36 energy diagram for sn2
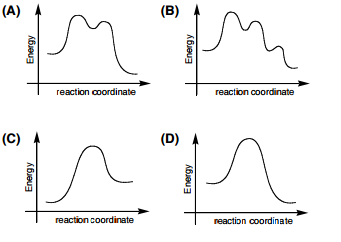
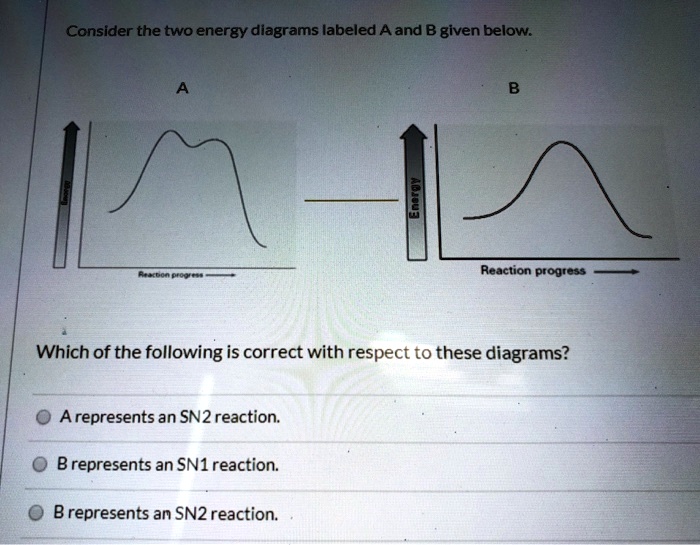
Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Considering the Sn1, SN2, E1, and E2 mechanisms, the energy diagram shown below corresponds to: energy rxn coordinate O only the Sp1 mechanism only the Sn2 mechanism both the Sn1 and E1 mechanisms O both the Sn2 and E2 mechanisms. 1. What does SN2 stand for? Ans: SN2 stands for Nucleophilic Substitution, Second Order (organic chemistry). 2. What is the difference between sn1 and sn2? Ans: The phase deciding the rate is unimolecular for SN1 reactions, whereas it is bimolecular for an SN2 reaction. SN1 is a two-stage system, while SN2 is a one-stage process.
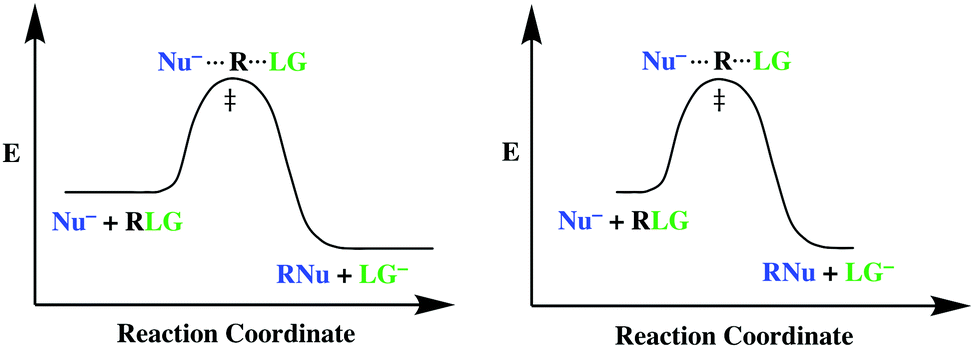
The S N 2 Reaction Notes: In the SN2 reaction, the nucleophile attacks from the most δ+ region: behind the leaving group. This is called a back-side attack. This back-side attack causes an inversion (study the previous slide): after the leaving group leaves, the other substituents shift to make room for the newly-bonded nucleophile, changing the stereochemistry of the molecule.
Energy diagram for sn2
The energy diagram of the E1 mechanism demonstrates the loss of the leaving group as the slow step with the higher activation energy barrier: The dotted lines in the transition state indicate a partially broken C-Br bond. The Br being the more electronegative element is partially negatively charged and the carbon is partially positively charged ... Potential Energy Diagram. We will be contrasting about two types of nucleophilic substitution reactions. One type is referred to as unimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN1), whereby the rate determining step is unimolecular and bimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN2), whereby the rate determining step is bimolecular. We will begin our ... Answer: SN2 rxn. is a one step, concerted; rxn is simply where nucleophile attack the saturated carbon centre / atom (bearing a suitable leaving group) from back side / 180° away from the leaving group (-L) . So, it's energy profile is simple . Draw it by using Gibbs free energy term, not enthalp...
