40 describe the rock layers shown in diagram a and any forces acting on the rock.
Correct answers: 3 question: Describe the rock layers shown in Diagram A and any forces acting on the rock. The lithological cycle or rock cycle is a concept of geology that describes the transitions of material in geological time that allow all rock to be transformed into one of three types: sedimentary rocks, metamorphic rocks and igneous rocks. [1] Rocks can pass through any of the three states when they are forced to break the balance. An igneous rock such as basalt can disintegrate and alter ...
🔴 Answer: 1 🔴 on a question Describe the rock layers shown in diagram a and any forces acting on the rock - the answers to brainsanswers.co.uk

Describe the rock layers shown in diagram a and any forces acting on the rock.
🔴 Answer: 2 🔴 on a question Describe the rock layers shown in Diagram A and any forces acting on the rock. - the answers to ihomeworkhelpers.com the compressional forces lead to the bending of rock layers and thus lead to the formation of fold mountains. In them the rock strata primarily of sedimentary rocks get folded, into wave like structure. This process of bending, sometimes warping and twisting of rock strata is referred to as their folding. Rock 3 is from the Swakane Biotite _____. (Fill in the blank with the rock type you identified. Hint: Depending on your specific rock sample, there are two possible names for this type of rock. The official name of this rock is based on its dark and light layers and high metamorphic grade, rather than its micaceous nature.)
Describe the rock layers shown in diagram a and any forces acting on the rock.. What conclusion can be made about the forces acting on the boulder? The forces acting on the boulder are balanced (net force equals zero). ... Fossils of trees were discovered in a sedimentary rock layer, and in a rock layer below were fossils of clams. ... The structural similarity shown in the diagram indicates that the pictured organisms ... Rock Cycle Diagram . Rocks are broadly classified into three groups: igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic, and the simplest diagram of the "rock cycle" puts these three groups in a circle with arrows pointing from "igneous" to "sedimentary," from "sedimentary" to "metamorphic," and from "metamorphic" to "igneous" again. The question whether a normal fault would result from the stresses being applied to the rock unit in diagram D is:. No, it would not result to a normal fault because shearing would bring about a different type of fault; The best description of the rock layers shown in Diagram A and any forces acting on the rock is:. The Diagram contains a part of a rock which has three dissimilar layers which ... Inter-layer forces ... obtained, such as on photographs, orientation data are presented on a rose diagram: Joints in a given orientation sector (e.g. within 10°) are counted. A radial line is drawn in the median ... front in terms of velocity and heterogeneities in the rock. Experiments show that the diverging rays
A useful way to illustrate how the three main types of rock are related to one another and how changes to rocks happen in a recurring sequence is the rock cycle. It can be presented in a diagram like the one below. The concept of the rock cycle is attributed to James Hutton (1726-1797), the 18th-century founder of modern geology. A free-body diagram for a left segment of the beam extending a distance x within region BC is shown in Fig. 6-4c. As always,V and M are shown acting in the positive sense. Hence, (3) (4) The shear diagram represents a plot of Eqs. 1 and 3, and the moment diagram represents a plot of Eqs. 2 and 4, Fig. 6-4d.These equations can The Rock Cycle. The rock cycle diagram clearly shows all the steps, components of the rock cycle including the end results and the movement of the process. If the diagram does not make sense, a simple explanation of all the steps at play and their end results is given below-Steps of the Rock Cycle Weathering The forces are unequal in size and act in opposite directions. (1) (b) A fisherman pulls a boat towards land. The forces acting on the boat are shown in Diagram 1. The fisherman exerts a force of 300 N on the boat. The sea exerts a resistive force of 250 N on the boat. Diagram 1 (i) Describe the motion of the boat.
