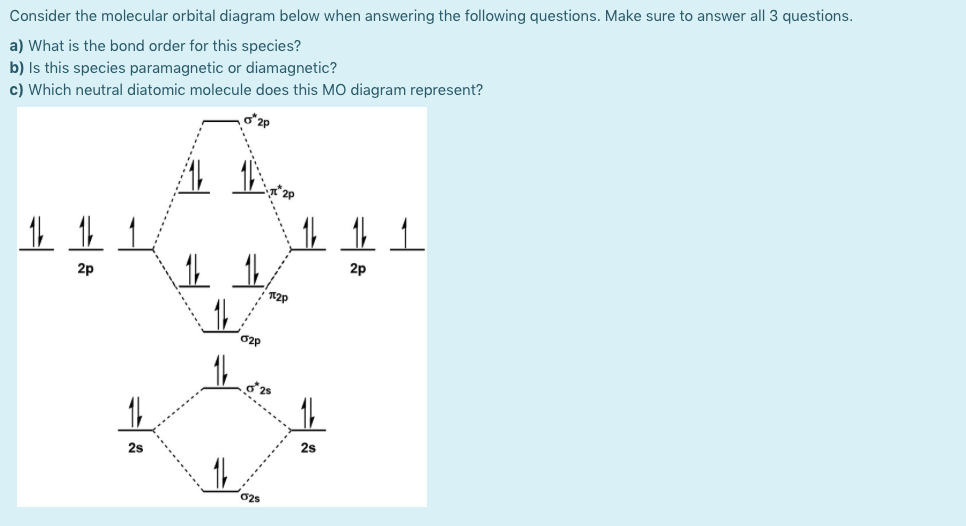
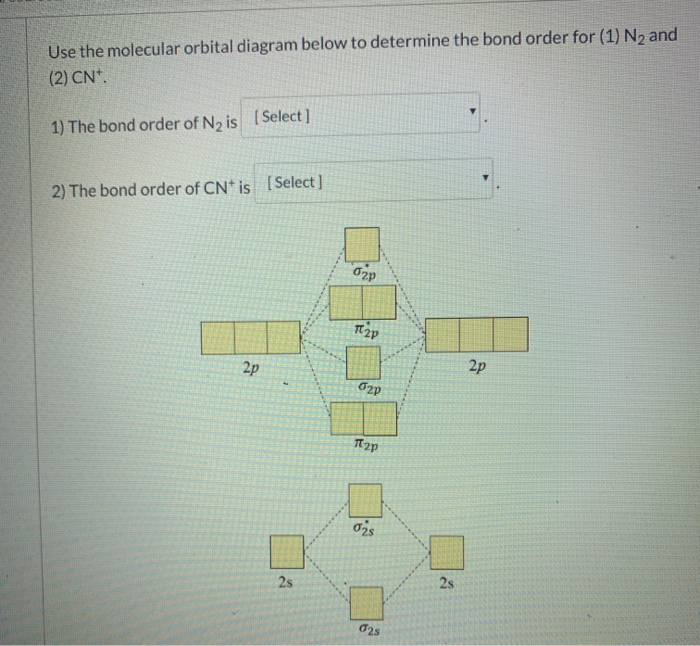
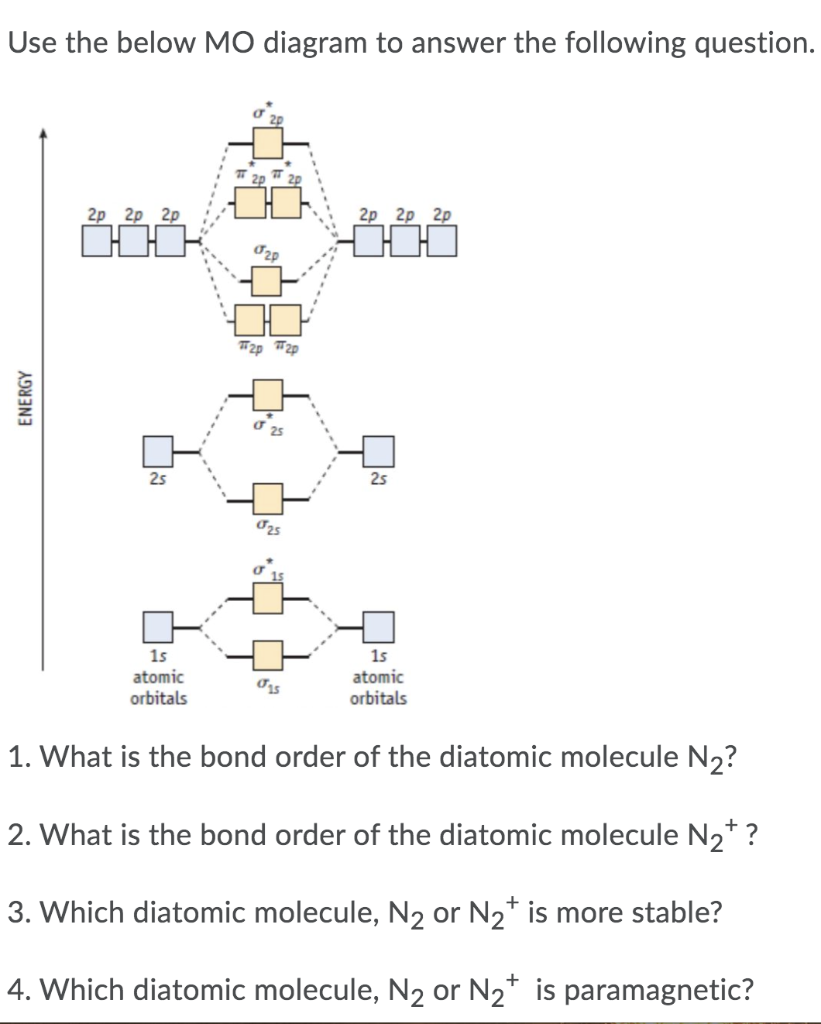
37 use the mo diagram provided below to answer the following questions: what is the bond order for n2?
