39 energy diagram with catalyst
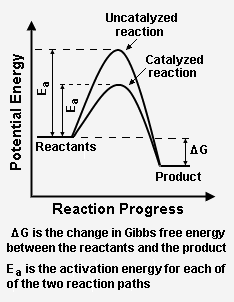
Draw an energy diagram for an endothermic reaction without a catalyst (use a solid line) and with a catalyst (use a dotted line). Label all parts of the diagram. Explain what a catalyst is and how a catalyst influences the rate of a reaction. Answer: A Catalyst lowers the activation energy so it increases the rate of reaction. This chemistry video tutorial focuses on potential energy diagrams for endothermic and exothermic reactions. It also shows the effect of a catalyst on the f...
Activation energy is the minimum energy needed for a reaction to occur when two particles collide. It can be represented on an energy level diagram . The diagram shows that when a catalyst is used ...

Energy diagram with catalyst
Diagrams like this are described as energy profiles.In the diagram above, you can clearly see that you need an input of energy to get the reaction going. Once the activation energy barrier has been passed, you can also see that you get even more energy released, and so the reaction is overall exothermic. Consider the following energy diagram showing a reaction with and without a catalyst.. High B D D Energy А Low Start of reaction End of reaction Fill in the blank with the appropriate letter (A, B, C, etc.). The heat of reaction would be represented by ; Question: Consider the following energy diagram showing a reaction with and without a ... Thermochemistry and Energy Diagrams. The activation energy ( Ea) of this reaction is. - 80 kJ. 240 kJ. 40 kJ. 160 kJ. 80 kJ.
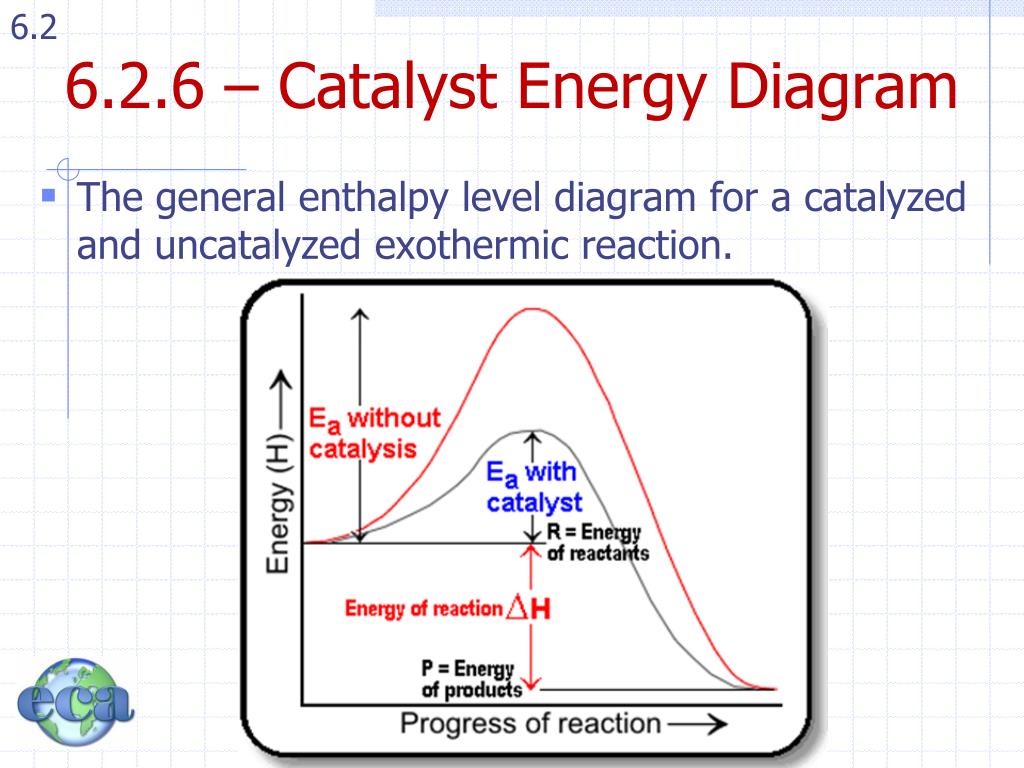
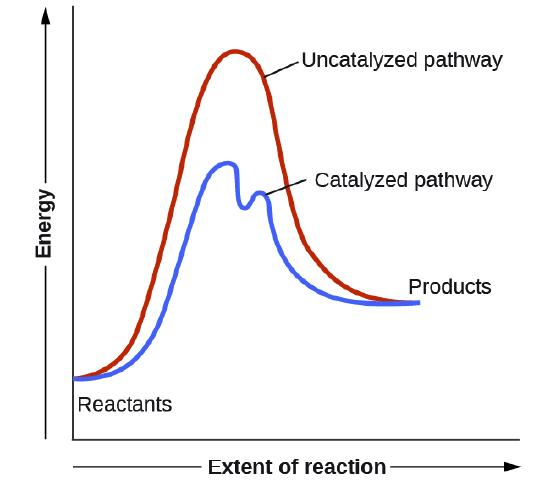
