39 mri pulse sequence diagram
Nov 29, 2021 — An MRI pulse sequence is a programmed set of changing magnetic gradients. Each sequence will have a number of parameters, and multiple ...
density weighting etc.), the pulse sequence parameters can be changed. Fig.1 shows the block diagram of the MRI scanner with pulse sequence generator. The signal received from the coils is given to the ADC for further processing during read out gradient. According to the received signal phase and frequency, the k
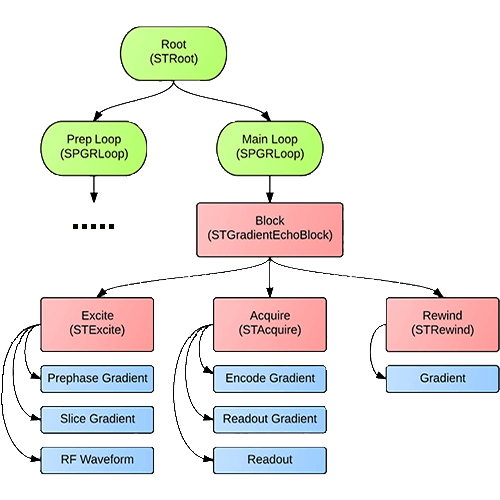
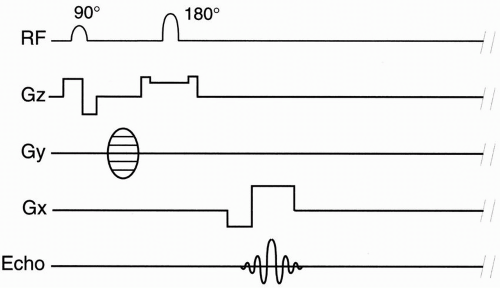
A pulse sequence diagram (PSD)illustrates the sequence of events that occur during magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It is a timing diagram showing the radio frequency (RF) pulses, gradients, and echoes.
Mri pulse sequence diagram
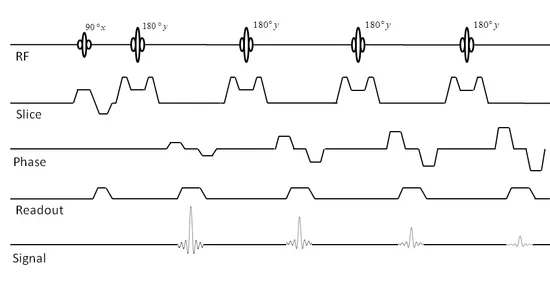
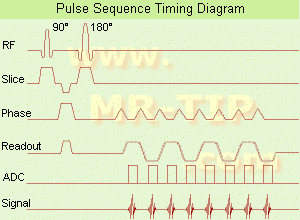
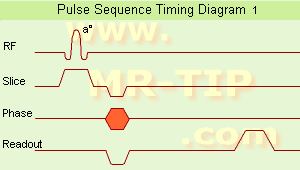
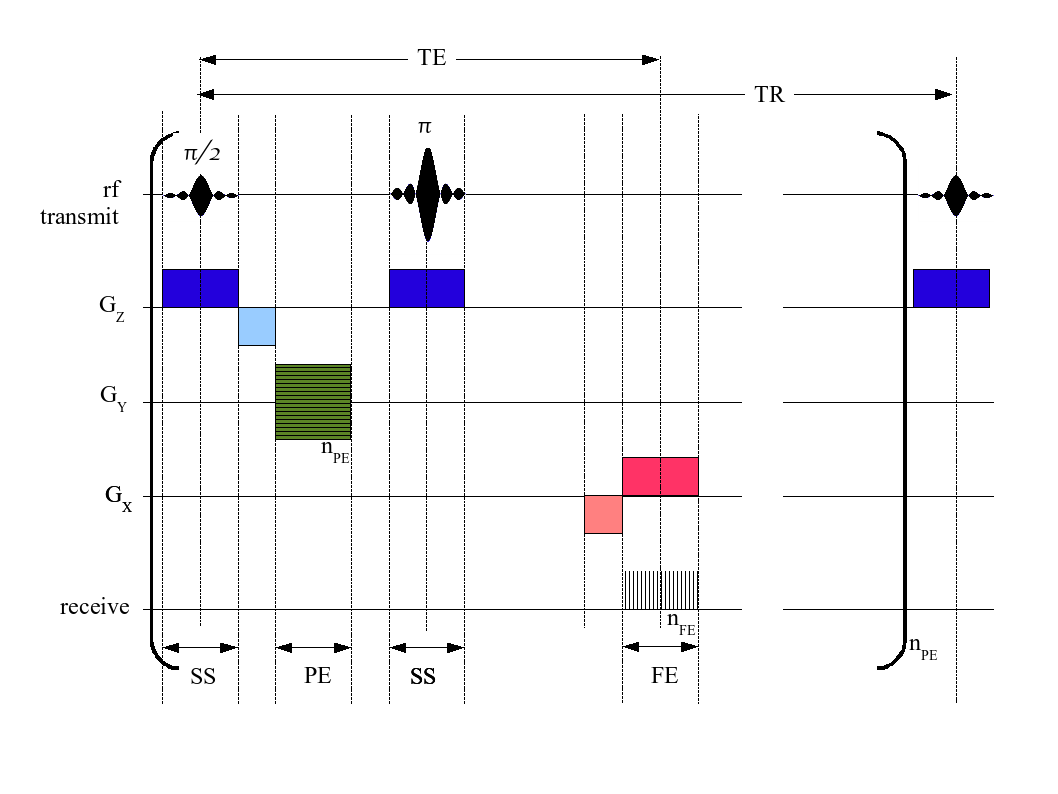
The timing diagram for an imaging sequence has entries for the radio frequency, magnetic field gradients, and signal as a function of time. The simplest FT imaging sequence contains a 90° slice selective pulse, a slice selection gradient pulse, a phase encoding gradient pulse, a frequency encoding gradient pulse, and a signal.
MRI Consultant 2 . Pulse Sequence Design Made Easier… A pulse sequence is a timing diagram designed with a series of RF pulses, gradients switching, and signal readout used in MR image formation. 3 . Pulse sequence components
