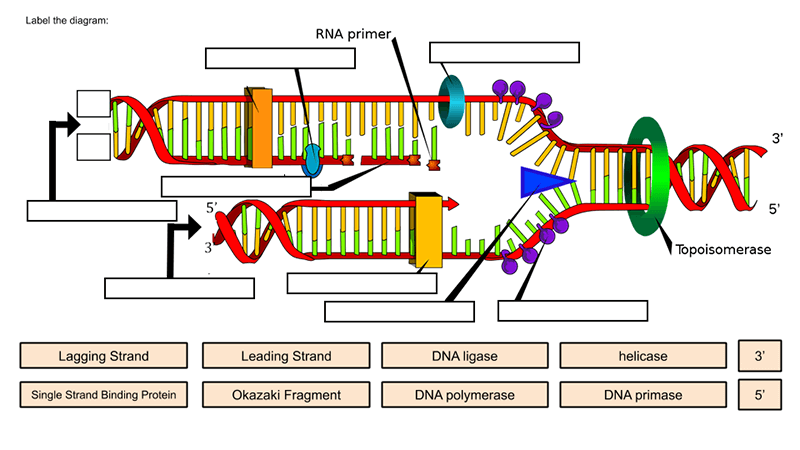
38 blank dna replication diagram
Helicase action in DNA replication. Enzymatic helicase action, such as unwinding nucleic acids is achieved through the lowering of the activation barrier of each specific action. The activation barrier is a result of various factors, and can be defined using the following equation, where = number of unwound ...
Structure of DNA. Before we jump into the process of replication, let us take a quick look at the structure of DNA. As we all know, DNA is the genetic code that helps our cells to develop and reproduce in a planned way. Because of which it is called the ‘Blueprint of Life’. DNA is the genetic material that defines cells in bodies. In order for a cell to duplicate and divide into its ...
This is the first, which looks at gene structure, expression, and regulation within the context of DNA structure and replication. The central dogma of. 0:27. molecular biology states that there is a sequential flow of information that ends with the generation of protein. Information cannot flow between proteins of actual protein to a nucleic acid.

Blank dna replication diagram
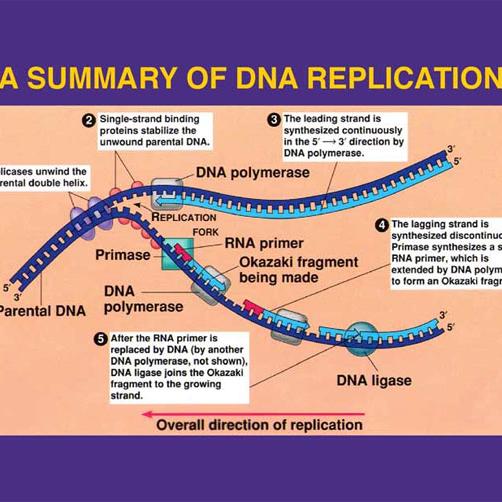
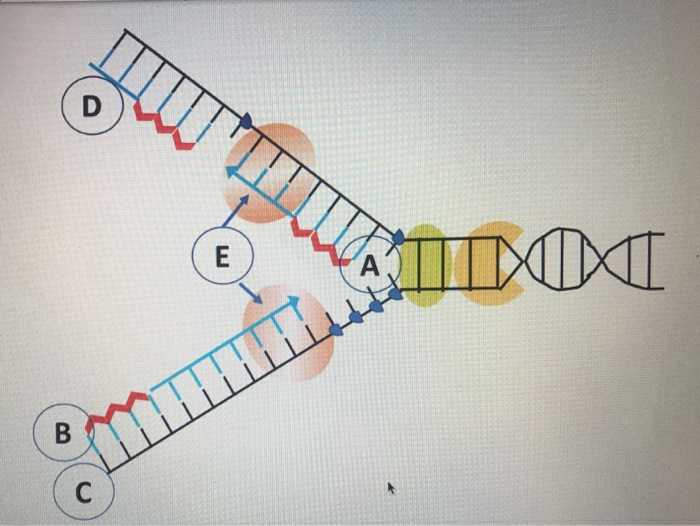
Diagram showing a replication bubble with replication forks on the left and the right of the origin of replication. The top parental DNA strand goes 5 prime to 3 prime and the bottom parental DNA strand goes 3 prime to 5 prime. At each replication fork, two DNA polymerases 3 are synthesizing two new daughter strands.