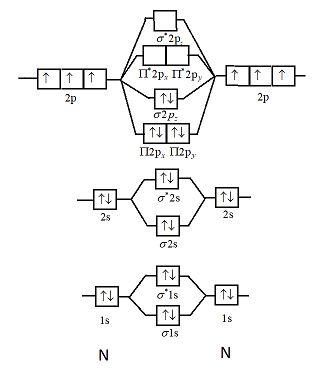
Show activity on this post. I have been taught that the MO diagram is different for molecules with 14 or less electrons than the one used for molecules with 15 or more electrons. For N X 2 the orbitals in increasing energy are: σ 1 s < σ 1 s ∗ < σ 2 s < σ 2 s ∗ < π 2 p x, π 2 p y < σ 2 p z < π 2 p x ∗, π 2 p y ∗ < σ 2 p z ∗ ...
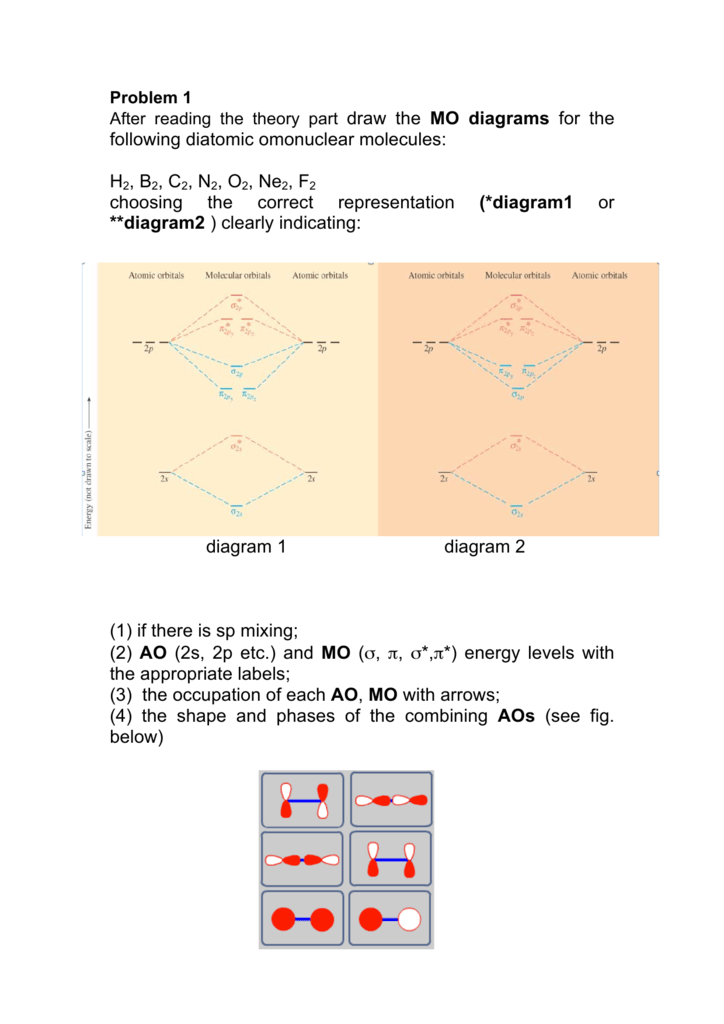
Answer the following questions, which pertain to binary compounds. (a) In the box provided below, draw a complete Lewis electron-dot diagram for the IF 3 molecule. One point is earned for a correct Lewis diagram (can be done with dots or lines).