Energy diagram for sn2. SN2 - Second-order Nucleophilic Substitution; SN2 - Second-order Nucleophilic Substitution ... Transition state and energy diagram of an S N 2 reaction: Chloroform hydrolysis. Due to their extremely short lifetime, transition states cannot be measured directly. They represent an energy maximum on the reaction coordinate. Transcribed image text: 4) Based on the Hammond Postulate, select the one that most closely resembles the target energy state in following Potential Energy Diagram: Target Energy State Potential energy D Reaction coordinate a 5) Select a FALSE statement about the SN2 & E2 mechanisms for the reaction between an Alkyl Halide (RX) reactant and an anionic reagent that could act as Nucleophile (Nu ... Oct 19, 2018 · Sn2 Energy Diagram. You may recall from general chemistry that it is often convenient to describe chemical reactions with energy diagrams. In an energy diagram. SN2 Reaction follows second order rate kinetics. It forms a product via one transition state. Transition state is the state at which it posses. SN2 Reaction follows second order rate ... 5. Question 5 - The Energy Diagram of SN2 reaction: Draw an energy diagram for the following S N 2 reaction. Label the axes, the Ea, the ΔH° and the transition state of the reaction.Assume the reaction is exothermic and ΔH° = -75 kJ/mol and Ea = 50 kJ/mol. Draw the structure of reactants and products on the diagram.You can put the reactants at any energy level and then draw the rest as ...
