35 construct the orbital diagram of the f– ion.
1 answerA neutral fluorine atom has 9 electrons. How many electrons does a F- ion have? FREE Expert Solution. We are asked to construct the orbital diagram of ... 21.03.2011 · The DS-1 Death Star Mobile Battle Station, also designated as the DS-1 Orbital Battle Station and referred to as the Ultimate Weapon in early development stages and later as the Death Star I and the First Death Star, was a moon-sized, deep-space mobile battle station constructed by the Galactic Empire. It had been designed to fire a single planet-destroying superlaser powered by massive kyber ...
23 Jun 2016 · 1 answerF−:1s22s22p6. Explanation: A good starting point for when you must find the electron configuration of an ion is the electron configuration ...
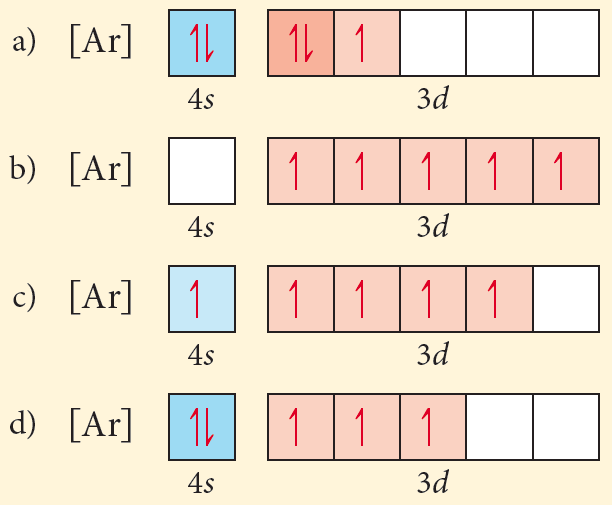
Construct the orbital diagram of the f– ion.
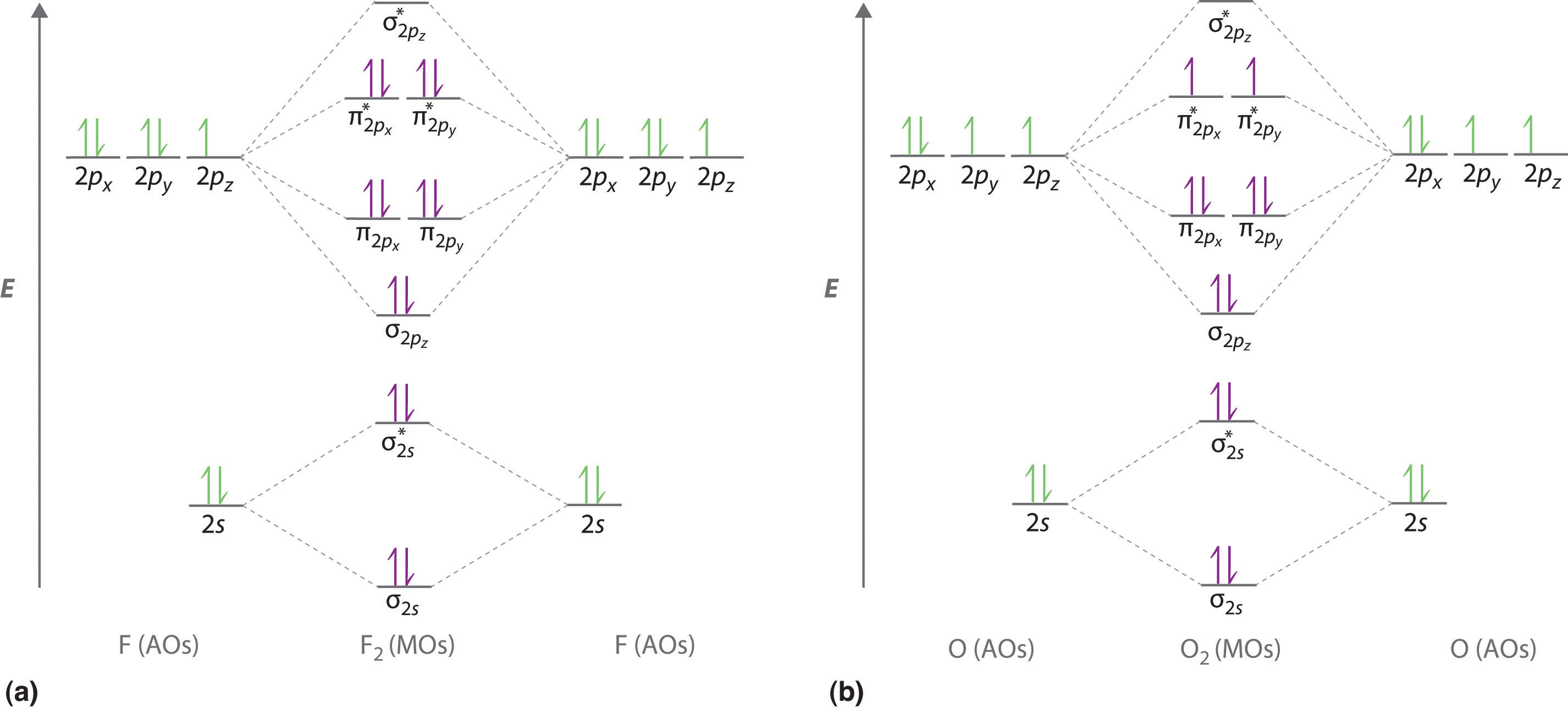
Ch4 hybridization diagram. Drawing and predicting the IBr3 molecular geometry is very easy by following the given method. •The electronic geometry is AX 2 •The hybridization on carbon therefore is sp. Consider the molecule below. All of the following statements concerning valence bond (VB) and molecular orbital (MO) bonding theories are correct EXCEPT. The hybrid orbitals are all ... 