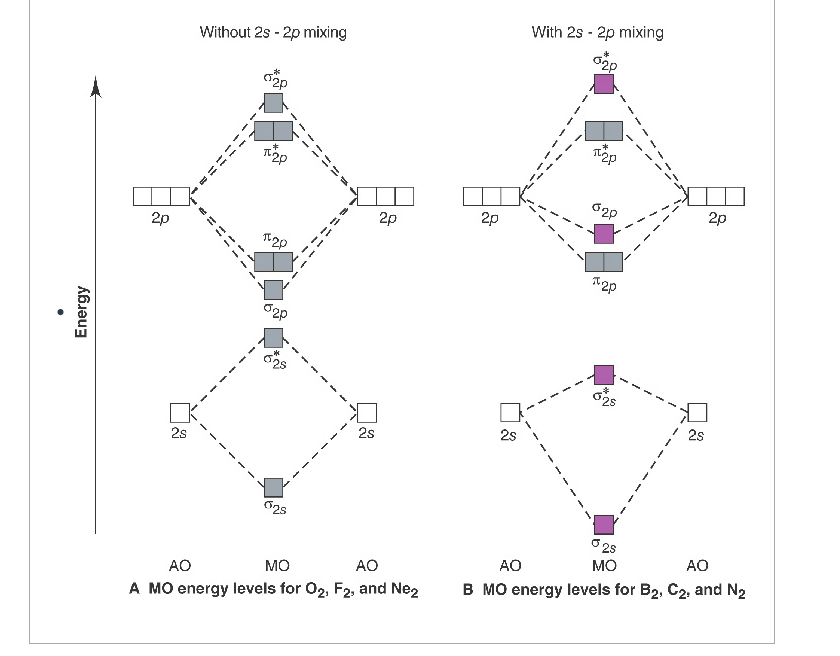
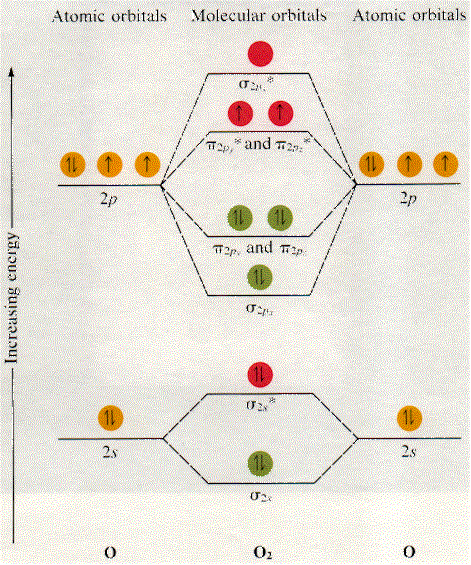
• The following diagram shows the molecular orbital energy level diagrams for the valence electrons in the homonuclear diatomic molecules C 2, N 2 and O 2. Complete the diagram by filling in the remaining valence electrons for each molecule and determining its bond order. Marks 6 Bond order: 2 3 2
Use the mo diagram provided below to answer the following questions: what is the bond order for n2?
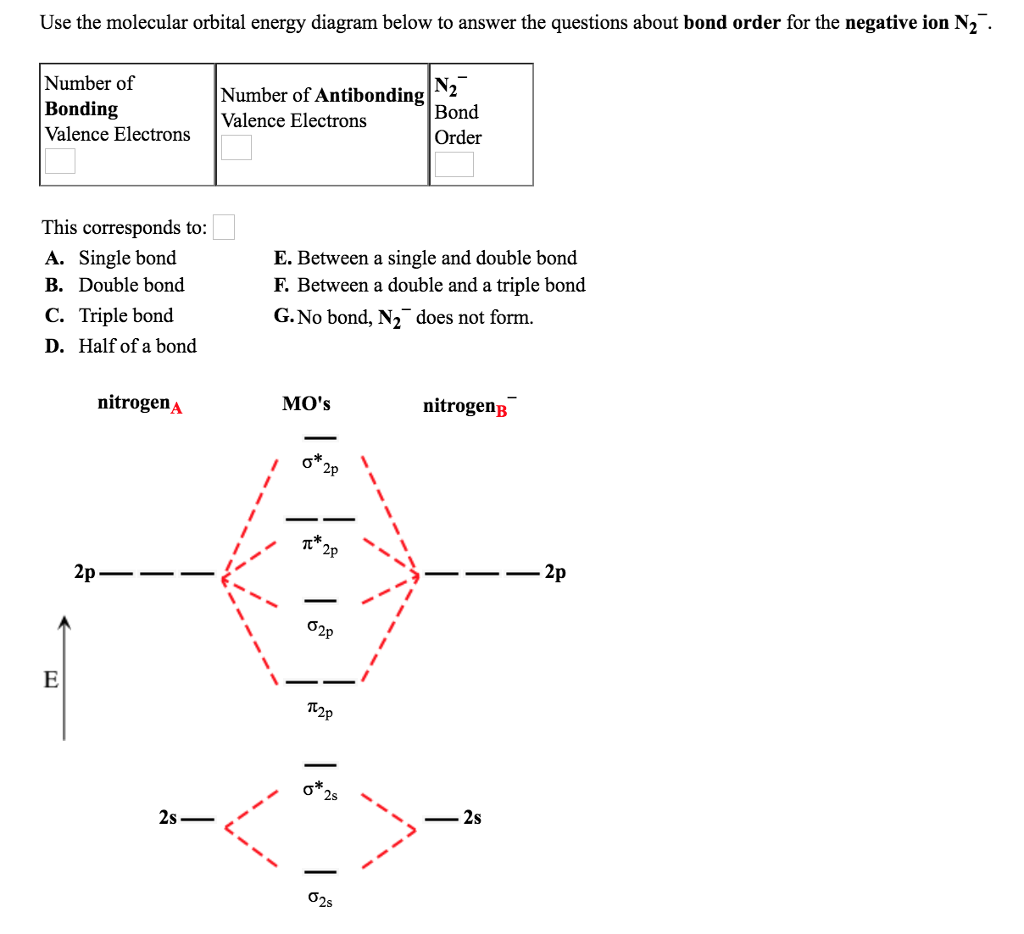
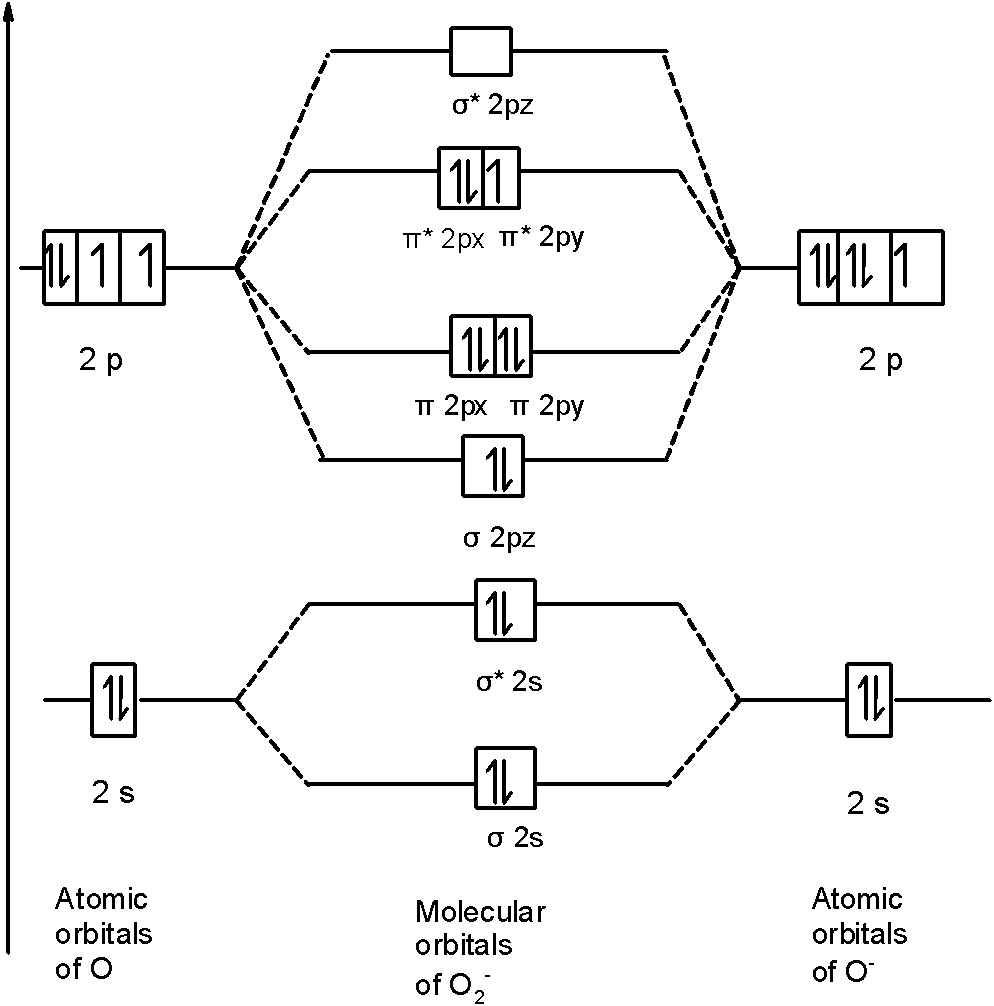