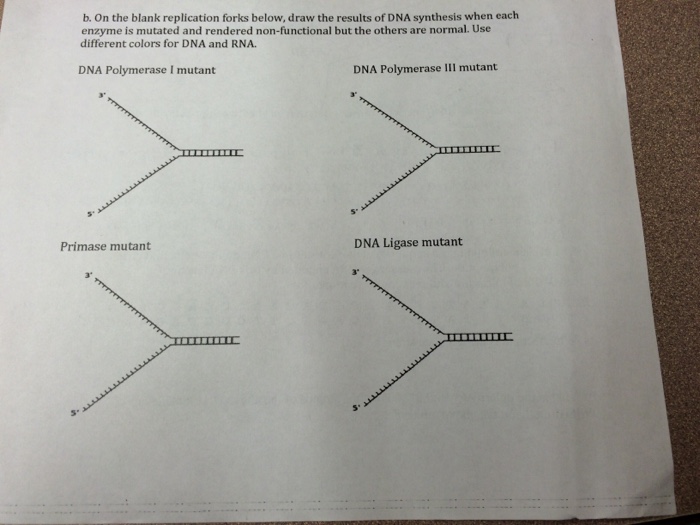
DNA replication would not occur without enzymes that catalyze various steps in the process. Enzymes that participate in the eukaryotic DNA replication process include: DNA helicase - unwinds and separates double stranded DNA as it moves along the DNA. It forms the replication fork by breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotide pairs in DNA.
3 Jan 2021 — The DNA replication process is semiconservative, which results in two ... Diagram showing 3 models of DNA replication. ... Fill in the Blank.
Blank dna replication diagram.
to separate the two DNA strands. As the DNA strands separate, a structure is created called the replication fork. The replication fork is the site at which DNA replication actually starts. Since DNA replication is bidirectional, that is it proceeds in both directions from the origin (Figure 3), there are actually two replication forks for each
This set of guided notes with biology doodles can be little anchor charts for your student to keep in their notebook! Using these pages, students can color, doodle, and make connections within the material as they takes notes in class. These 3 student pages include: * A page all about DNA Replication Basics (Semi-conservative model of replication) * A page all about Replication Enzymes
DNA Dna and Rna Webquest Flashcards Quizlet November 20th, 2018 - a specific sequence of three adjacent bases on a strand of DNA or RNA that provides genetic code information for a particular amino acid enzyme similarThe History of DNA Webquest Flashcards | Quizlet History Of Dna Webquest Worksheet Answers Written By Desain Rumah Sunday, December 1, 2019 Add …
DNA viruses The genome replication of most DNA viruses takes place in the cell's nucleus. If the cell has the appropriate receptor on its surface, these viruses enter the cell either by direct fusion with the cell membrane (e.g., herpesviruses) or—more …
DNA replication fork. RNA primer. Captions. The factual accuracy of this diagram or the file name is ...
21 Jul 2021 — The first step in DNA replication is to 'unzip' the double helix structure of the DNA? molecule. This is carried out by an enzyme? called ...
A replication fork is formed which serves as a template for replication. nucleotide 2. 14 Label the diagram at right using the following terms: DNA Before replication DNA polymerase Helicase New complimentary DNA strands Old template DNA strands Replicated DNA 15 What is the ultimate source of almost all mutations in an organisms' DNA?In DNA Interactive: Code, learn …
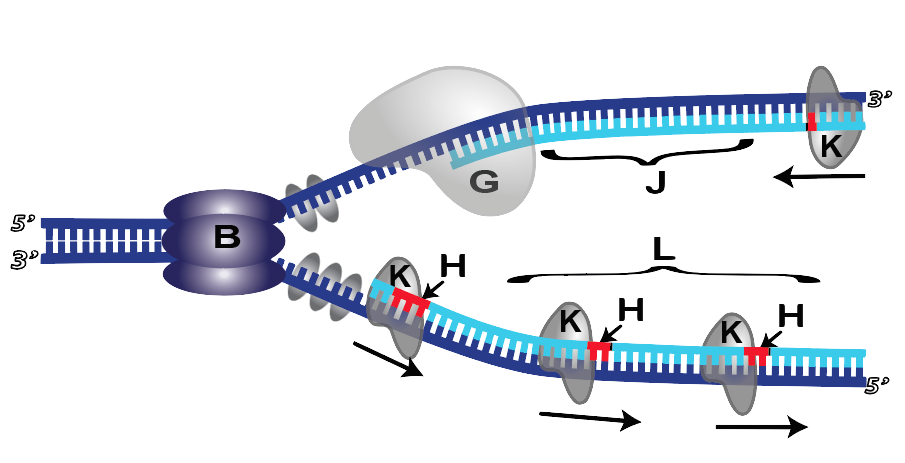
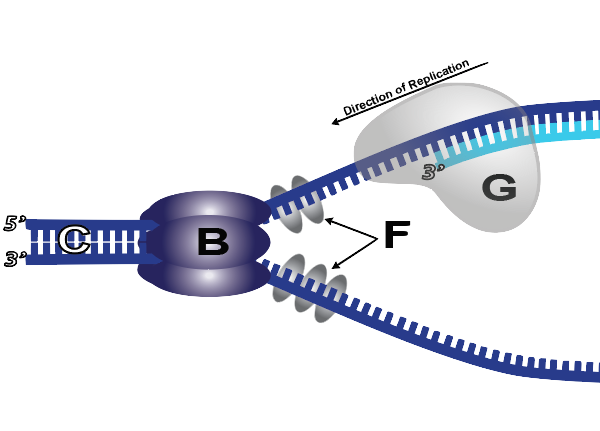
6.The diagram below shows a DNA molecule in the process of replication. Arrows show the direction of new DNA synthesis. a.Some of the enzymes and features are labeled, but some labels are incomplete or have been omitted.