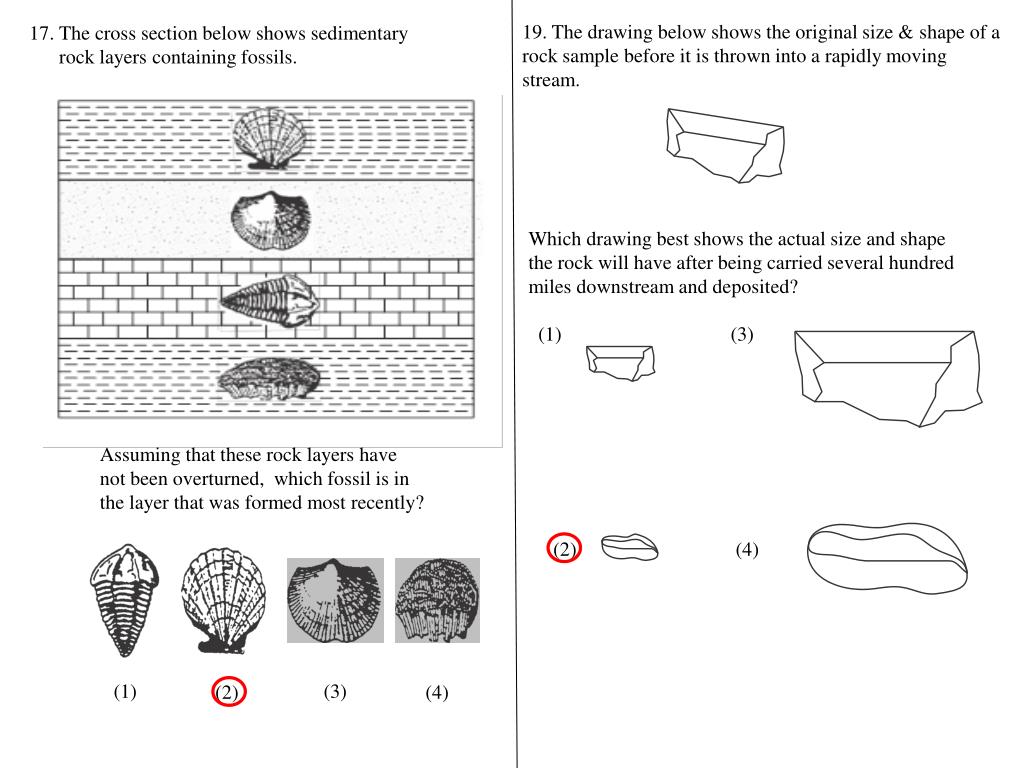
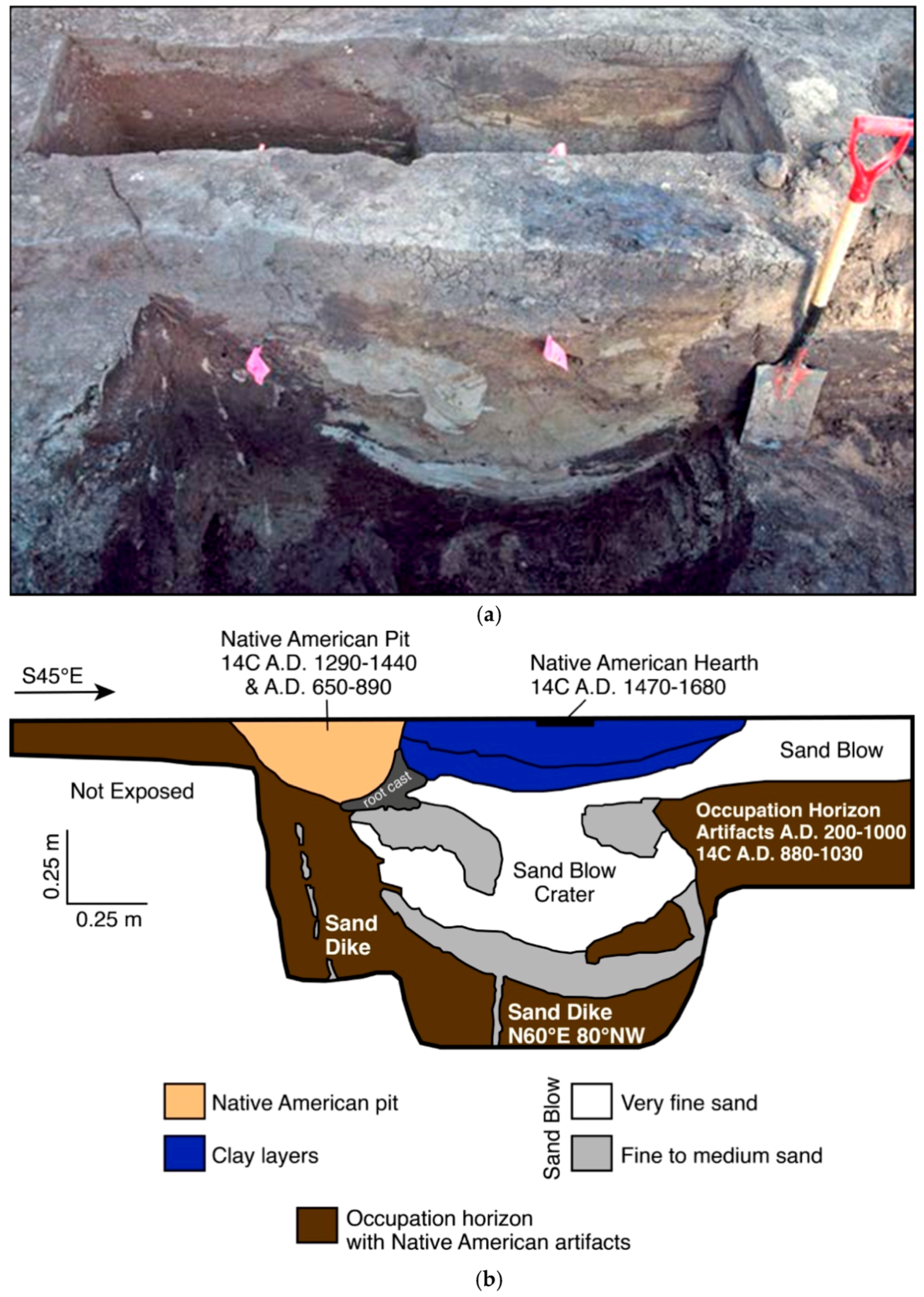
Sedimentary Structures. STRATIFICATION refers to the way sediment layers are stacked over each other, and can occur on the scale of hundreds of meters, and down to submillimeter scale. It is a fundamental feature of sedimentary rocks. This picture from Canyonlands National Monument/Utah shows strata. exposed by the downcutting of the Green River. Use the diagram to answer each question. In diagram B, which type of fault will form if the stress force continues? Explain. 1 See answer bestanswergiverever is waiting for your help. Add your answer and earn points. zainabekram2 zainabekram2 Figure A shows cross section of a land form or rock. In Figure B, compression stress is applied on it. Rock strata refers to stacked-up layers of sedimentary rock. Other kinds of rock can have layering in them but the word 'strata' is reserved for sedimentary rocks, rocks composed of individual ... 30 seconds. Report an issue. Q. The diagram shows different layers of sedimentary rock. Each layer is labeled with a letter. answer choices. The left part of Layer B is younger than the right part. The left part of Layer F is the same age as Layer M. Layer R is older than Layer M.