Use the MO energy level diagram below to identify which one of the following statements is NOT correct. (Use only valence electrons) The superoxide has a stronger bond than the peroxide The superoxide has a shorter bond than the peroxide The bond order of the peroxide is 1 Oxygen, O2, has a longer bond than either of these oxides
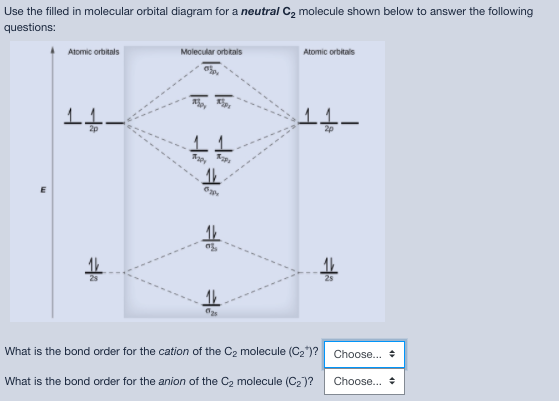
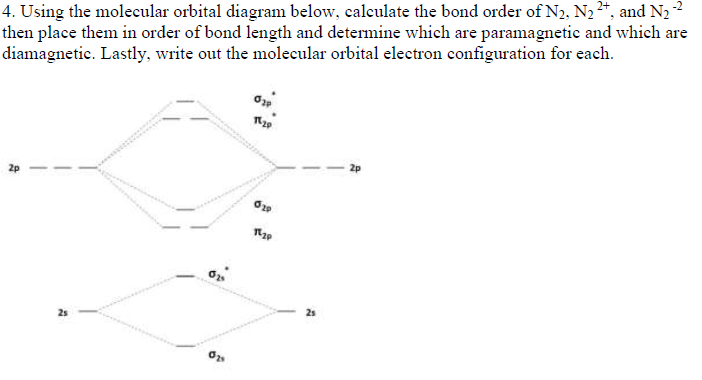
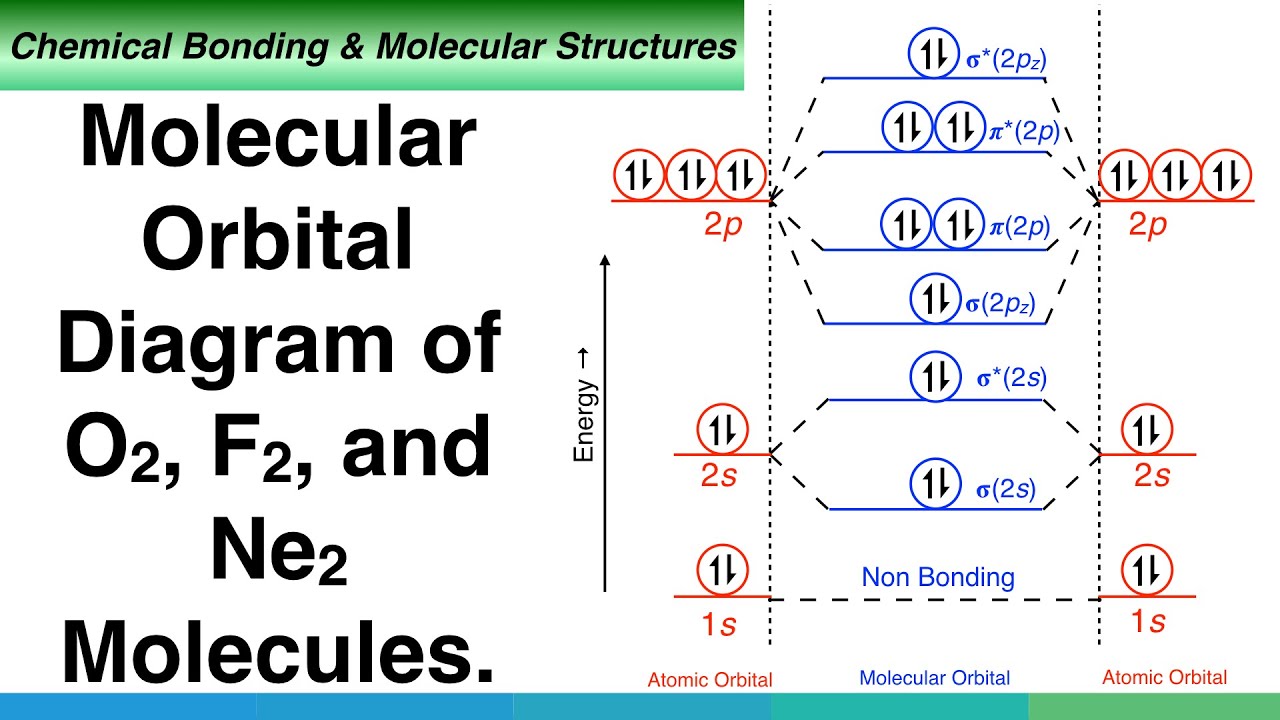
Use the MO diagram provided below to answer the following questions: What is the bond order for N2? Is N2 paramagnetic or diamagnetic? What is the bond order for N2-? Is N2- paramagnetic or diamagnetic? What is the bond order for N2+? Is N2+ paramagnetic or diamagnetic? Which of the three has the longest bond? Which of the three has the ...
