37 molecular orbital diagram for h2 and bond order
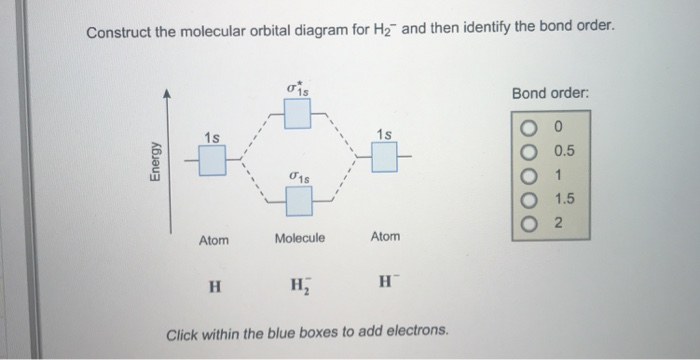
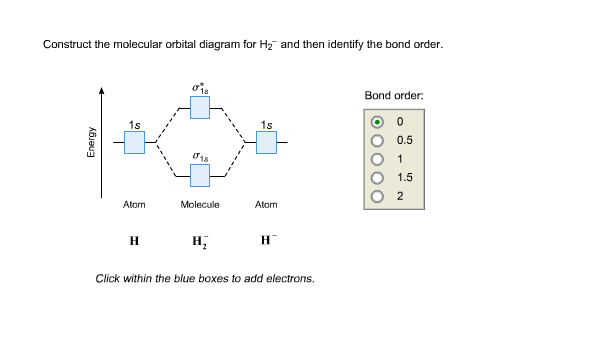
Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, and its molecule \ (\ce {H2}\) is get a sigma (s) bonding orbital, denoted as s1s in the diagram here.
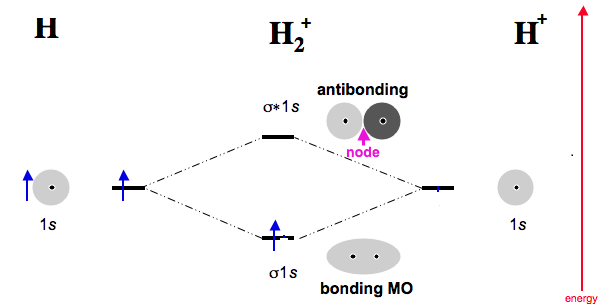
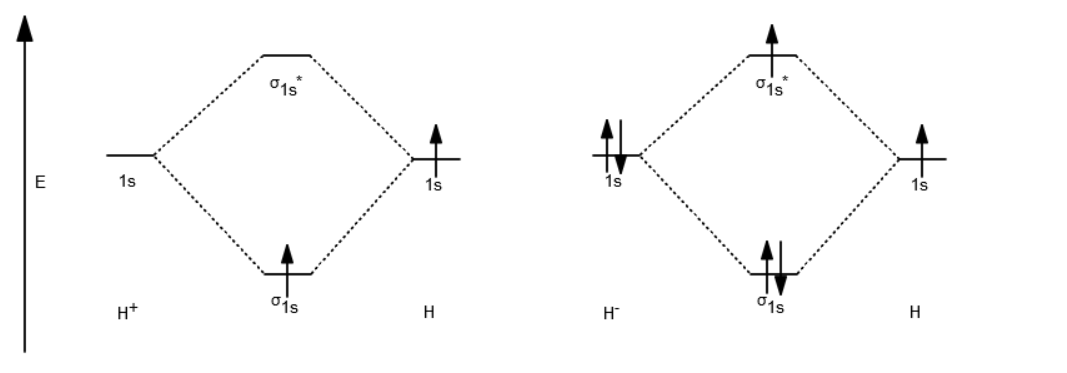
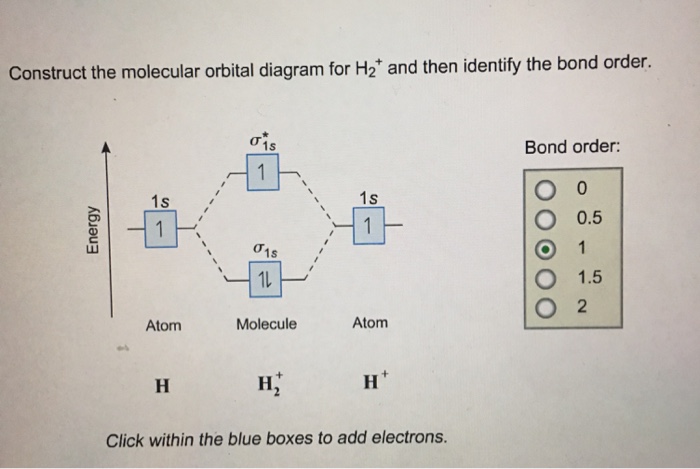
Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, H− 2 has three electrons while H+ 2 has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one σ1s and one σ* 1s MO by conservation of orbitals. If you calculate their bond order, you get: BOH+ 2 = 1 2(Bonding − Antibonding)
This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for the H2+ ion. The bond order of H2+ is also calculated and the meaning of this number ...

