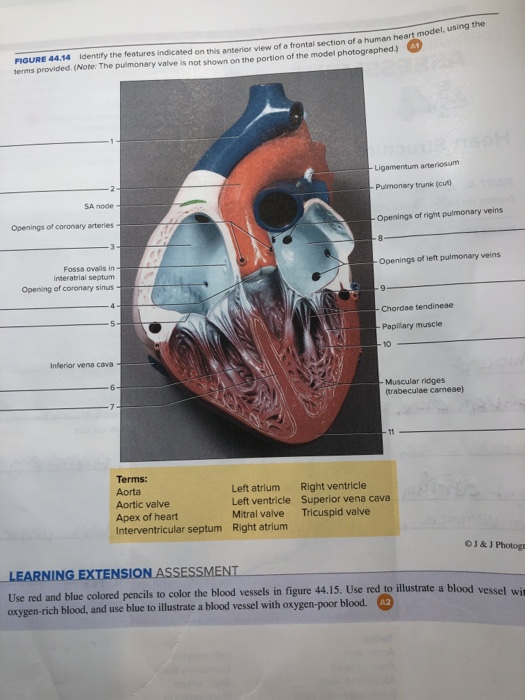
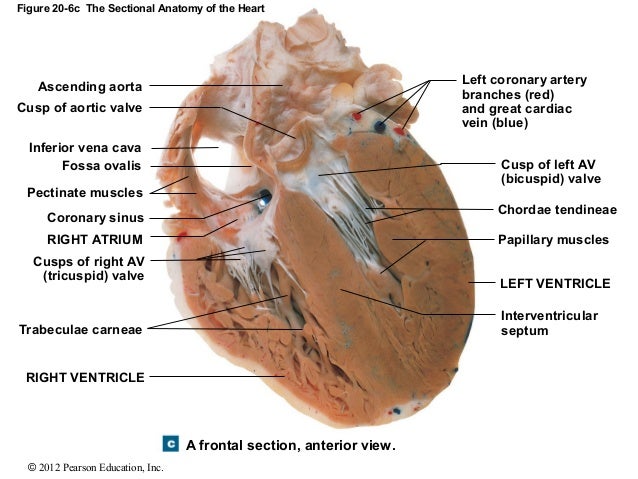
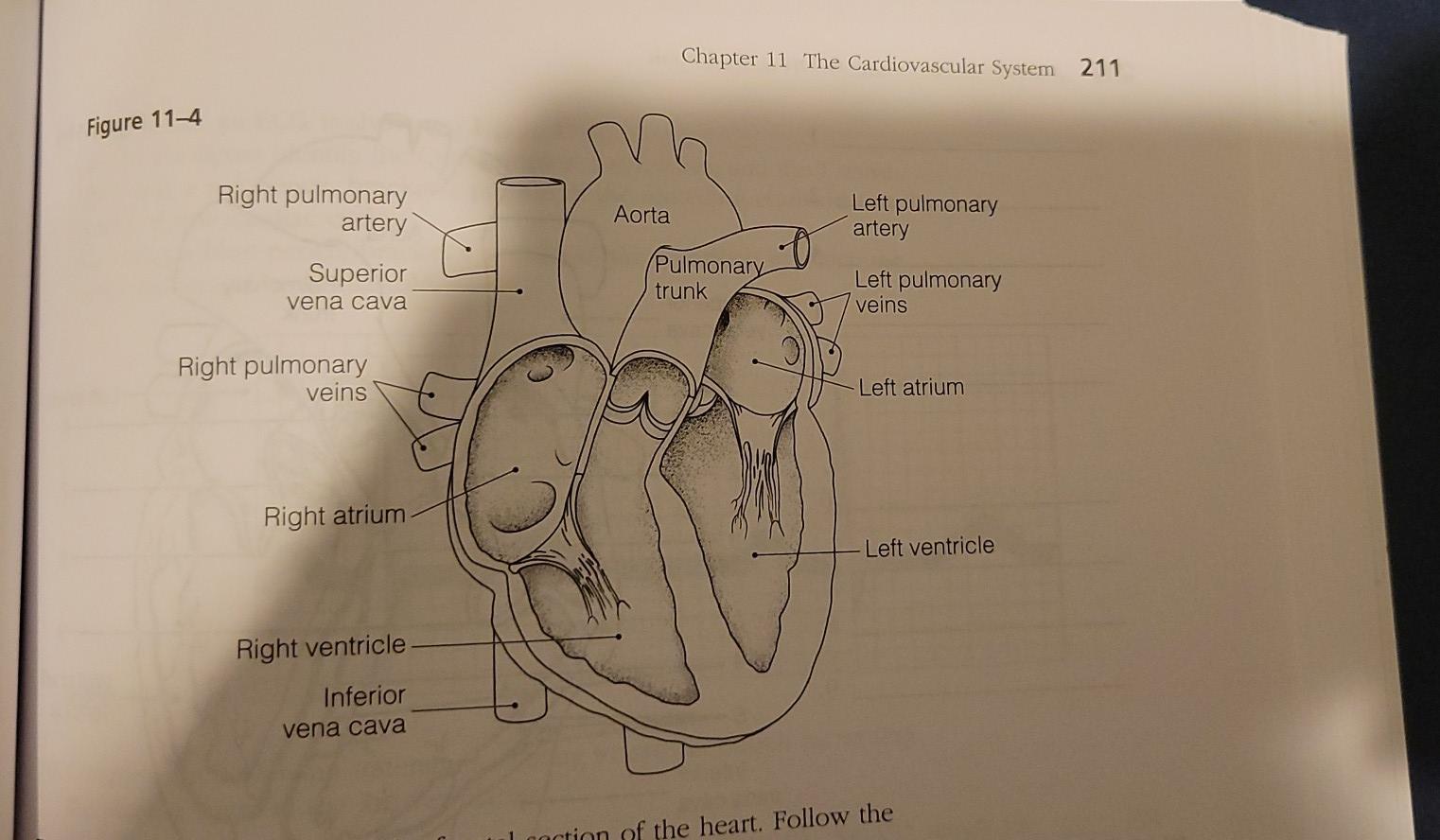
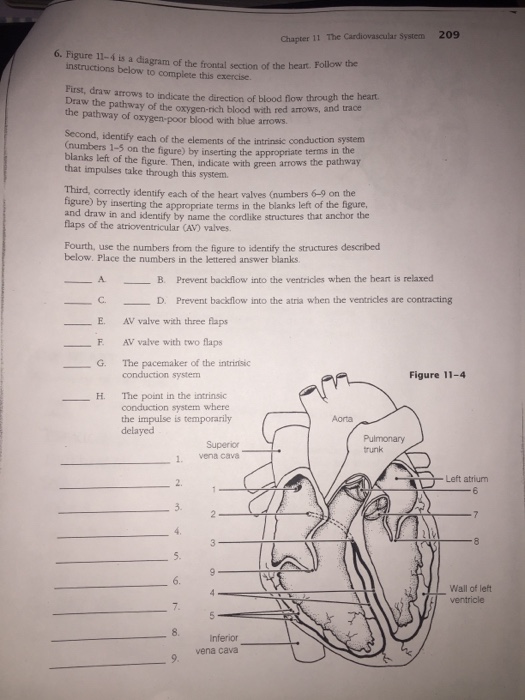
40 figure 11-4 is a diagram of the frontal section of the heart
The cerebral cortex has 4 main lobes - frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal lobe - and their location, function, and anatomy all differ. We will use labeled diagrams and lateral images of the brain (side views) to walk through each lobe of the cerebrum. Every EZmed post is filled with simple tricks to remember the content ... Identify Various Parts Of A Human Heart: Trivia Quiz. The heart is the most important organ in the body. It is in charge of keeping the processes within the body moving by facilitating the transfer of blood throughout the body. The quiz below is to test out interesting facts you may know about the heart.
Figure 11.4. 4 shows the change in potential of the axon membrane during an action potential. The nerve goes through a brief refractory period before racing resting potential. During the refractory period, another action potential cannot be generated. In myelinated neurons, ion flows occur only at the nodes of Ranvier.