Pulse sequences MRI. 78 terms. MRI Review Questions Pg 248-284. 64 terms. MRI PULSE SEQUENCES- ARRT REVIEW. 77 terms. Chapter 2 - MRI in practice. OTHER SETS BY THIS CREATOR. ... Start studying Pulse Sequence Diagrams. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Home Browse. Browse. Languages.
Mri pulse sequence diagram.
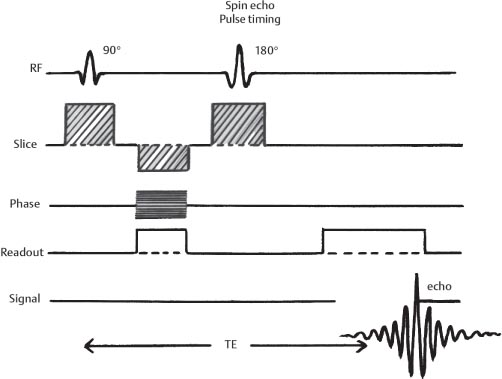
We can draw a diagram of the pulse sequence: Simplified pulse diagram of the spin echo sequence. The top line shows the radiofrequency pulses sent from the scanner, while the middle line shows the MR signal. Note the free induction decay right after the 90-degree pulse and the spin echo at time TE.
Citation, DOI and article data Spin-echo pulse sequences are one of the earliest developed and still widely used (in the form of fast spin-echo) of all MRI pulse sequences. The pulse sequence timing can be adjusted to give T1-weighted, proton density, and T2-weighted images.
Download scientific diagram | (a): Pulse sequence diagram for ... matrix. from publication: Multichannel Compressive Sensing MRI Using Noiselet Encoding ...
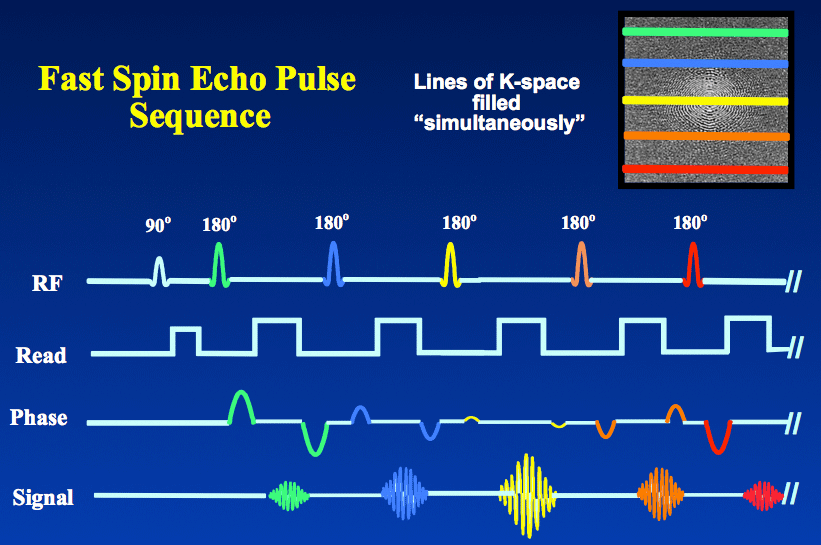
e-MRI Sequences . The spin echo sequence is made up of a series of events : 90° pulse - 180° rephasing pulse at TE/2 - signal reading at TE. This series is repeated at each time interval TR (Repetition time). With each repetition, a k-space line is filled, thanks to a different phase encoding.