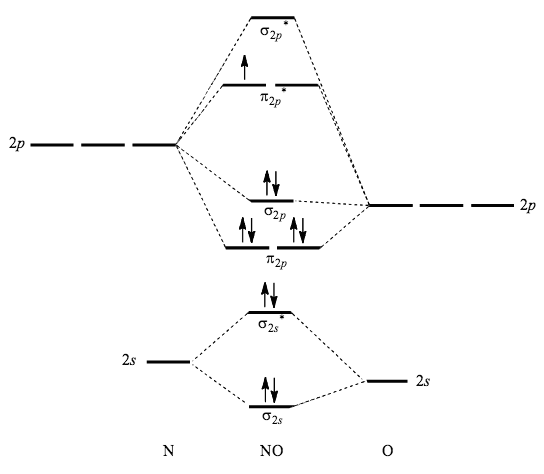
The MO diagram for "NO" is as follows (Miessler et al., Answer Key): (The original was this; I added the orbital depictions and symmetry labels. For further discussion on the orbital energy ordering being "N"_2-like, see here and comments.) Quick overview of what the labels correspond to what MOs: 1a_1 is the sigma_(2s) bonding MO. 2a_1 is the sigma_(2s)^"*" antibonding MO. 1b_1 is the pi_(2p ...
Use the mo diagram provided below to answer the following questions: what is the bond order for n2?.