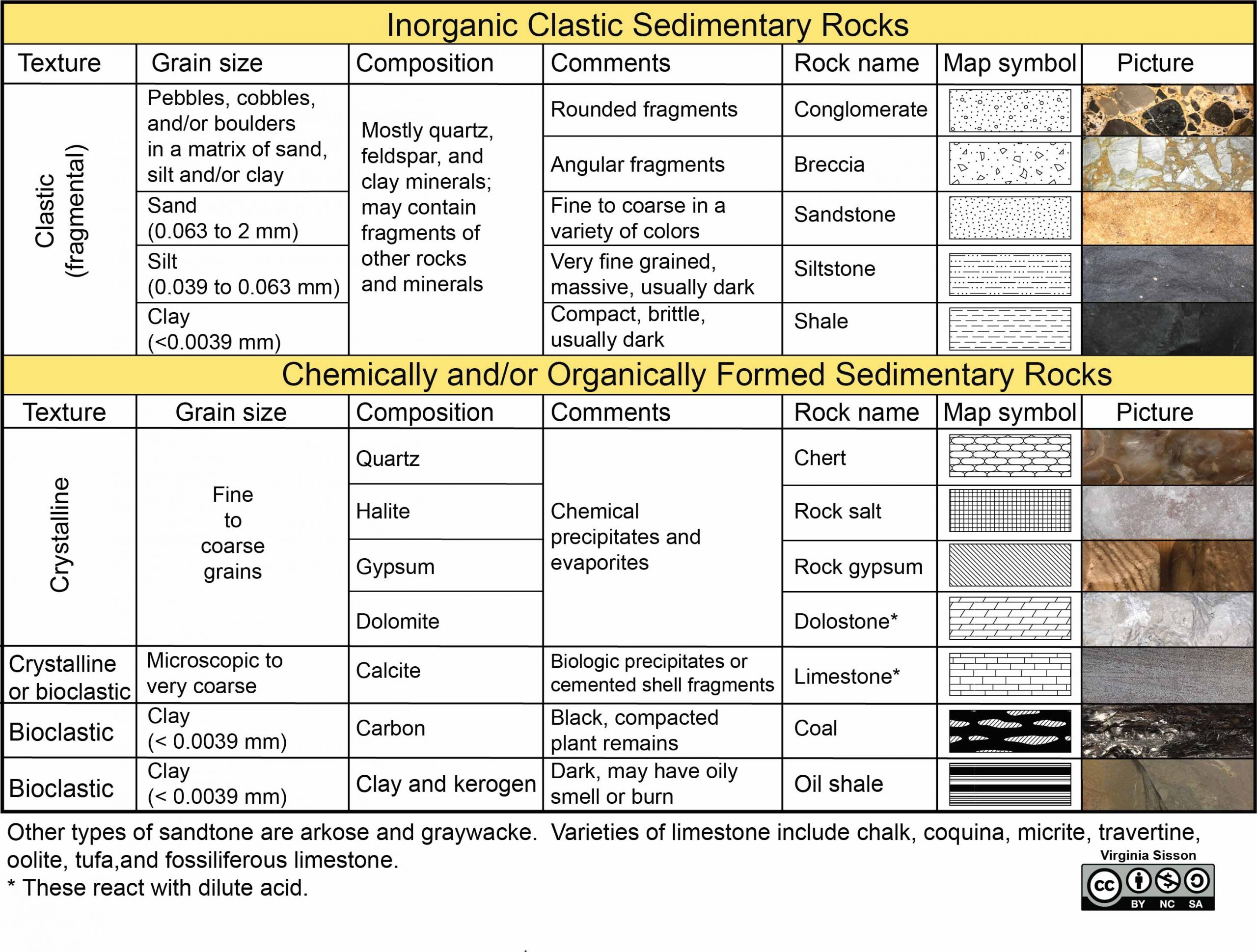
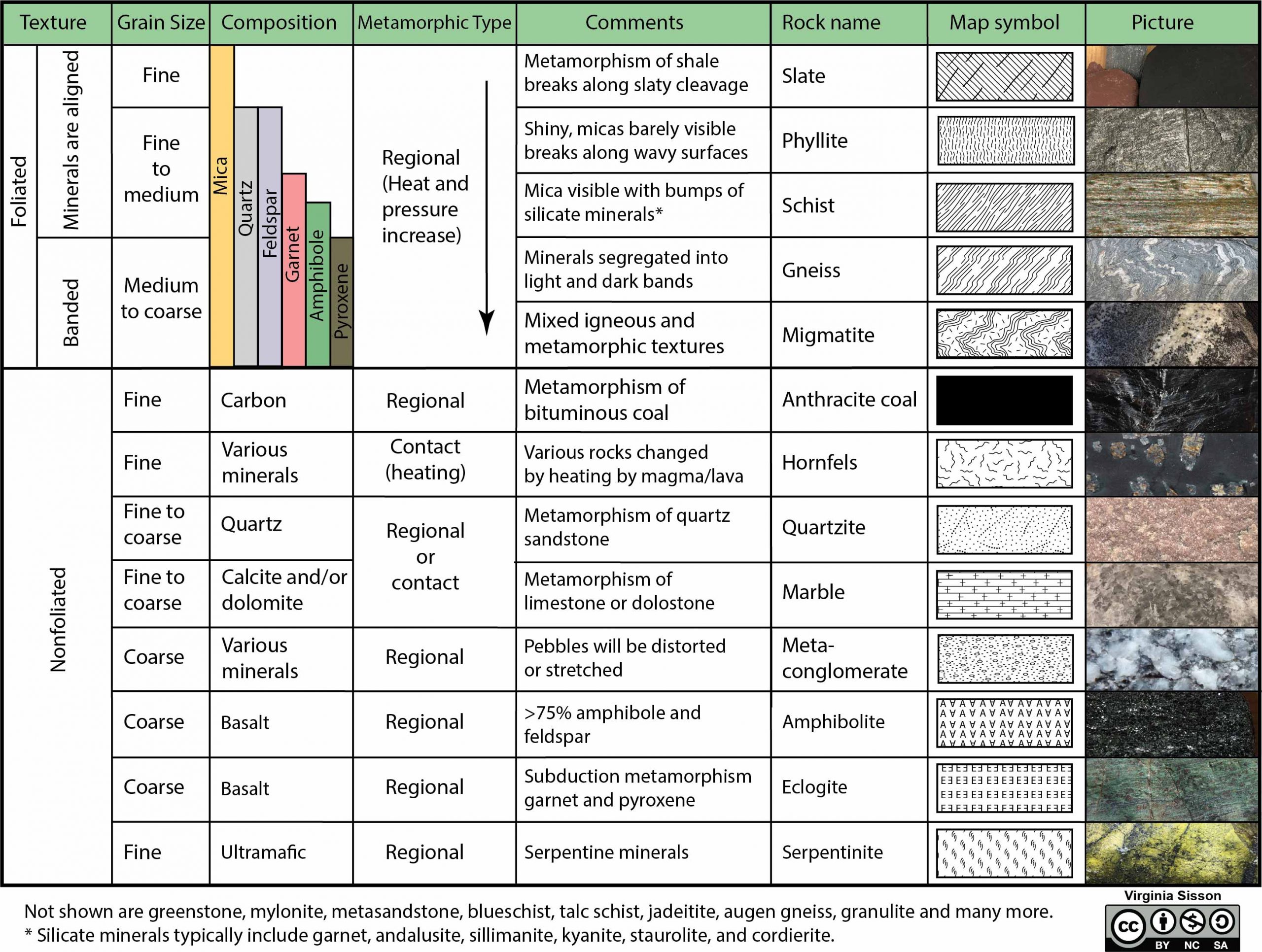
Noun. any rock derived from magma that was poured out or ejected at the Earth's surface. foliation. Noun. layering that occurs when pressure squeezes flat or long minerals so they become aligned. igneous rock. Noun. rock formed by the cooling of magma or lava. intrusive igneous rock.
Presents the three major rock types and the processes that lead to their formation in the rock cycle. %. Progress. MEMORY METER. This indicates how strong in your memory this concept is. Practice. Preview. Assign Practice. Progress.