DNA Replication. Printable Drawing. Notes - DNA Replication. Quizlet - DNA Replication.
(B) This schematic illustrates the two (more...) The synthesis of new DNA strands complementary to both strands of the parental molecule posed an important ...
DNA replication: ¥Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation ¥Occurs in S phase of cell cycle ¥Process of DNA duplicating itself ¥Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose the bases in each strand of DNA ¥Each unpaired nucleotide will attract a complementary nucleotide from the medium
3. The chart below lists several enzymes important in DNA replication. Put the numbers in the blanks to indicate the order in which these enzymes work during replication. If an enzyme is not involved in replication, put a zero in its blank. 3 Main DNA polymerase 4 Gap-filling DNA polymerase 2 Primase 1 Helicase 0 RNA polymerase 5 Ligase
In this diagram showing the replication of dna label the following terms. Basic features of dna replication: The structure of dna dna replication is said to be semi conservative because each strand acts as a template to construct the other half of the molecule. Draw neat and labelled diagram of replication fork.
DNA replication Stage one. The DNA is unwound and unzipped. The helix structure is unwound. Special molecules break the weak hydrogen bonds between bases, which are holding the two strands together.
–Helicase begins to unwind the DNA at the ORIGIN OF REPLICATION (a specific DNA nucleotide sequence) It’s common to only show one strands sequence of bases, since the other can be inferred. Helicase enzymes move in both directions from the Point of Origin, forming a REPLICATION BUBBLE. At either end of the replication bubble is a REPLICATION FORK, a Y-shaped region where the new strands of ...
a. a strand of DNA b. two complementary strands of DNA c. a strand of RNA d. a chain of amino acids . Use the diagram below for Questions 30-32 . 30) Structure X was made in the a. nucleus b. cytoplasm c. lysosome d. vacuole 31) The process represented in the diagram is most closely associated with the cell organelle known as the a. nucleolus b ...
The strand of DNA that contains the information used to make a new strand of DNA during DNA replication is called the blank strand. parent When two strands of DNA associate to form a double helix, the bases on opposite strands of DNA interact via hydrogen bonds.
DNA replication blank.svg. English: DNA replication or DNA synthesis is the process of copying a double-stranded DNA molecule. This process is paramount to all life as we know it. Date. 13 September 2009, 09:38 (UTC) Source. DNA_replication_en.svg. Author.
short segment of RNA used to initiate synthesis of a new strand of DNA during replication The primer synthesized by primase enzyme. DNA Polymerase on Leading Strand. synthesizes new DNA only in the 5' to 3' direction. Ligase. An enzyme that connects two fragments of DNA to make a single fragment. Lagging Strand . The strand in replication that is copied 3' to 5' as Okazaki fragments and then ...
Ib dna structure replication review key 2 6 2 7 7 1 from dna replication worksheet chapter 5 the structure and function of large biological molecules. Such as png jpg animated gifs pic art symbol blackandwhite pic etc. Step 1 of dna replication. Regardless of where dna replication occurs the basic process is the same.
Diagram 1. Label the side that is mitosis and meiosis. 2. Draw an arrow indicate DNA replication (S-stage). ... For each of the following statements write in the blank if it applies to mitosis or meiosis. 1. Makes 4 daughter cells _____ ... It is a set of DNA that is put together and all works together to give one big set of directions. The ...
Mechanism of DNA replication is the direct result of DNA double helical structure proposed by Watson and Crick. It is a complex multistep process involving many enzymes. 1. Initiation: It involves the origin of replication. Before the DNA synthesis begins, both the parental strands must unwind and separate permanently into single stranded state ...