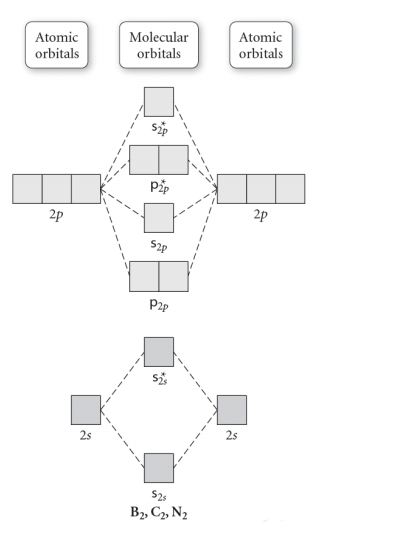
draw the molecular orbital diagram for B2. the number of electrons in the pi2p molecular orbital is. 1. ... what is the bond order for N2. 3. what is the bond order for O2 ... pi molecular orbital system extending above the plane of the,sigma system of the carbonate ion and an antibonding pi molecular orbital system extending below the plane of ...
Jun 28, 2019 · The following four spheres represent an mg atom an mg2 ion a s atom and a s2 ion not necessarily in that order. Use the mo diagram provided below to answer the following questions. The following diagram shows the molecular orbital energy level diagrams for the. B for n2 the mo diagram is. Chem1101 2014 j 5 june 2014. Sodium and bromine b.
Write the molecular orbital diagram of N2+ and calculate their bond order why nitrogen have different structure of molecular orbital theory An atomic orbital is monocentric while a molecular orbital is polycentric. Explain
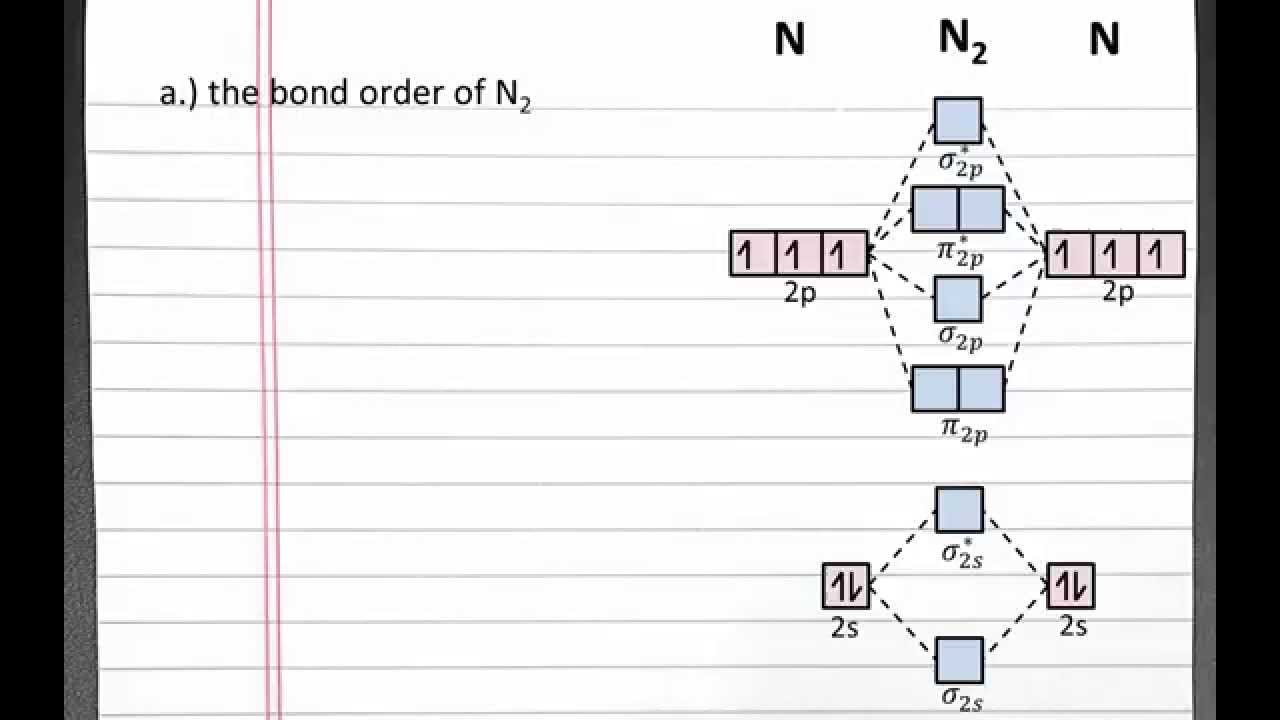
Answer (1 of 2): Let me explain the molecular orbital diagram of N2 using its diagram. one atom of nitrogen has 7 electrons so a N2 molecule will have 14 electrons so first 2 electrons go in 1s sigma bond next 2 in 1s sigma anti bond orbital next 2 in 2s sigma bond orbital next 2 in 2s sigma...
Answer (1 of 8): CN+ is a diatomic molecule, so to answer the question you need to start with two pieces of information: 1) the molecular orbital energy diagram for a diatomic molecule, and 2) the number of electrons in the molecule. CN+ has 12 electrons, 6 from C, 7from N, minus one for the posi...