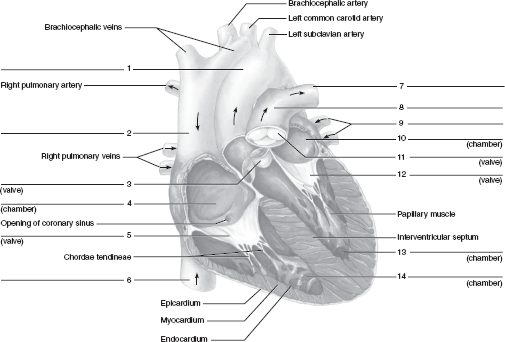
Figure 11-4 is a diagram of the frontal section of the heart
The reason why so bookshops have so much self help section. So many snake oil salesmen want to sell "solutions" to the beikambings. And many people buy many books to search for the solution, but likely, if you can't think for yourself, you'll probably find it hard to find the solution. Carefully study the diagram of the human respiratory system with labels A, B, C and D. Select the option which gives correct identification and main function and /or characteristic.(A) (i) Trachea: It is supported by bony rings for conducting inspired air.(B) (ii) Ribs: When we breathe out, ribs are The adult human brain weighs on average about 1.2-1.4 kg (2.6-3.1 lb) which is about 2% of the total body weight, with a volume of around 1260 cm 3 in men and 1130 cm 3 in women. There is substantial individual variation, with the standard reference range for men being 1,180-1,620 g (2.60-3.57 lb) and for women 1,030-1,400 g (2.27-3.09 lb).
Figure 11-4 is a diagram of the frontal section of the heart. The heart pumps around 5.7 litres of blood in a day throughout the body. The heart is situated at the centre of the chest and points slightly towards the left. On average, the heart beats about 100,000 times a day, i.e., around 3 billion beats in a lifetime. The average male heart weighs around 280 to 340 grams (10 to 12 ounces). The midsagittal section of the brain shows the three major parts of the brain, which are the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem.These brain parts are marked with visible gross features like the gyri (singular: gyrus) and sulci (singular: sulcus) of the cerebrum. They are each also divided into subparts or regions for simplified localization of structures, for example, the brainstem is ... Anatomy and Physiology is a dynamic textbook for the yearlong Human Anatomy and Physiology course taught at most two- and four-year colleges and universities to students majoring in nursing and allied health. A&P is 29 chapters of pedagogically effective learning content, organized by body system, and written at an audience-appropriate level. The bony orbit. The bony orbit is composed of seven bones. They form a pyramidal structure with the apex facing posteriorly (Figure 1). The walls of the orbit are as follows:. Roof: the orbital part of the frontal bone, with a small contribution from the sphenoid bone; Medial wall: lacrimal, maxilla, ethmoid and sphenoid bones; Floor: the majority is formed by the orbital part of the maxilla ...
Features include 4: increased left ventricular internal end-diastolic diameter (LVIDd) parasternal long axis LVIDd >5.3 cm (females) or >5.9 cm (males) elevated left ventricular volumes. diastolic volumes >104 mL (females) or >155 mL (males) systolic volumes >49 mL (females) or >58 mL (males) A midsagittal section of the body would pass through the: A) kidney B) lung C) heart D) spleen E) leg Create an account to start this course today Used by over 30 million students worldwide Answer -. When it pumps the blood to the organs, the heart is contracted . When it receives the blood from the lungs, the heart is relaxed . In this figure, contraction in both ventricles is due to the fact that blood is pumping out. In the left ventricle, the oxygenated blood is pumping to other parts of the body. Clinical Relevance - Additional Heart Sounds. Occasionally within clinical practice, additional heart sounds can be heard; these are termed S 3 and S 4 and can be heard in the following situations:. S 3: this sound can sometimes be heard early in diastole (following S 2).It is normal in young people or athletes; however, it often indicates congestive heart failure in older patients.