Energy diagram with catalyst. The catalyst provides an alternative, lower-energy, pathway for the reaction to follow, using a lower-energy intermediate product (lower-energy activated complex). If the catalyst is a solid, it can do this by providing a surface on which the reactant molecules can "stick" in the correct orientation, increasing the rate at which successful ... Example 12.7.1: Using Reaction Diagrams to Compare Catalyzed Reactions — The catalyst provides a different reaction path with a lower activation energy. As ... Explain the function of a catalyst in terms of reaction mechanisms and potential energy diagrams List examples of catalysis in natural and industrial processes Among the factors affecting chemical reaction rates discussed earlier in this chapter was the presence of a catalyst , a substance that can increase the reaction rate without being ... Figure 6 shows the generic potential energy diagram with a catalyst and noncatalyst in a hypothetical exothermic chemical reaction. Catalyst works by providing ...
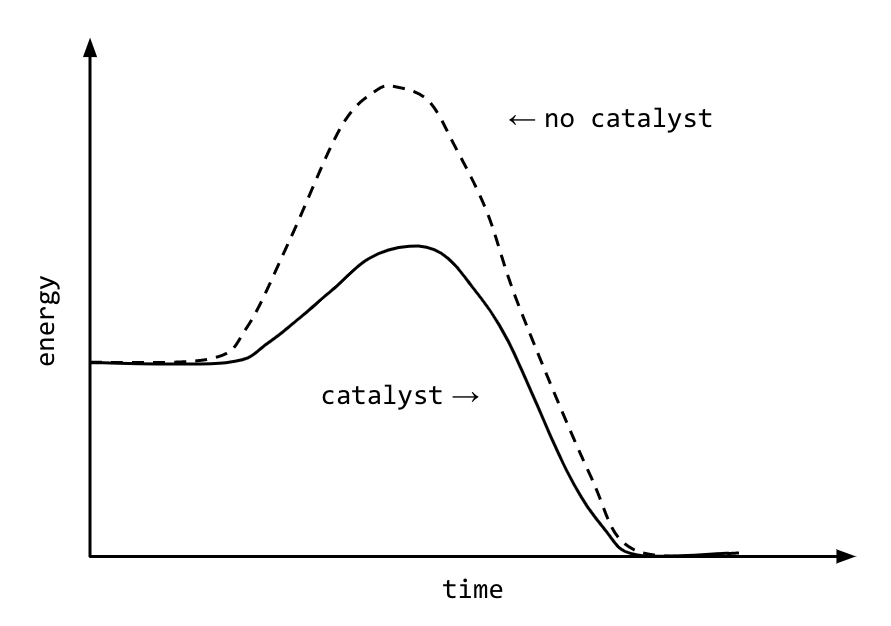
So understanding how catalyst affect the energy diagrams is pretty important. You'll have questions on that. And understanding how that energy diagram works, but it's actually graphing is also pretty important as well. So hopefully this is helped you understand exactly what energy diagrams are used for and how they work. Catalysts. A catalyst provides an alternative reaction pathway which involves less energy and so the catalyst lowers the activation energy. Ea is the minimum amount of energy for a reaction to occur. It is the amount of energy required to create an activated complex. 4. What happens when a catalyst is used in a reaction? A catalyst changes the reaction mechanism, in the process lowering the activation energy. 5. Name 4 things that will speed up or slow down a chemical reaction. Potential energy barriers for catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions; The potential energy diagram compares the potential energy barriers for the catalysed and uncatalysed reactions. The barrier for uncatalysed reaction (E a) is larger than that for the same reaction in the presence of a catalyst E a.