Check all that apply. a) Li2^+ b) Li2^-. Q. Use molecular orbital theory to predict whether or not each of the following molecules or ions should exist in a relatively stable form. Drag the... Q. Arrange the following in order of decreasing bond energy. A blank molecular orbital diagram (Figure 1) has been provided to help you.
In this case, the difference is the H-X-H bond angle which decreases from o to 90 o Molecular Orbital Theory - . Item 2: Part A Complete the MO energy diagram for the N2+ ion by dragging the electrons Electron with spin up., ↑, ↑↓, ↓ in the figure given below.M.O. diagram for N2+Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia
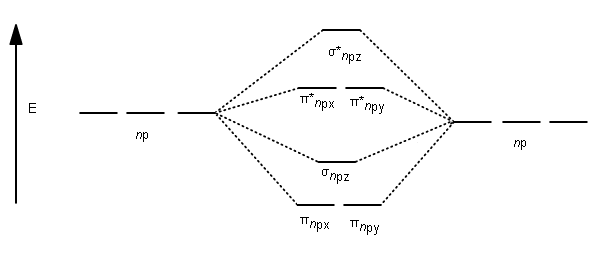
4 Lecture 2 Pi bond (π): bonding molecular orbital -The bonding electron density lies above and below, or in front and in back of the bonding axis, with no electron directly on the bonding axis, since 2p orbitals do not have any electron density at the nucleus.
2. Use the MO diagrams provided. 17. Refer to your MO diagrams. According to molecular orbital theory, what is the bond order for each of the following: a. C22- d. Li2 18. Refer to the MO Diagrams. According to molecular orbital theory, which of the following lists ranks the fluorine species in terms of increasing bond order? d. F2 < F22+ < F22 ...
Transcribed image text: Use the MO diagram provided below to answer the following questions: • What is the bond order for N? [Select] • Is N2 paramagnetic or diamagnetic?__ (Select] netic? _ [ Select] • What is the bond order for N? (Select] • Is N2 paramagnetic or diamagnetic?__ (Select] • What is the bond order for Not?
Answer (1 of 6): The bond order of N2+ is 2.5 . * Total no. of electrons in N2+ : 13 * Its electronic configuration is : σ1s² σ*1s² σ2s² σ*2s² π 2py² [π2pz² σ2px1 ] * Bond order = 1/2[Nb-Na], where, Nb=no. of electrons in bonding molecular orbital and Na= no. of electrons in anti-bonding mole...
Dec 15, 2019 · Use the mo diagram provided below to answer the following questions what is the bond order for c2. You get c2 by adding one electron to the lowest energy empty mo and c2 by taking one electron away from the highest energy filled mo. Single bond double bond triple bond half of a bond between a single and double bond between a double and a triple ...
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
Draw the molecular orbital diagram for B 2. The number of unpaired electrons in the B 2 molecule is _____. (a) zero (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3 (e) 4 8. Which one of the following statements is false? (a) Valence bond theory and molecular orbital theory can be described as two different views of the same thing.
(a) Use the MO diagram from Figure 2.18 from the textbook: The electron configuration for O 2 - is 1σ g 2 1σ u 2 2σ g 2 2π u 4 2π g 3. This leaves 1 unpaired electron and gives a bond order of 1.5. (b) Use the same MO diagram as in (a), giving an electron configuration for O 2 + of: 1σ g 2 1σ u 2 2σ g 2 2π u 4 2π g 1.
Bond order of B2 molecule. So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = .5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond.
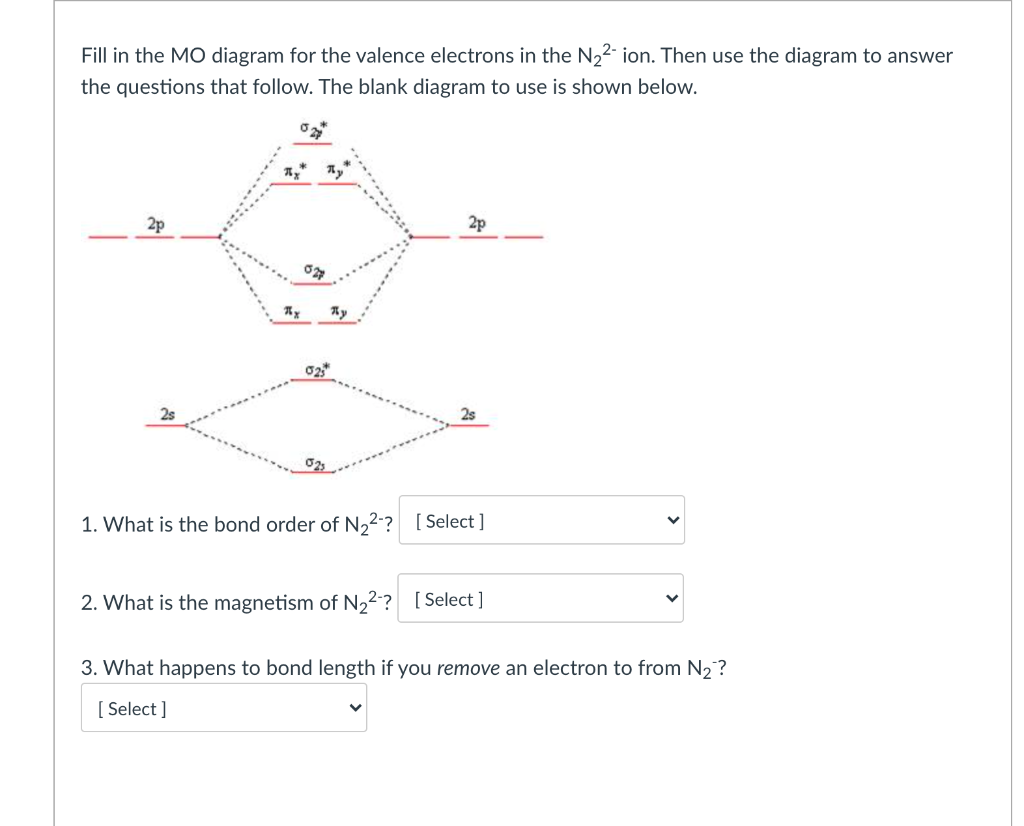
The bond order tells us the stability of a bond: a higher bond order means the bond is more stable. Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons present. Step 2: Draw the molecular orbital diagram.
