons. · The energy gap ...Nov 19, 20191 answer · Top answer: Given figure shows energy level diagram for Hydrogen atom.
Energy levels of the molecule LCAO: Energy Level Splitting and the Energy Matrix Element Bonding Anti-bonding Energy level diagram going from two isolated atoms to the molecule: 2:E1s 1:EA 1:EB 2Vss The two 1s orbitals on each Hydrogen atom combine to generate two molecular orbitals - the bonding orbital and the anti-bonding orbital - with ...
A Hydrogen atom has only one single electron revolving around the nucleus at the lowest energy level. When we heat a hydrogen atom, the electron gains energy ...1 answer · Top answer: Hint: Energy level diagram is the direct consequence of the principal quantum number - ‘n’. Energy diagram is necessary to determine the energy difference ...
Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply.
figures. (d) Draw an energy level diagram for hydrogen, and . draw vertical arrows to indicate each of these three electron transitions on the diagram. Label your lines "a", "b", and "c". Refer to lecture 5 notes for examples of energy level . diagrams. (a) E = 2.04 x 10-18. J (b) E = 2.08 x 10-19. J (c) E = 4.09 x 10-19. J (d) 2 ...
Bohr's model of hydrogen is based on the nonclassical assumption that electrons travel in specific shells, or orbits, around the nucleus. Bohr's model calculated the following energies for an electron in the shell, : Bohr explained the hydrogen spectrum in terms of electrons absorbing and emitting photons to change energy levels, where the ...
Energy level diagrams and the hydrogen atom. It's often helpful to draw a diagram showing the energy levels for the particular element you're interested in. The diagram for hydrogen is shown above. The n = 1 state is known as the ground state, while higher n states are known as excited states. If the electron in the atom makes a transition from a particular state to a lower state, it is losing energy.
Draw and label an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. In your diagram show how the series of lines in the ultraviolet and visible regions of its emission spectrum are produced, clearly labelling each series. showing y-axis labelled as energy/E / labelling at least two energy levels; showing a minimum of four energy levels/lines with convergence; showing jumps to n = 1 for ultraviolet ...
Draw a Neat and Labelled Energy Level Diagram and Explain Balmer Series and Brackett Series of Spectral Lines for Hydrogen Atom. Maharashtra State Board HSC Science (Computer Science) 12th Board Exam. Question Papers 181. Textbook Solutions 11950. MCQ Online Tests 60. ...





















0 Response to "38 draw and label an energy level diagram for hydrogen"
Post a Comment