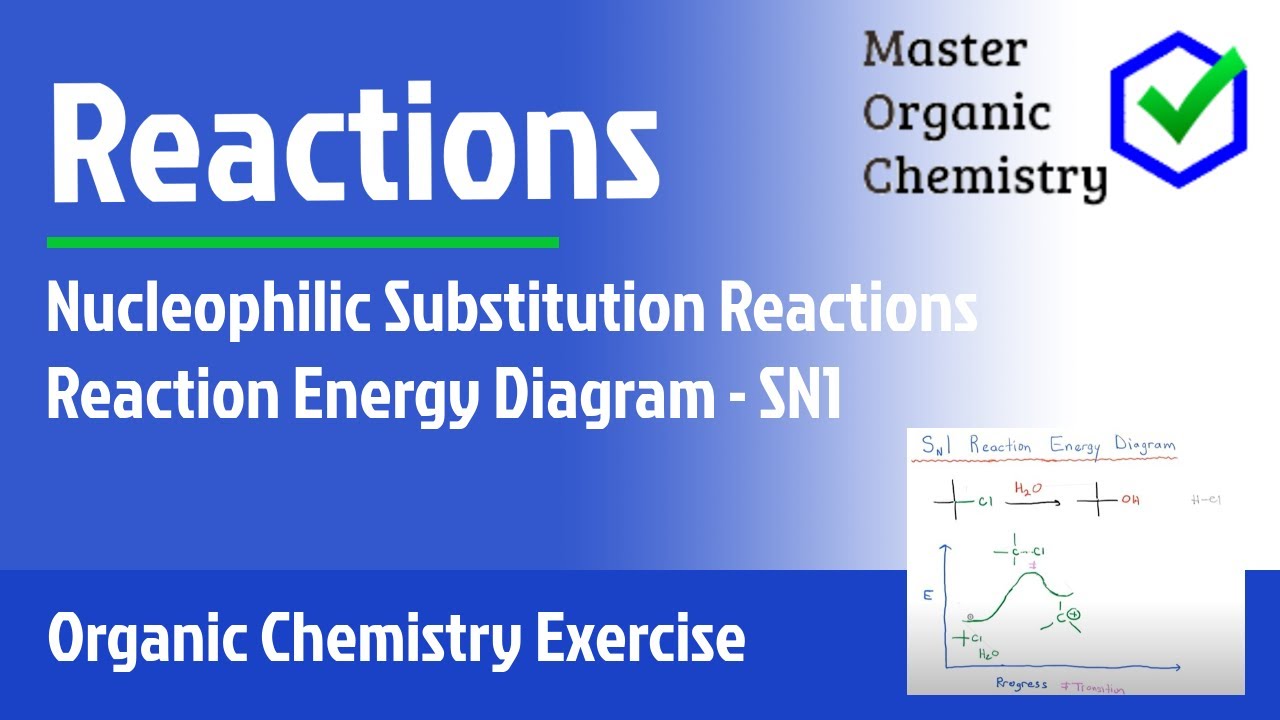
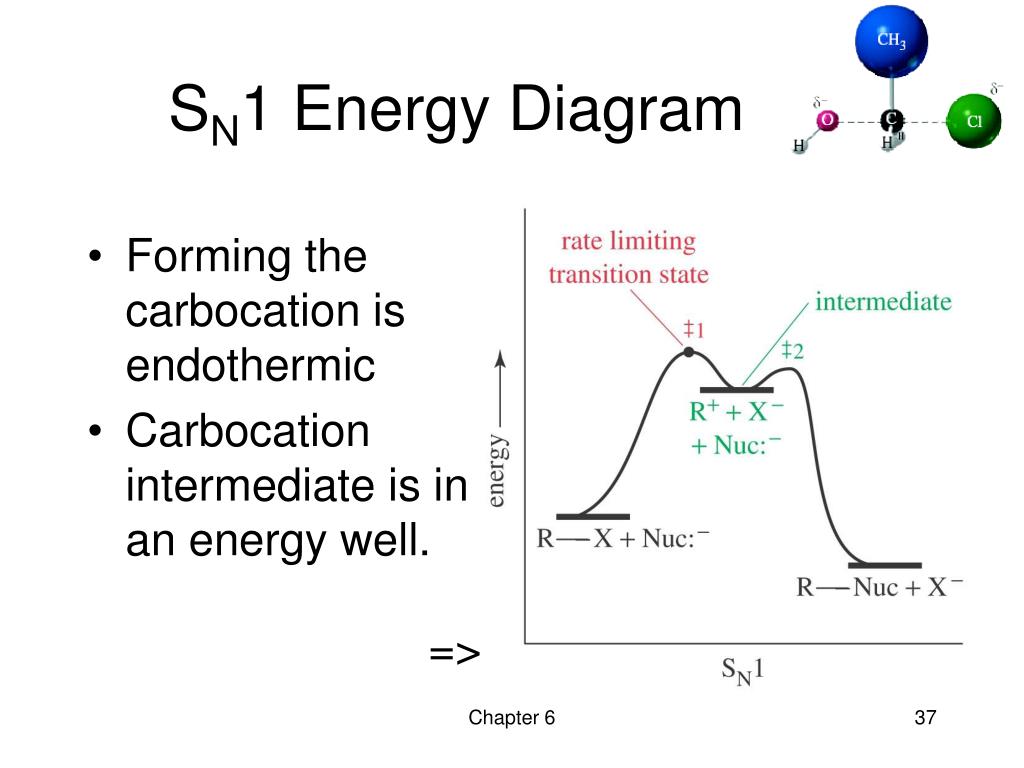
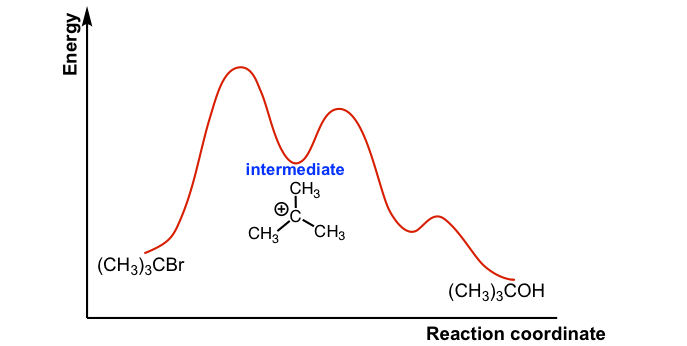
7.4 SN1 Reaction Mechanism, Energy Diagram and Stereochemistry. The reaction between tert -butylbromide and water proceeds via the SN1 mechanism. Unlike S N 2 that is a single-step reaction, S N 1 reaction involves multiple steps. Reaction: (CH 3) 3 CBr + H 2 O → (CH 3) 3 COH + HBr. In step 1, C—Br bond breaks and Br departs with the ... Sn2 Energy Diagram. Fig Transition state and energy diagram of an S N 2 reaction: Chloroform hydrolysis. They represent an energy maximum on the reaction coordinate. SN2 Reaction follows second order rate kinetics. It forms a product via one transition state. Transition state is the state at which it posses. It starts with the kinetics of SN2 ... 7.2 SN2 Reaction Mechanism, Energy Diagram and Stereochemistry. SN2 Reaction Mechanism. Let’s still take the reaction between CH 3 Br and OH – as the example for S N 2 mechanism. S N 2 mechanism involves two electron pair transfers that occur at the same time, nucleophile attacking (red arrow) and leave group leaving (blue arrow). Construct the gas phase Reaction Coordinate Diagram for the Cl + CH3Cl SN2 reaction by plotting the relative energy in kJmol 1 versus Cl + C | {z} Distance H3 Cl. Place the Reaction Coordinate Diagram on the graph provided below and plot the energies on a relative energy scale. Label the various species along the reaction pathway. 0 5 10 15 20 ...