30.11.2021 · Once Molecular orbital practice problems Ch301 fall 2009 work 7 answer key Molecular Orbital Theory Purdue University April 17th, 2019 - Valence Bond Model vs Molecular Orbital Theory Construct a molecular orbital diagram for the O 2 molecule Click here to check your answer to Practice Problem 9 Bond Order The number of bonds between a pair of atoms Electron configuration and … We will now construct the ground-state electron configuration and orbital diagram ... Nitrogen (atomic number 7) fills the 1s and 2s subshells and has one ...
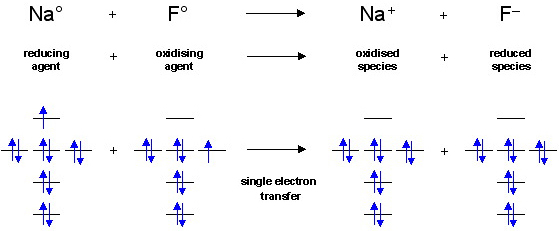
Construct the orbital diagram of the f– ion.. The first example looks at a nitrogen atom. The diagram is created using the electron configuration. Degenerate orbitals and how to fill them is discussed. The ... Chapter 1: Molecular Orbital Concepts A. Concepts of MO Theory. 1. Strong Covalent Bonds. Consider the pi bond of ethene in simple molecular orbital terms (The qualitative results would be the same for any pi or sigma bond. q The overlap of the two atomic orbitals (AO’s) results in the formation of two molecular orbitals (MO’s), one of which is lower in energy than the original AO’s (the ... The Lewis Structure (electron dot diagram) of each ion is used to construct the Lewis Structure (electron dot diagram) for the ionic compound. The Lewis structure of a positive ion (cation) is positioned adjacent to the Lewis structure of a negative ion (anion). If the charge on the positive ion is greater than the charge on the negative ion, draw another Lewis structure for another negative ... Once we have the configuration for Fe, the ions are simple. When we write the configuration we'll put all 26 electrons in orbitals around the nucleus of the ...