The bond order tells us the average number of bonds between the bonded atoms. In a diatomic molecule such as `O_2`, the bond order simply tells the number of bonds between the two atoms. The bond order can be interpreted from MO diagrams using the following formula: `"Bond Order" = 1/2 [("Bonding "e^-)-("Antibonding " e^-)]`
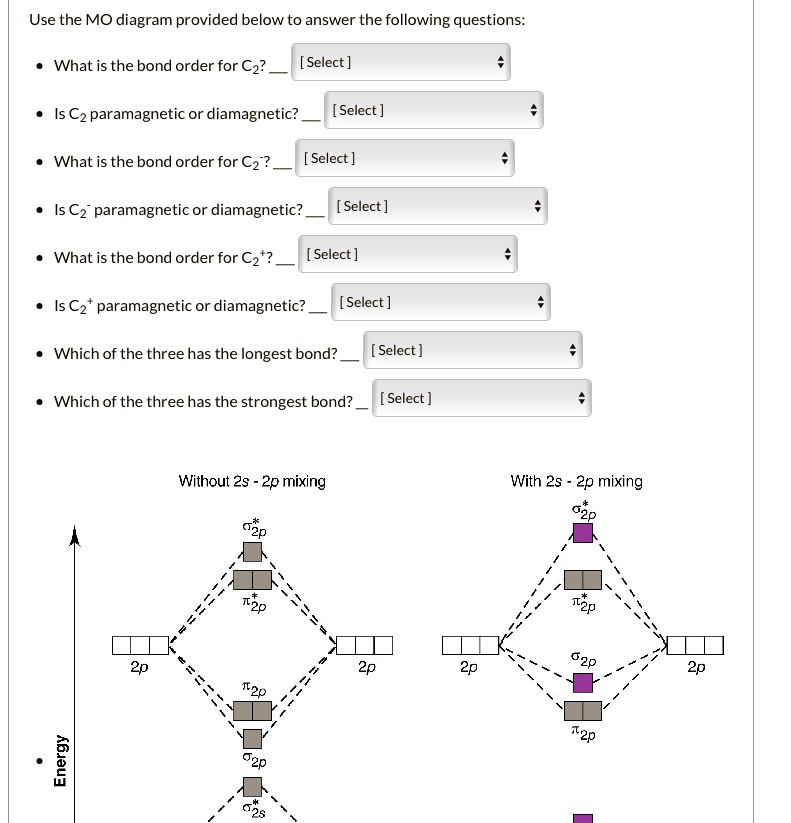
This problem has been solved! Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: Use the MO diagram provided below to answer the following questions: • What is the bond order for C2?_ [Select] • Is C2 ...
Answer: For the purposes of this class, N2+ and N2- will be considered equal as they both have a bond order of 2.5. In advanced inorganic courses you will learn about group theory which is a tool to predict the energies of different molecular orbitals. By using a combination of group theory and computational methods, or by using X ray ...
The anion is phosphate, which is written as PO3−4. Step 3: Use the minimum number of cations and anions needed to make the sum of all charges in the formula equal to zero. The Li+ cation has a 1+ charge and the PO3−4 has a 3− charge. In order to balance the charges, three Li+ cations are needed for every PO3−4 anion.
The anion is phosphate, which is written as PO3−4. Step 3: Use the minimum number of cations and anions needed to make the sum of all charges in the formula equal to zero. The Li+ cation has a 1+ charge and the PO3−4 has a 3− charge. In order to balance the charges, three Li+ cations are needed for every PO3−4 anion.
Transcribed Image Text. Use the MO diagram (below) to calculate the bond order for OF. Tp Op Os 1 3 Os 4 C 7 9. +/- х 100 + LO. check_circle.







![Best Answer] draw the molecular orbital diagram of N2 and ...](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/d20/b492acf8cb9ff01954c3929a3b7a93c7.jpg)


0 Response to "37 use the mo diagram provided below to answer the following questions: what is the bond order for n2?"
Post a Comment