Draw a hypothetical free-energy diagram for the SN2 reaction of iodide anion with 1-chlorobutane. Label the diagram as in Fig. 6.4, and assume it is exergonic but without specific values for ˆ†G€¡ and ˆ†Go. The potential energy diagram for an SN 2 reaction is shown below. Upon nucleophilic attack, a single transition state is formed. Upon nucleophilic attack, a single transition state is formed. A transition state, unlike a reaction intermediate, is a very short-lived species that cannot be isolated or directly observed. http://Leah4sci.com/substitution-elimination presents: SN2 Energy Diagram Need help with Orgo? Download my free guide '10 Secrets to Acing Organic Chemistry'... energy diagram below. gas phase reactions polar solvent phase reactions Carbocations are more stable and have smaller energy differences in solution than the gas phase. (But methyl and primary are still too unstable to form in solution and we won't propose them in this book.) Solvent / ion interactions are the most significant
Energy diagrams SN1 and SN2. Jessica L. Santos. 699 followers. Organic Chemistry Reactions. Chemistry Help. Ap Chem. School Hacks. School Tips. Study Hard. Calculus. Study Materials. Science And Nature. More information.... More like this. Organic Chemistry Reactions. Chemistry Help ...
No base = SN1/SN2, but we already knew that. 3) Leaving group: Cl is a decent leaving group. Decent LG = SN2. 4) Solvent: acetone is a polar aprotic solvent = SN2. 5) Substrate: It's secondary at the leaving group = SN1 OR SN2. Almost all of the factors point to an SN2 reaction, with the notable exception of the type of substrate.
The reaction energy diagram for an SN2 reaction, showing the backside attack and transition state with 5 groups attached to carbon.MOC members get access to ...
SN2 Reactions on 2-Chlorobutane. Stereochemistry in the SN1 Reaction (7.4B) 7-26 Inversion and Retention of Configuration. Racemic Product. 7.5 Reaction Rates of SN Reactions 7-28 Reaction Rates (7.5A) 7-28 SN2 Reaction Rates. SN1 Reaction Rates. Activation Energies (7.5B) 7-29 Energy Diagram for an SN1 Reaction.
Oct 24, 2018 · Energy Diagram For Sn2. It starts with the kinetics of SN2 reaction and covers the energy diagrams including questions on activation energy, enthalpy, the order of reaction and curved. SN2 Reaction follows second order rate kinetics. It forms a product via one transition state. Transition state is the state at which it posses.
Energy profile diagram of SN 1 reaction: Stereochemistry of SN 1 reaction: In SN 1 reaction, carbocations are formed as the intermediate which are trigonal and planar. Carbocation has a flat structure so that nucleophile can attack it from either side (i.e. front or back) resulting in the formation of two products, one with retention of ...
Considering the SN1, SN2, E1 and E2 mechanisms, the energy diagram shown below corresponds toa) only the SN1 mechanism.b) only the SN2 mechanismc) both the SN1 and E1 mechanismd) both the SN2 and E2 mechanism
The S N 1 reaction energy diagram illustrates the dominant part of the substrate with respect to the reaction rate. The rate-determining step is the formation of the . Substitution Reactions (SN2 versus SN1) SN1. Elimination Reactions: E2 versus E1. Substrate: Alkene Stability Generic Reaction-Energy Diagrams.
The change in energy for the above reaction is represented in the energy level diagram given below. SN2 is a single-step reaction, so the diagram only shows one curve. The lower energy of the products CH 3 OH and Br - compared to the reactants CH 3 Br and OH - suggests that the reaction is exothermic and that the products are more stable.
SN2 reaction coordinate diagram. In this diagram, there are really only three parts: the reagents, the transition state, and the products. The transition state is the point in the reaction with the highest energy level, and the difference in energy between the reagents and transition state is called the activation energy (often abbreviated as Ea).
Proticii. Aproticiii. Solvent Polarity1. Dielectric constant2. Non-polar solvent (nps)3. Polar solvent (ps)4. Border line solventCurrent LectureI. SN2 examplesa. Example:b. Example:c. Example:II. Energy Diagrams: show change in energy during a reaction. When bonds break, there is an increase in energy. When bonds form, there is a decrease in ...
Answer: SN2 rxn. is a one step, concerted; rxn is simply where nucleophile attack the saturated carbon centre / atom (bearing a suitable leaving group) from back side / 180° away from the leaving group (-L) . So, it's energy profile is simple . Draw it by using Gibbs free energy term, not enthalp...
Potential Energy Diagram. We will be contrasting about two types of nucleophilic substitution reactions. One type is referred to as unimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN1), whereby the rate determining step is unimolecular and bimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN2), whereby the rate determining step is bimolecular. We will begin our ...
The energy diagram of the E1 mechanism demonstrates the loss of the leaving group as the slow step with the higher activation energy barrier: The dotted lines in the transition state indicate a partially broken C-Br bond. The Br being the more electronegative element is partially negatively charged and the carbon is partially positively charged ...





.png)







/chapter7/pages5and6/page5and6_files/sn2phenoxyenergy.png)







0 Response to "36 energy diagram for sn2"
Post a Comment