1 answerOrbital diagram of F− F −. The atomic number of F is 9. After removing one electron, fluorine becomes F− F − and in this case... Transcribed image text: Construct the orbital diagram of the F^- ion. A neutral fluorine atom has 9 electrons. How many electrons does a F^- ion have? In molecular orbital theory (fully delocalized canonical orbitals or localized in some form), the concept of a lone pair is less distinct, as the correspondence between an orbital and components of a Lewis structure is often not straightforward. Nevertheless, occupied non-bonding orbitals (or orbitals of mostly nonbonding character) are frequently identified as lone pairs. Lone pairs in ... Diagram of the S and P orbitals: The s subshells are shaped like spheres. Both the 1n and 2n principal shells have an s orbital, but the size of the sphere is larger in the 2n orbital. Each sphere is a single orbital. p subshells are made up of three dumbbell-shaped orbitals. Principal shell 2n has a p subshell, but shell 1 does not.
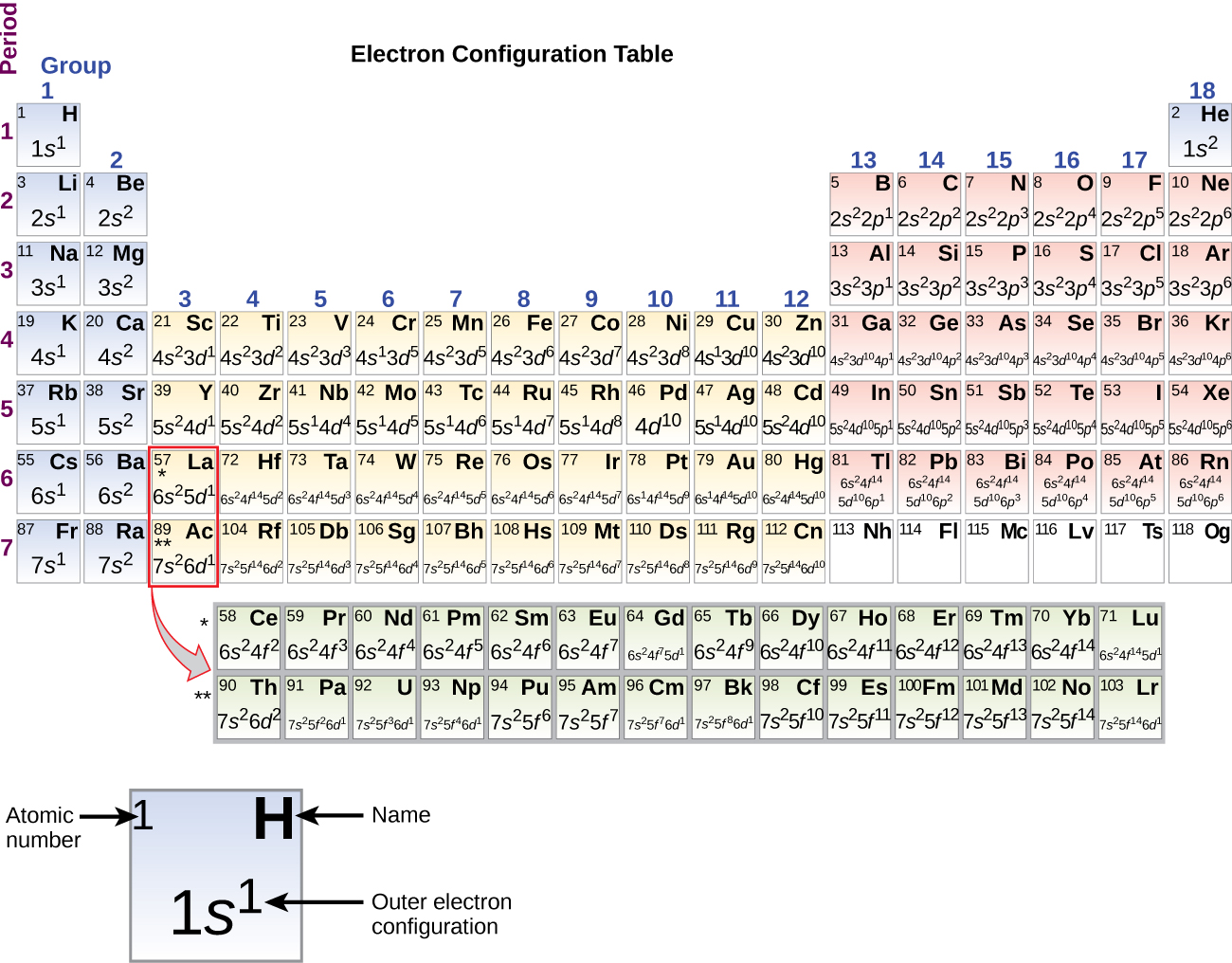
An orbital-filling diagram shows the number of electrons in each orbital, which are shown in order of energy. The placement of electrons in orbitals follows a certain set of rules. Lower energy subshells fill before higher energy subshells. The order of filling is 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p. The periodic table can be used to help you remember ... The International Space Station (ISS) is a modular space station (habitable artificial satellite) in low Earth orbit.It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. 15.01.2018 · a, Schematic of the Cu 2+ ion cycling method for Cu 2 O and Cu nanocubes (NCs) on Cu foils. b, Galvanostatic cycling of Cu foil in 0.1 M Cu(NO 3) 2 … We will now construct the ground-state electron configuration and orbital diagram ... Nitrogen (atomic number 7) fills the 1s and 2s subshells and has one ...