An MRI pulse sequence is a programmed set of changing magnetic gradients. Each sequence will have a number of parameters, and multiple sequences grouped together into an MRI protocol. Parameters A pulse sequence is generally defined by multiple parameters, including: time to echo (TE) time to repetition (TR) flip angle field of view and matrix size
Applying a pulse - B1 B0 Mz B1 z-axis Mxy x-y plane Resultant magnetic field on the voxel α The longer the RF pulse is applied, and the stronger it is, the bigger the deflection of the net magnetic field, that is, the bigger the angle α. It can reach 90, or even 180 degrees. The bigger α, the longer it takes to recover when the RF is ...
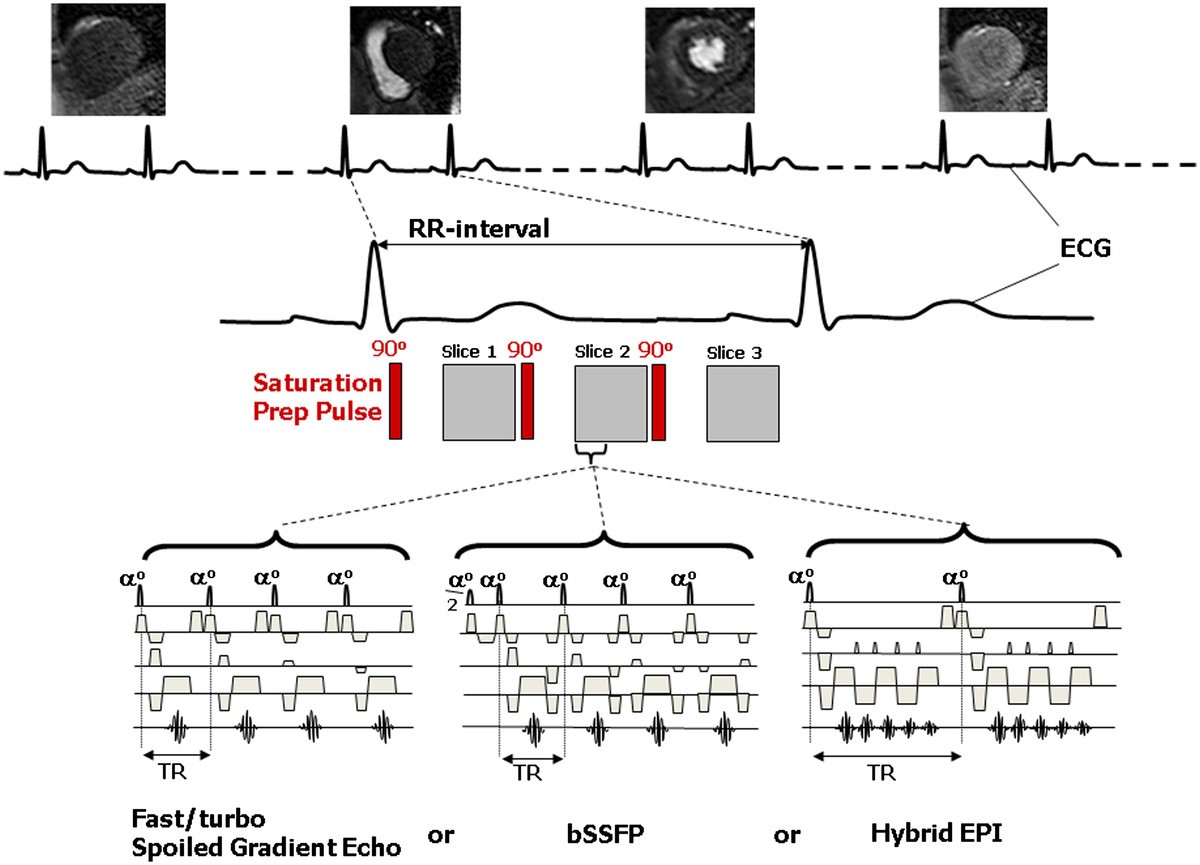
Pulse sequences are computer programs that control all hardware aspects of the MRI measurement process. Usual to describe pulse sequences, is to list the repetition time (TR), the echo time (TE), if using inversion recovery, the inversion time (TI) with all times given in milliseconds, and in case of a gradient echo sequence, the flip angle.