The diagram in this worksheet shows the cycle for cellular respiration. Match the letter in the diagram with the label. What was made per glucose molecule. Cell respiration key diagrams atp structure 1. The student should fill in the blanks with the appropriate process in the cycle. What was the end molecule.
replication fork: the Y-shaped structure formed during the initiation of replication semiconservative replication: the method used to replicate DNA in which the double-stranded molecule is separated and each strand acts as a template for a new strand to be synthesized, so the resulting DNA molecules are composed of one new strand of nucleotides ...
Diagram of DNA Replication DNA Replication in Prokaryotes: DNA replication in prokaryotes is formed when an enzyme named helicase separates the DNA strands at the origin of replication. The DNA becomes highly coiled ahead of the fork of replication. The topoisomerase breaks DNA s phosphate backbone ahead of the replication fork.
In the diagram below, the plane drawn behind the peptide bond indicates the: H C Ca N H R O Ca ... replication of human DNA is that the 5'-triphosphate nucleotide ... Enter the appropriate letter in each blank. All items will be used once. 34. Match these molecules to …
DNA replication always begins at an origin of replication. ... The diagram below shows a replication bubble with synthesis of the leading and lagging strands on both sides of the bubble. ... Match the words in the left-hand column with the appropriate blank in the sentences in the right-hand column. 1.
Match each statement below with the appropriate letter from the replication fork diagram on the right. One letter per blank, but you may use the letters more ...
It stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is called a nucleic acid because it was first found in the nucleus. We now know that DNA is also found in organelles, the mitochondria and chloroplasts, though it is the DNA in the nucleus that actually controls the cell's workings. In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick established the structure of DNA.
Base-Pairing Underlies DNA Replication and DNA Repair. As discussed briefly in Chapter 1, DNA templating is the process in which the nucleotide sequence of a DNA strand (or selected portions of a DNA strand) is copied by complementary base-pairing (A with T, and G with C) into a complementary DNA sequence ().This process entails the recognition of each nucleotide in the DNA template strand by ...
DNA and Replication: Quiz, Homework or Study Guide. This document consists of 50 fill in the blank questions and 5 short answer questions on the structure and function of DNA and replication. Both printable and digital versions are included. The questions range from very basic to advanced.
DNA Structure & Replication How is the genetic information stored and copied? Why? DNA is the molecule of heredity. It contains the genetic blueprint for life. For organisms to grow and repair damaged cells, each cell must be capable of accurately copying itself. So how does the structure of DNA allow it to copy itself so accurately that cells can then replicate during cell division? Model 1 ...
____ 45. DNA replication results in two DNA molecules, a. each with two new strands. b. one with two new strands and the other with two original strands. c. each with one new strand and one original strand. d. each with two original strands. ____ 46. During DNA replication, a DNA strand that has the bases CTAGGT produces a strand with the bases ...
Matthew Meselson (1930-) and Franklin Stahl (1929-) devised an experiment in 1958 to test which of these models correctly represents DNA replication (Figure 11.5).They grew E. coli for several generations in a medium containing a "heavy" isotope of nitrogen (15 N) that was incorporated into nitrogenous bases and, eventually, into the DNA. This labeled the parental DNA.
This quiz on the structure of DNA and replication will keep your students studying in the days leading up to the unit exam. The document (BOTH printable and digital versions included) consists of a 2 page quiz containing 34 questions.Question types include fill in the blanks and short answer questions.
Quiz: DNA Replication (with some DNA structure review). The quiz below uses a combination of diagrams, multiple choice, and fill-in-the blanks to help you ...
Diagram showing 3 models of DNA replication. In the conservative model the ... There were three models suggested for DNA replication. ... Fill in the Blank.
Translesion synthesis employs an alternate DNA polymerase that can substitute for a DNA polymerase that has stalled at the replication fork due to DNA damage. Specialized DNA polymerases, that are active in regions with DNA damage, have active sites that can accommodate fluctuations in DNA topography that enable them to bypass the lesions and …
Label the diagram below with the following labels: Anaphase Interphase Mitosis . Cell division (M Phase) Interphase Prophase . Cytokinesis Interphase S-DNA replication . G1 - cell grows Metaphase Telophase . G2 - prepares for mitosis . Then on the diagram, lightly color the G1 phase . BLUE, the S phase YELLOW,
Working with Molecular Genetics Chapter 5, DNA Replication I, v2 5 Fig. 5.3. Diagram of the addition of nucleotides in a new strand of DNA during semiconservative replication. The parental DNA strands are shown in black and the new DNA strands and deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates are in blue. The DNA strands are


















0 Response to "38 blank dna replication diagram"
Post a Comment