Describe the rock layers shown in Diagram A and any forces acting on the rock. Diagram A shows a section of rock that contains three different layers. All layers are parallel and are equal in thickness. There are no forces being exerted on the rock layers. Contrast the plate movements that cause the stresses in Diagrams B and C. The compression in diagram B occurs when one plate pushes against ...
Geography, 22.10.2020 21:01, limelight11 Describe the rock layers shown in Diagram A and any forces acting on the rock.
The arrows also show that the forces are acting in opposite directions. ... but the rock doesn't move. Draw a force diagram that shows how the forces work as you are pushing on the rock. 3. A strong adult pulls a desk to the right. At the same time, a small ... a force diagram, and describe how the forces act on the apple to make it fall.
The oldest rock layers are at the bottom and the newest layers are at the top. We can tell about the Earth's history by looking at the different layers. The upper layers, those that are closest to the surface of the Earth, are the newest layers to be laid down. Layers below are older.
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
Answer: 3 📌📌📌 question Describe the rock layers shown in diagram a and any forces acting on the rock. - the answers to e-studyassistants.com
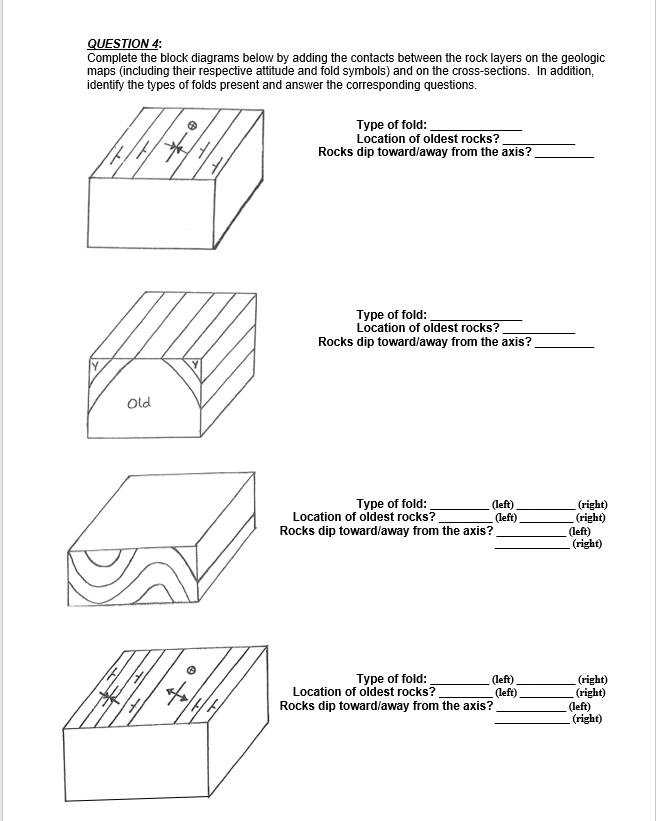
Flexural folds form when layers slip as stratified rocks are bent. This results in the layers maintaining their thickness as they bend and slide over one another. These are generally formed due to compressional stresses acting from either side. Flow folds form when rocks are very ductile and flow like a fluid. Different parts of the fold are ...
3 answers1) No, because shearing causes strike-slip faults or normal faults are caused by tension. 2) Diagram A shows a section of rock that contains three different ...