Molecular orbital diagram for h2 and bond order
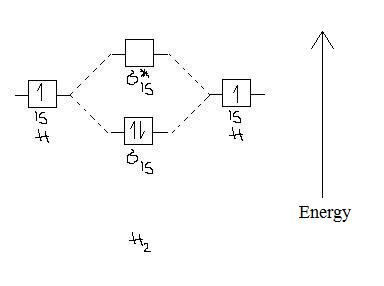
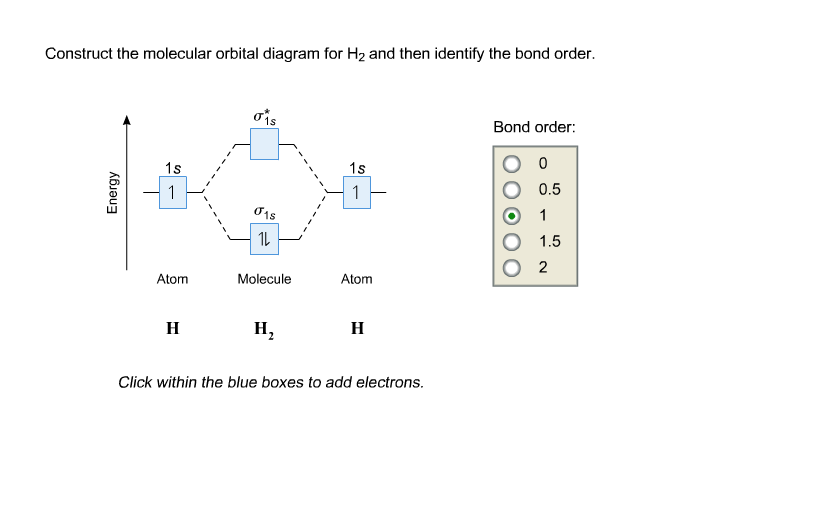
3 Feb 2021 — For H2, bond order = 1/2 (2-0) = 1, which means H2has only one bond. The antibonding orbital is empty. Thus, H2 is a stable molecule. Again, in ...
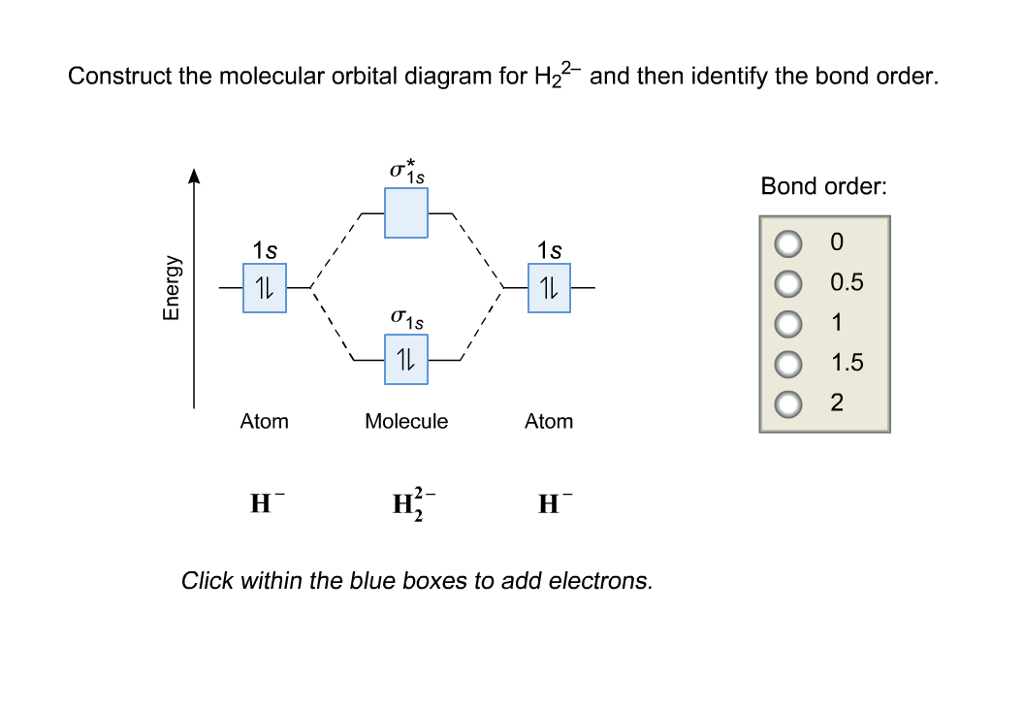
This problem has been solved! A.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2^2+ and then identify the bond order. B.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2 and then identify the bond order. C.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2^- and then identify the bond order. D.Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2^+ and then ...
Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes to add electrons. Question: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order.
Molecular orbital diagram for h2 and bond order.
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Hydrogen Gas (H2).Fill from the bottom up, with 2 electrons total.Bonding Order is 1, and it is Diamagnetic.sigma2s(2)Check me ...
Molecular orbital diagram of hydrogen molecule: Bond order: From the molecular orbital diagram, there are 2 electrons in bonding molecular orbital and there is no anti – bonding molecular orbital. The bond order can be determined by substituting those values using bond order formula. Take care while calculating the bond order.
The valence molecular orbital diagram for the cation f2+ is shown. which of the following options correctly interpret this diagram? * F2+ has a stronger bond than F2 *The olecular orbital bond order is equal to 3/2. Sigma Bonds vs. Pi Bonds. Sigma bond allows free rotation about the bond axis. Pi bonds restrict rotation about the bond axis. The valence molecular orbital diagram …
Molecular orbital diagram: The molecular orbital diagram consists of two types of bond. They are sigma bond (σ) \left( \sigma \right) (σ) and pi bond (π) \left( {\rm{\pi }} \right) (π). The electrons first fill the lower energy level 2s and then moves to the higher energy level 2p. Also, the electrons first fill the bonding molecular ...
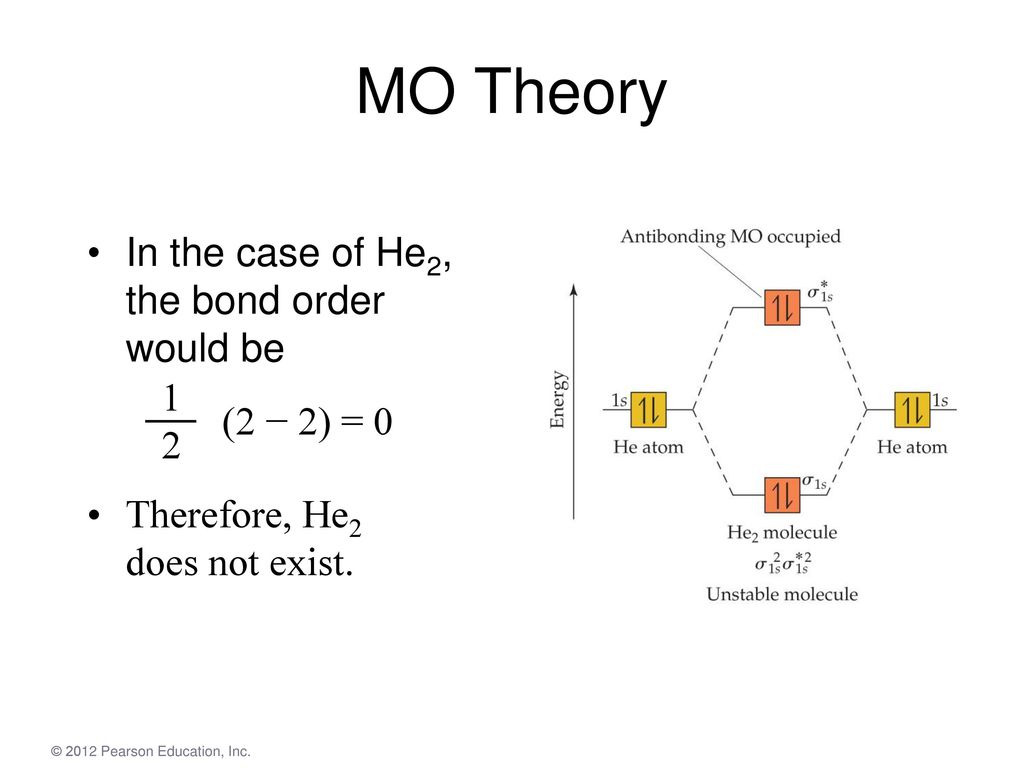
04.09.2021 · Bond Order. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. ... {bond\: order\: in\: H2}=\dfrac{(2−0)}{2}=1\] Because the bond order for the H–H bond is equal to 1, the bond is a single bond. A helium atom has two electrons, both of which are in its 1s orbital. Two helium …
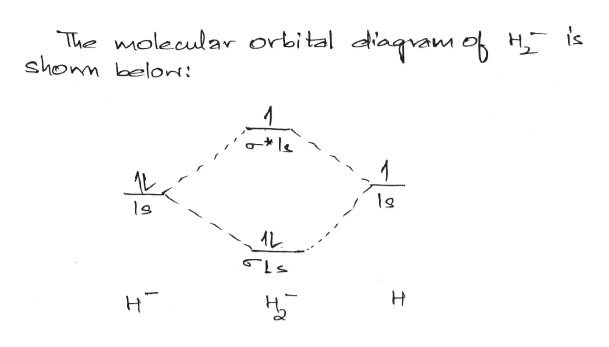
Answer (1 of 4): In order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2- is to be drawn. According to MOT number of atomic orbitals combined is equal to total number of molecular orbitals formed.Electronic configuration of H is 1s1. when two hydrogen atoms come closer, then on combi...
Molecular Orbital Theory is primarily used to explain the bonding in molecules that cannot be explained by Valence Bond Theory. These are molecules that generally involve some form of resonance. Resonance implies that a bond is neither single nor double but some hybrid of the two. Valence bond theory only describes the bonding of single or double or triple bonds. It …
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine …