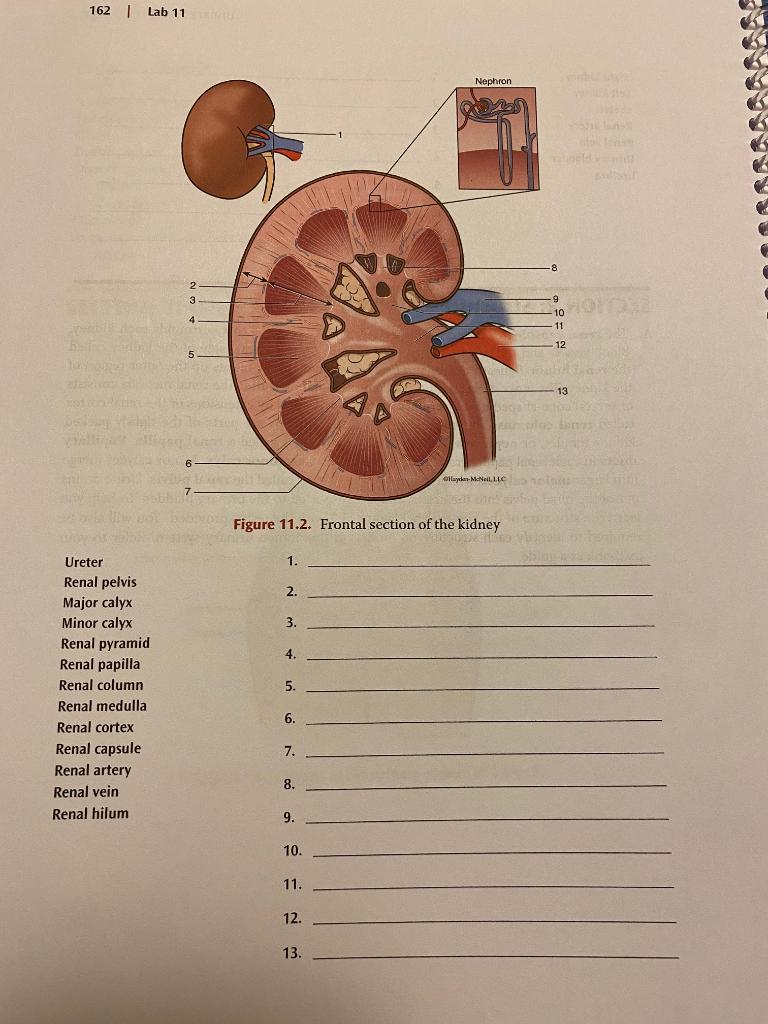
Coronal section of the brain at the level of the thalamus. The frontal and temporal lobes are observed in their previously described locations. The body of the corpus callosum forms the roof of the body of the left and right lateral ventricles, which are separated from each other by the septum pellucidum.The insula of Reil and the Sylvian fissure maintain their lateral relationship to the ... The cardiovascular system circulates oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. PIXOLOGICSTUDIO/Science Photo Library/Getty Images Heart . The heart is the organ that supplies blood and oxygen to all parts of the body. This amazing muscle produces electrical impulses through a process called cardiac conduction.These impulses cause the heart to contract and then relax, producing what is known as ... The human body contains five organs that are considered vital for survival. They are the heart, brain, kidneys, liver, and lungs. The locations of these five organs and several other internal organs are shown in Figure 10.4. 2. If any of the five vital organs stops functioning, the death of the organism is imminent without medical intervention. The lower quadrants may seem a little less exciting than the upper quadrants, but they are vitally important. In the Right Lower Quadrant, or RLQ, you find the cecum, appendix, portions of small ...
The path of blood through the heart begins with the right atrium receiving blood, which has circulated through most of the body. This blood is relatively low in oxygen because most of it has already been delivered to different organs and tissues. This blood is also relatively high in carbon dioxide, which is a product of metabolism in the tissues.
Electrical impulses, controlled by the cardiac conduction system, make the heart muscle contract and relax, creating the rate and rhythm of your heartbeat. 1 Here are the steps of blood flow through the heart and lungs: The blood first enters the right atrium. The blood then flows through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle.
Muscular System. The muscular system is responsible for the movement of the human body. Attached to the bones of the skeletal system are about 700 named muscles that make up roughly half of a person's body weight. Each of these muscles is a discrete organ constructed of skeletal muscle tissue, blood vessels, tendons, and nerves.
What Are Heart Valves? Valves are flap-like structures that allow blood to flow in one direction. Heart valves are vital to the proper circulation of blood in the body. The heart has two kinds of valves, atrioventricular and semilunar valves. These valves open and close during the cardiac cycle to direct the flow of blood through the heart chambers and out to the rest of the body.
There are 4 chambers, labeled 1-4 on the diagram below. To help simplify things, we can convert the heart into a square. We will then divide that square into 4 different boxes which will represent the 4 chambers of the heart. The boxes are numbered to correlate with the labeled chambers on the cartoon diagram.
An understanding of brain arterial vascular territories is important in understanding stroke and complications from surgery and endovascular procedures.. Although one could be excused for thinking that within the brain, such a carefully organized organ, blood supply would be constant, the truth is that a great deal of variety exists.
The nasal cavity is a roughly cylindrical, midline airway passage that extends from the nasal ala anteriorly to the choana posteriorly.[1] It is divided in the midline by the nasal septum. On each side, it is flanked by the maxillary sinuses and roofed by the frontal, ethmoid, and sphenoid sinuses in an anterior to posterior fashion.[1] While seemingly simple, sinonasal anatomy is composed of ...