Layla drew a diagram of forces acting on the rock in Earth's crust. She drew arrows pointing inwards, representing forces pressing on the rock. Which formation could this diagram represent? A. A mid- ocean rift B. a transform fault <-----C. A fold mountain D. A rift valley
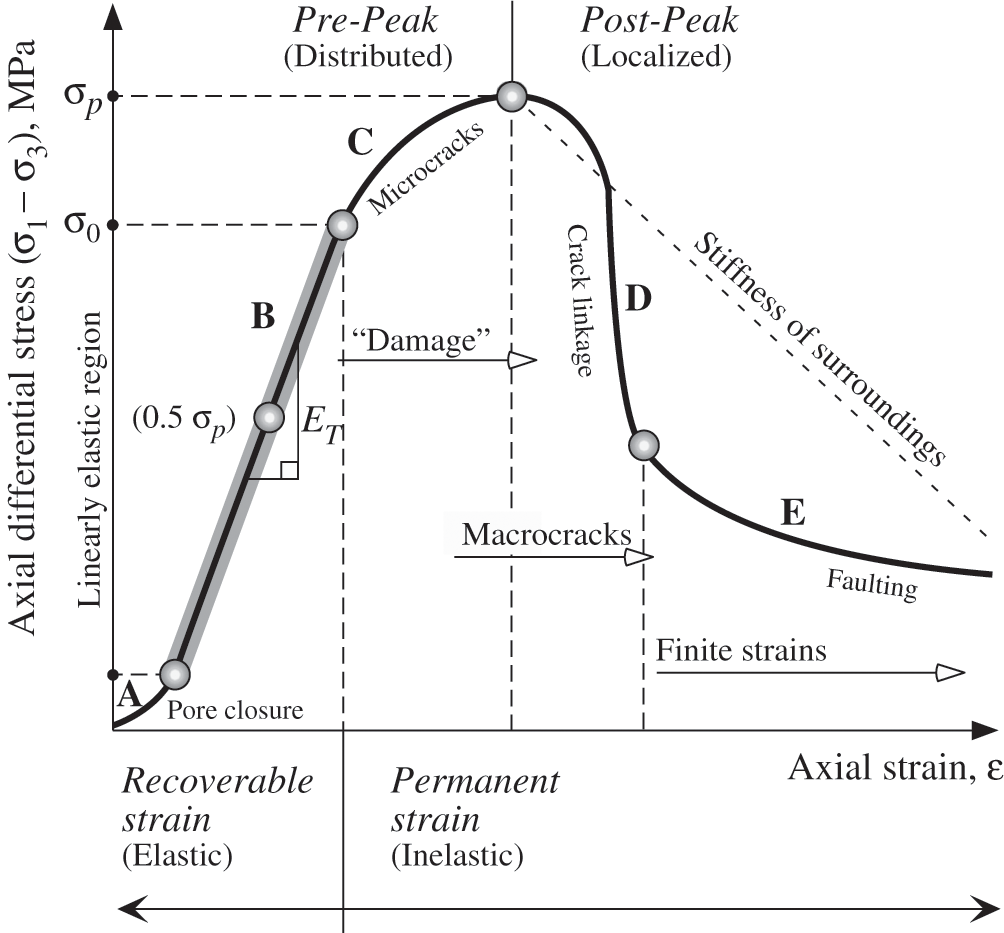
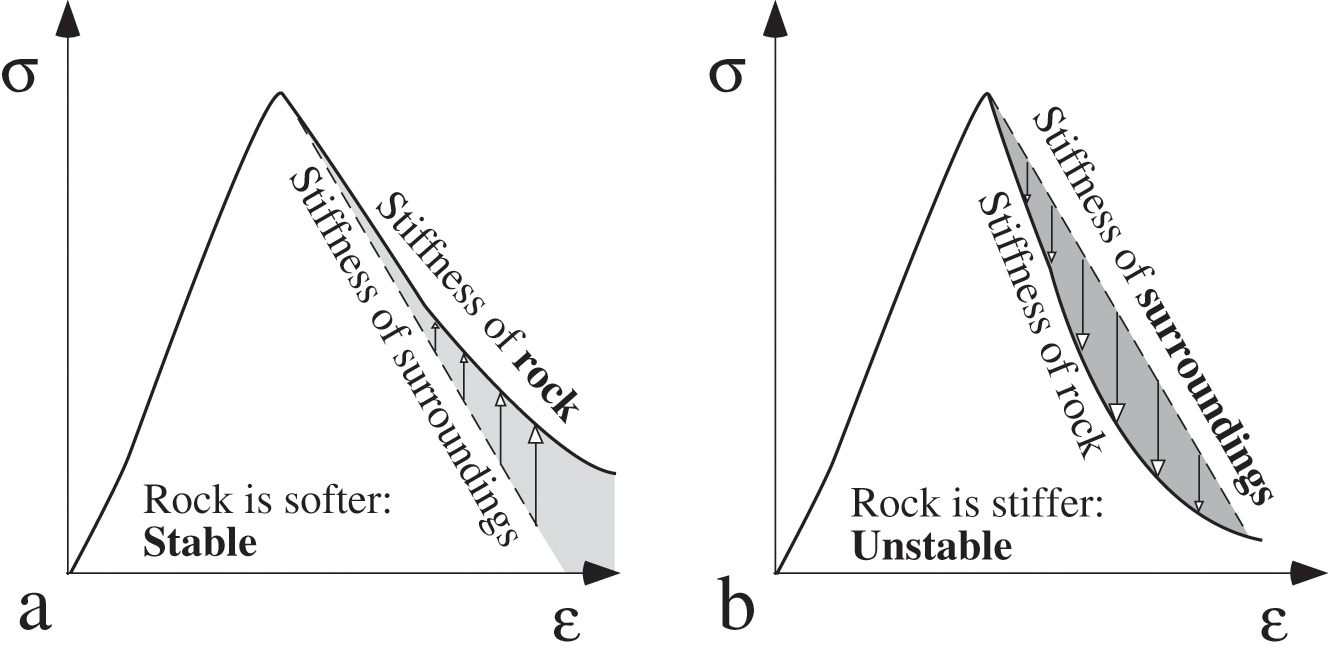
Stages of Rock Deformation. As rocks are stressed, they go through stages of deformation. At first, the rock is strained enough that its shape or size may change, but the change is reversible.
another. This does not mean that rocks move through the rock cycle in a particular order. As the illustration shows on page 507, a rock at any point in the cycle can change in two or three different ways. Like all cycles, the rock cycle has no beginning or ending but goes on continually. Rock Types The three types of rocks are classified by how ...
Describe the rock layers shown in Diagram A and any forces acting on the rock. Describe the rock layers shown in Diagram A and any forces acting on the rock. Post navigation. Previous Post. Previous If you will add a 1/2 teaspoon of sugar in 2 tablespoon of water and stir and continually add another. Next Post.
We can also better understand rock structures if we consider the orientations of the stresses acting on a body (Figure 7.4).For example, tension occurs where the stresses point away from one another and tend to pull the rock body apart. In con-trast, compression tends to press a body of rocks together.Three distinct types of
Describe the rock layers shown in Diagram A and any forces acting on the rock. Related Question & Answers. When rock fragments get compressed and hardened ...
Describe the rock layers shown in Diagram A and any forces acting on the rock. 62. In diagram B, which type of fault will form if the stress force continues? Explain. 63. What caused the rock layers to take on the shape shown in diagram C? 64. Contrast the plate movements that cause the stresses in diagrams B and C.
Rock 3 is from the Swakane Biotite _____. (Fill in the blank with the rock type you identified. Hint: Depending on your specific rock sample, there are two possible names for this type of rock. The official name of this rock is based on its dark and light layers and high metamorphic grade, rather than its micaceous nature.)
the compressional forces lead to the bending of rock layers and thus lead to the formation of fold mountains. In them the rock strata primarily of sedimentary rocks get folded, into wave like structure. This process of bending, sometimes warping and twisting of rock strata is referred to as their folding.
🔴 Answer: 2 🔴 on a question Describe the rock layers shown in Diagram A and any forces acting on the rock. - the answers to ihomeworkhelpers.com





















0 Response to "40 describe the rock layers shown in diagram a and any forces acting on the rock."
Post a Comment