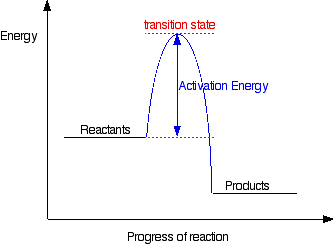
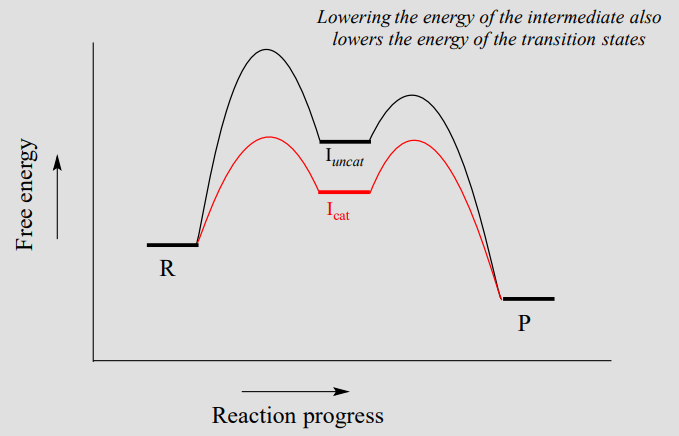
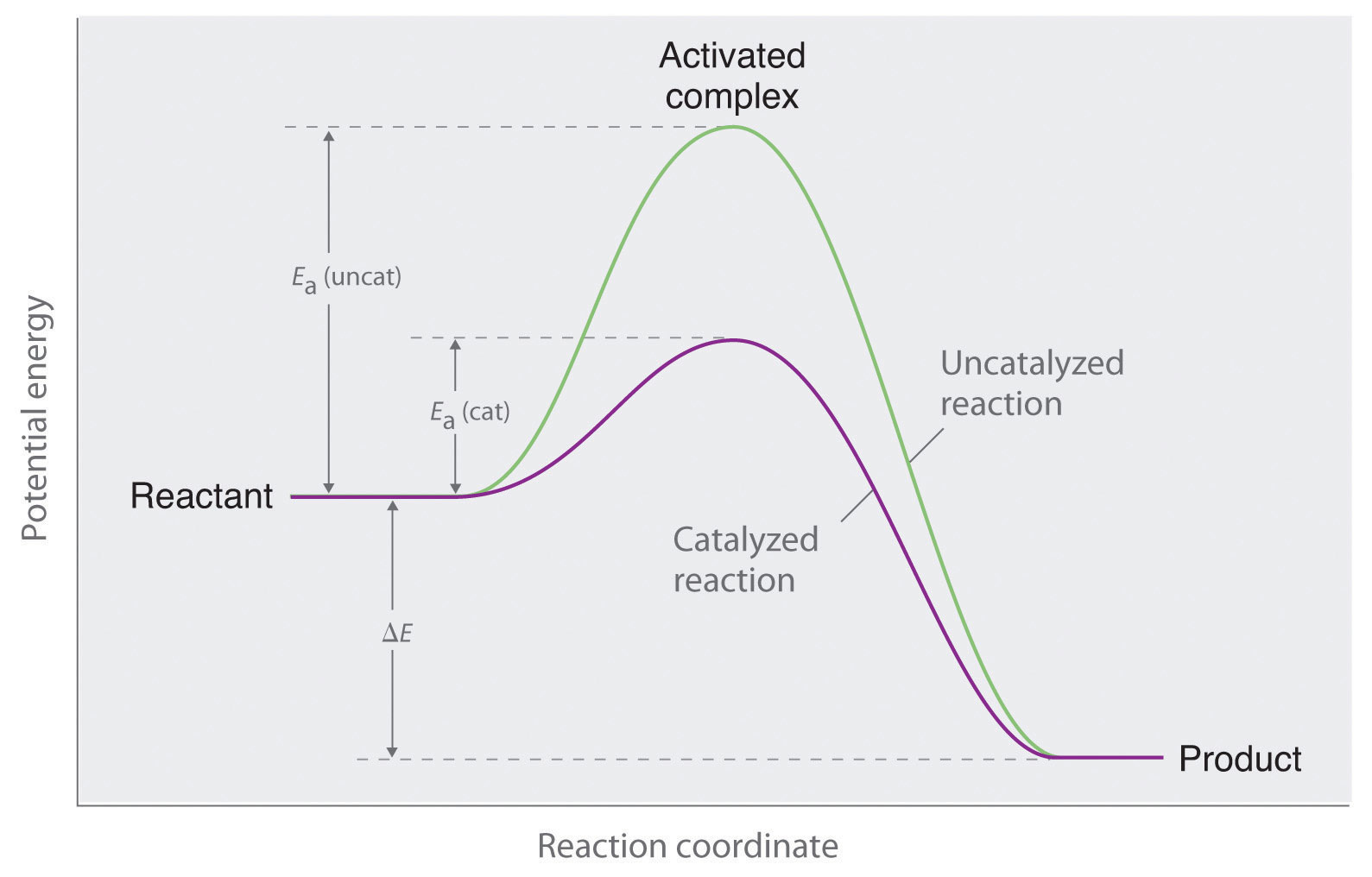
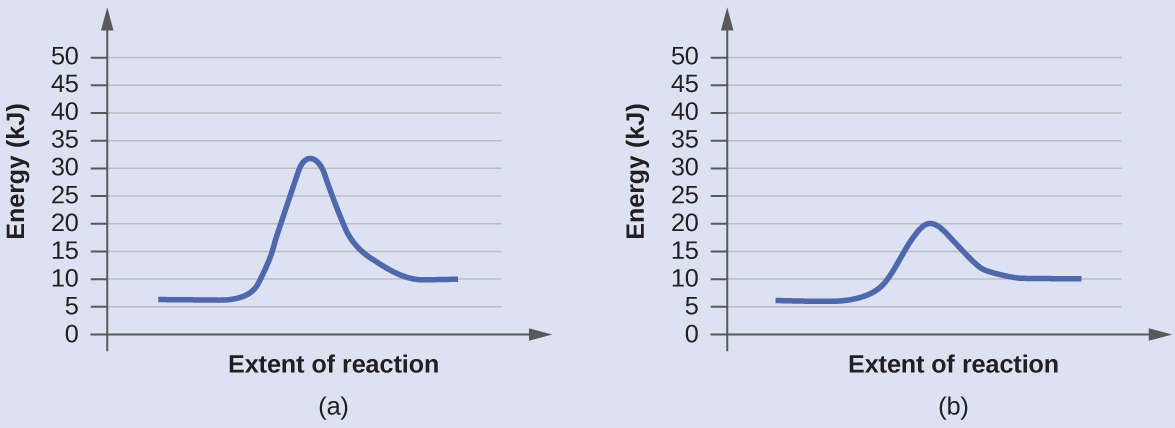
This potential energy diagram shows the effect of a catalyst on the activation energy. The catalyst provides a different reaction path with a lower activation energy. As shown, the catalyzed pathway involves a two-step mechanism (note the presence of two transition states) and an intermediate species (represented by the valley between the two ... Potential energy diagram of a heterogeneous catalytic reaction, with gaseous reactants and products and a solid catalyst. Note that the uncatalyzed reaction has to overcome a substantial energy barrier, whereas the barriers in the catalytic route are much lower. The energy diagram of Fig. 1.2 illustrates several important points: This indicates the use of a catalyst in diagram (b). The activation energy is the difference between the energy of the starting reagents and the transition state—a maximum on the reaction coordinate diagram. The reagents are at 6 kJ and the transition state is at 20 kJ, so the activation energy can be calculated as follows: E a = 20 kJ − 6 ... 22 May 2017 — When a catalyst is added, it provides an alternative pathway for the ... the energy of the products however, as seen in the diagram below ...1 answer · See below. Explanation: A reaction needs a certain amount of energy, called the activation energy, for its reactants to form products. When a catalyst ...