Problem: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order. Click thin the blue boxes to add electrons.Bond order: a) 0 b) ...1 answer · Top answer: Total valence electrons: 3 e-Molecular orbitalBond orderBond order = 12[# of e- in bonding MO - # of e- in antibonding MO ]Bond order =12(2-1)Bond ...
The general procedure for constructing a molecular orbital diagram for a reasonably simple molecule can be summarized as follows: 1. Assign a point group to the molecule. 2. Look up the shapes of the SALCs. 3. Arrange the SALCs of each molecular fragment in increasing order of energy, first noting whether they stem from s, p, or d orbitals (and put them in the order s < p < …
04.03.2021 · Describe the essential difference between a sigma and a pi molecular orbital. Define bond order, and state its significance. Construct a "molecular orbital diagram" of the kind shown in this lesson for a simple diatomic molecule, and indicate whether the molecule or its positive and negative ions should be stable. The molecular orbital model is by far the most …
In molecular orbital theory, bond order is also defined as the difference, divided by two, between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons; this often, but not always, yields the same result. Bond order is also an index of bond strength, and it is used extensively in valence bond theory. Dihydrogen (H 2) This MO diagram depicts the molecule H 2, with the …
01.11.2021 · It’s very interesting to draw the energy level diagram of the atoms. Read more What is the Bond Order in F2? Answer- 1 is the bond order for an f2 molecule. We calculate the bond order with the help of molecular orbital theory or bond order theory. The theory and the explanation of how the f2 molecule has 1 as its bond order, which is detailed in the next …
Testin g qualitative MO theory prediction of Bond Order with experiment for homonuclear diatomics made from elements in the 1st row of the Periodic Table (using the “Molecular Orbital Aufbau” principle): BondOrder [# ' # ' ]/2≡−bondinge s antibondinge s [D.A. McQuarrie, Quantum Chemistry]
The MOT diagram for H2 H 2 is formed by the overlap of 1s atomic orbitals. Its shell has two molecular orbitals. one is bonding (σ 1s) and the other is anti-bonding (σ *1s ). The H 2 molecule has two electrons and these can be accommodated in the σ 1s molecular orbital.




















0 Response to "37 molecular orbital diagram for h2 and bond order"
Post a Comment