The block diagram of a typical MRI system with the components, pulse sequence and image display highlighted. When an animal, human or tissue sample is placed in a magnetic field (B 0 ), the ...
A pulse sequence is a timing diagram designed with a series of RF pulses, gradients switching, and signal readout used in MR image formation. 3 Pulse sequence components Pulse Sequences generally have the following characteristics: An RF line characterizing RF Pulse applications Gradients switching to encode the volume for spatial localization
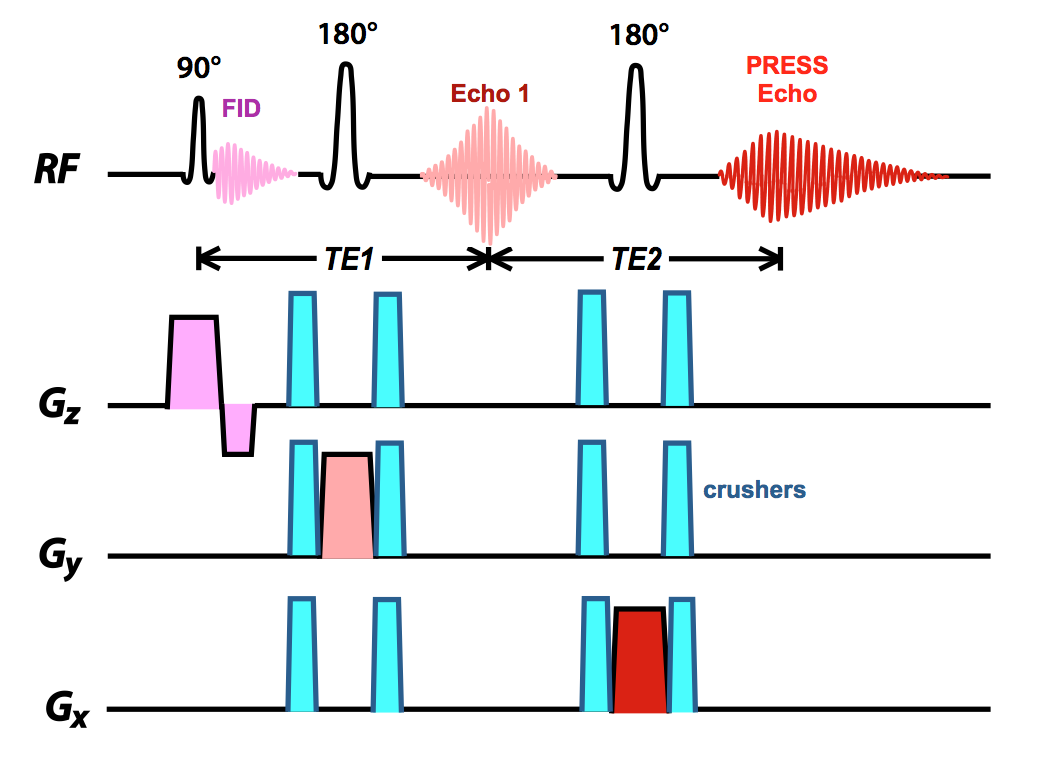
A pulse sequence diagram for a spin-echo imaging sequence showing the waveforms applied on the radiofrequency, the three channels for the orthogonal magnetic field gradients, and the receiver channel of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner. The activity along the gradient and radiofrequency "channels" of the scanner is shown in separate rows.
Section 1: Introduction to Pulse Sequences (8:05) Section 2: Overview of Timing Diagrams (15:46) Section 3: Types of Pulse Sequences (34:55) Section 4: History of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (16:40) MRI Vendor Acronyms for Pulse Sequences. Slides: Pulse Sequence Design. Week 5: Test (20 Questions)
(SE) The most common pulse sequence used in MR imaging is based of the detection of a spin or Hahn echo. It uses 90° radio frequency pulses to excite the magnetization and one or more 180° pulses to refocus the spins to generate signal echoes named spin echoes (SE).