The rest of the paper has been organised as follows: in Section 2, the literature review is included. Section 3 describes about components which are used for designing the proposed system. Section 4 illustrates the proposed system with a block diagram along with a brief explanation of the methodology with a flowchart in Section 5.
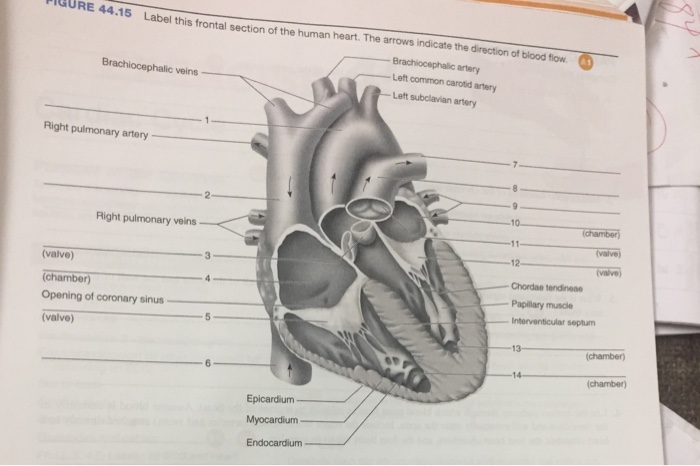
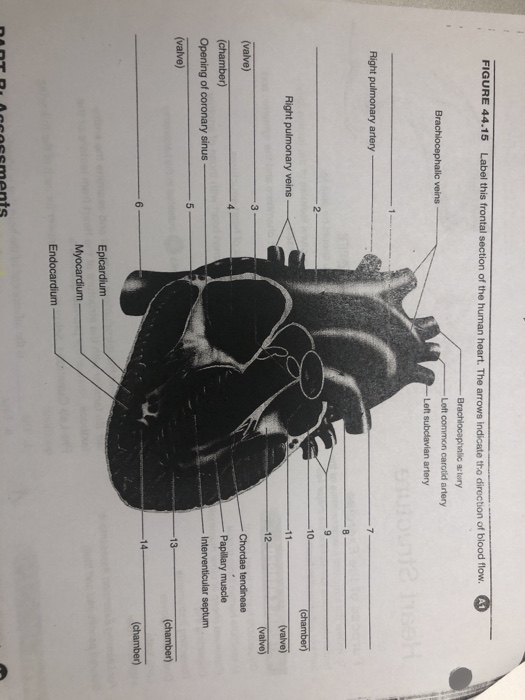
Four Chambers of the Heart and Blood Circulation. The shape of the human heart is like an upside-down pear, weighing between 7-15 ounces, and is little larger than the size of the fist. It is located between the lungs, in the middle of the chest, behind and slightly to the left of the breast bone. The heart, one of the most significant organs ...
The septum pellucidum (meaning translucent wall in Latin - SP), also known as the ventricle of Sylvius, is a thin, triangular double membrane separating the frontal horns of the right and left lateral ventricles of the brain. It extends between the anterior portion of the corpus callosum, and the body of the fornix and its width varies from 1.5 to 3.0 mm
Your heart is an amazing organ. It continuously pumps oxygen and nutrient-rich blood throughout your body to sustain life. This fist-sized powerhouse beats (expands and contracts) 100,000 times ...
The adult human brain weighs on average about 1.2-1.4 kg (2.6-3.1 lb) which is about 2% of the total body weight, with a volume of around 1260 cm 3 in men and 1130 cm 3 in women. There is substantial individual variation, with the standard reference range for men being 1,180-1,620 g (2.60-3.57 lb) and for women 1,030-1,400 g (2.27-3.09 lb).
Carefully study the diagram of the human respiratory system with labels A, B, C and D. Select the option which gives correct identification and main function and /or characteristic.(A) (i) Trachea: It is supported by bony rings for conducting inspired air.(B) (ii) Ribs: When we breathe out, ribs are
The reason why so bookshops have so much self help section. So many snake oil salesmen want to sell "solutions" to the beikambings. And many people buy many books to search for the solution, but likely, if you can't think for yourself, you'll probably find it hard to find the solution.





















0 Response to "40 figure 11-4 is a diagram of the frontal section of the heart"
Post a Comment