30.11.2021 · Once Molecular orbital practice problems Ch301 fall 2009 work 7 answer key Molecular Orbital Theory Purdue University April 17th, 2019 - Valence Bond Model vs Molecular Orbital Theory Construct a molecular orbital diagram for the O 2 molecule Click here to check your answer to Practice Problem 9 Bond Order The number of bonds between a pair of atoms Electron configuration and …
Ch4 hybridization diagram. Drawing and predicting the IBr3 molecular geometry is very easy by following the given method. •The electronic geometry is AX 2 •The hybridization on carbon therefore is sp. Consider the molecule below. All of the following statements concerning valence bond (VB) and molecular orbital (MO) bonding theories are correct EXCEPT. The hybrid orbitals are all ...
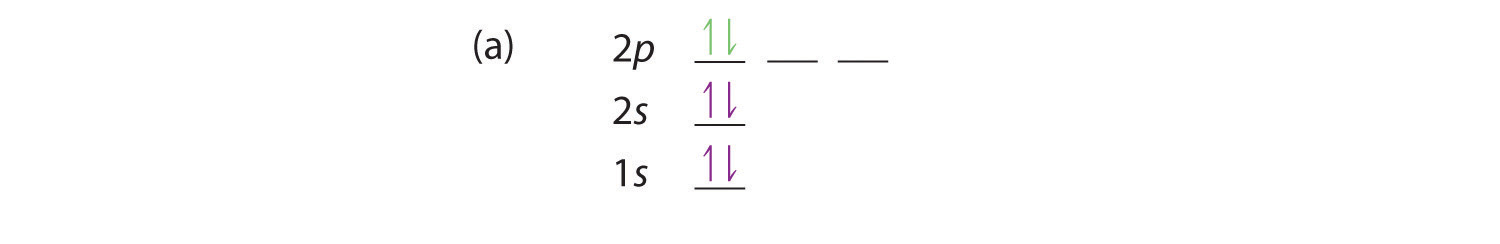









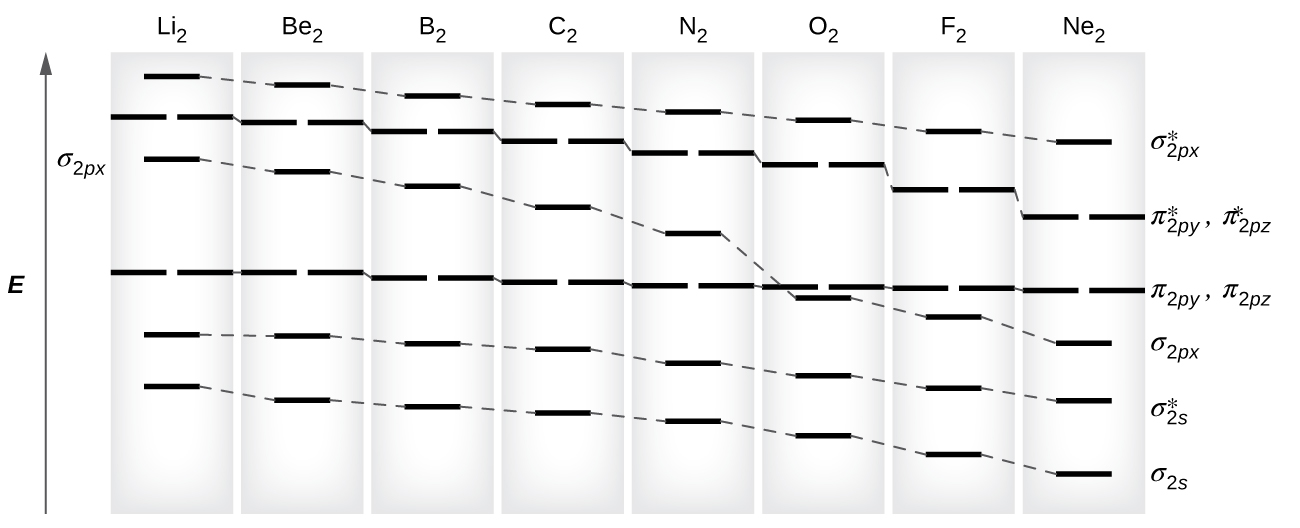

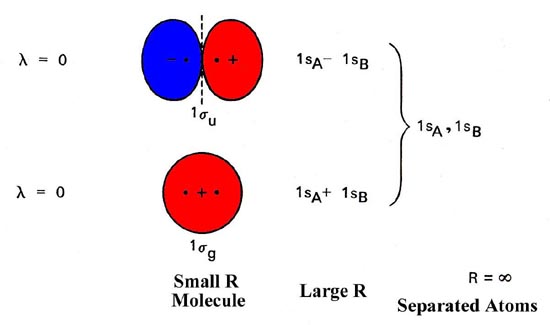
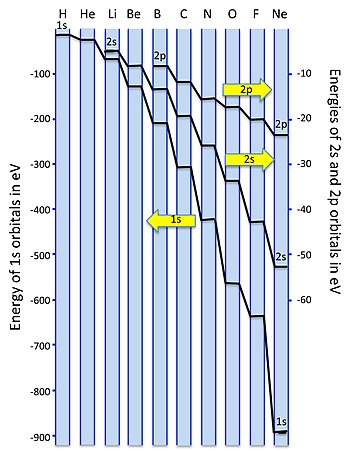



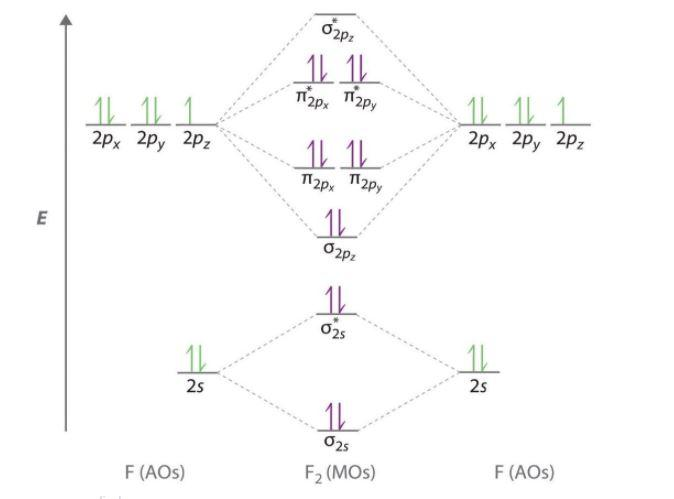






0 Response to "35 construct the orbital diagram of the f– ion."
Post a Comment