Pulse Sequences. Here we cover the formation of the MR signal along with the four most commonly used pulse sequences. Take me to the first Q&A!
Pulse Sequence •Pulse sequence shows the timing of RF pulses and gradients •Determines the type of image •T1, T2, DWI •Some qualities of pulse sequences have special names •Inversion Recovery - 180 pulse before tip pulse •Spin Echo - 180 pulse after tip pulse (Prince)
@JP-Ellis MRI pulse sequence are diagrams used in magnetic resonance imaging. I didn't explained it because I think that who knows how to draw them also knows what they are. I'm sorry for not having described it well. I edited the question adding an image as example. - Marta.
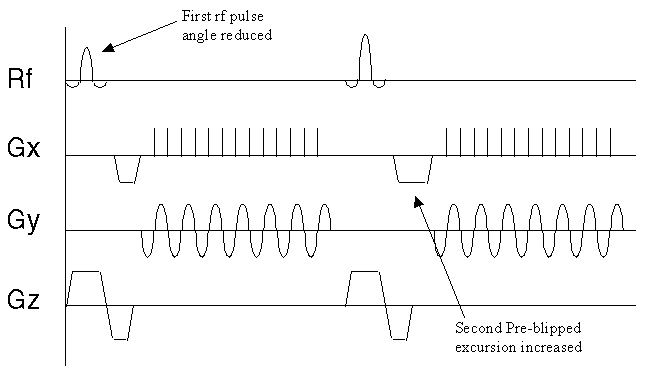
In the FSE/TSE pulse sequence diagram above you will note that each positive phase encode gradient is paired with a negative gradient immediately after the echo. This rewinds the phase at each step allowing each line of k-space to be traversed in the same direction. The refocusing pulses need not be exactly 180° .
Outline. Image Acquisition Review. Pulse Sequence Diagram. Sequence Classifications. •. By RF Pulse Usage. •. By Readout. Sequences with Novel Contrast ...48 pages
pulse sequence. A _____ is a set of specifically timed instructions to the magnet telling it how images. should look with regards to the tissue being sampled. gradient echo. The ____ sequence lacks a 180° refocusing RF pulse, making it more susceptible to magnetic field inhomogeneities. gradient echo.
The pulse sequence diagram is a schema of the timing of instructions sent to the RF generator and gradient amplifiers. There are only two fundamental types of MR pulse sequences: SE and GRE. All other MR sequences are variations of these, with different parameters added on.
An MRI pulse sequence is a programmed set of changing magnetic gradients. Each sequence will have a number of parameters, and multiple sequences are. The schematic figures of a pulse sequence timing diagram illustrate the steps of basic hardware activity that are incorporated into a pulse sequence.
Timing diagram for a spin echo type of pulse sequence. An MRI sequence in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a particular setting of pulse sequences and pulsed field gradients, resulting in a particular image appearance. The spin echo sequence is made up of a series of events: 90° pulse - ° rephasing pulse at TE/2 - signal reading at TE.
(SE) The most common pulse sequence used in MR imaging is based of the detection of a spin or Hahn echo. It uses 90° radio frequency pulses to excite the magnetization and one or more 180° pulses to refocus the spins to generate signal echoes named spin echoes (SE).
Timing diagram for an MRI spin echo pulse sequence. Graphical representation of a pulse sequence for a homonuclear NOESY experiment. The three bars represent three 90° pulses. An INEPT NMR pulse sequence for a heteronuclear experiment. The thin bar denotes a 90° pulse, while the thick bar denotes a 180° pulse.
In the 90-FID pulse sequence, net magnetization is rotated down into the X'Y' plane with a 90° pulse. The net magnetization vector begins to precess about the +Z axis. The magnitude of the vector also decays with time. A timing diagram is a multiple axis plot of some aspect of a pulse sequence versus time. A timing diagram for a 90-FID pulse ...
that are most commonly used to diagram pulse sequences (1-3) as well as the echoes detected, including the Hahn echo (with use of a spin-echo [SE] pulse sequence) and the gradient echo (GRE) (10). It is important to recognize these symbols, because they are invariably used to rep-resent TR and TE. TR is the time (usually measured in millisec-
















0 Response to "39 mri pulse sequence diagram"
Post a Comment