by T Tatsuoka · 2013 · Cited by 18 — Simplified energy diagrams are useful in visualizing chemical reactions from a different perspective, such as thermochemistry and reaction ...Experimental Overview · Experimental Results · Schematic Energy Diagram
The second energy profile diagram should be for the reaction with the catalyst. Each energy profile diagram should include: Question: 3. In the last part of the lab, a catalyst was added to the reaction, and it clearly increased the rate of reaction. Sketch two energy profile diagrams. The first energy profile diagram should be for the reaction ...
58 Describe how the potential energy diagram will change if a catalyst is added. Answer--> the activation energy would be lower: 1/06. 16 In a chemical reaction, the difference between the potential energy of the products and the potential energy of the reactants is defined as the
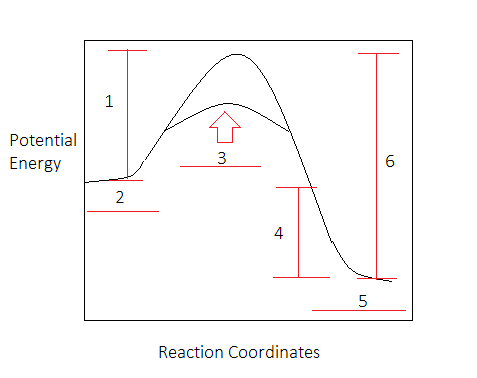
Consider the energy diagram below. A graph of reaction progression on the horizontal axis versus energy on the vertical axis. A line starts flat low on the vertical axis, the flat area is labeled A. It rises sharply to peak, labeled C, then falls a short distance before levelling off, labeled D.

Explain With The Help Of A Potential Energy Diagram That The Catalyst Increases The Rate Of The Reaction Chemistry Shaalaa Com
Energy Changes in Catalytic Reactions . The question may arise as to how does the catalyst enhance the rate of reactions? This can be explained with the help of an energy diagram as in Figure. It has been shown that a catalyzed reaction has lower activation energy than the same reaction taking place in the absence of the catalyst. This is ...
A catalyst does not affect the energy of reactant or product, so those aspects of the diagrams can be ignored; they are, as we would expect, identical in that respect. There is, however, a noticeable difference in the transition state, which is distinctly lower in diagram (b) than it is in (a).
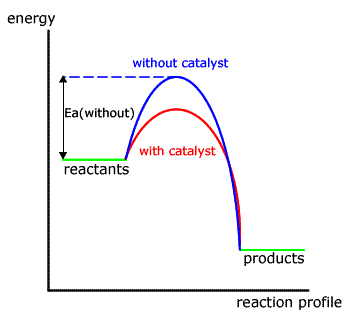
Catalysts speed up a reaction by changing how it proceeds. They intervene to provide an easier way to convert reactants into products. In terms of energy, they provide an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy.We can draw this in an energy profile diagram. whereby the "hump" that represents activation energy, E a is lower.. A lower activation energy means a lower ...
Reaction Coordinate Diagrams It is helpful to visualize energy changes throughout a process on a reaction coordinate diagram like this one for the rearrangement of methyl isonitrile. Reaction Coordinate Diagrams The diagram shows the energy of the reactants and products (and, therefore, E). The high point on the diagram is the transition state.
Why does a potential energy diagram showing the effect of a catalyst on activation energy not move left on the reaction pathway scale (compared to uncatalysed reaction) if a catalyst speeds up reac...
Energy Diagrams: Drawing it Out Why are we learning this? Energy diagrams show how a reaction works. Energy diagrams display The energy of reactants and products The energy needed for a reaction to occur The energy absorbed or released due to reaction Energy Diagram Parts Potential Energy of the reactants Potential Energy of the products Activation Energy E - the amount of energy required to ...
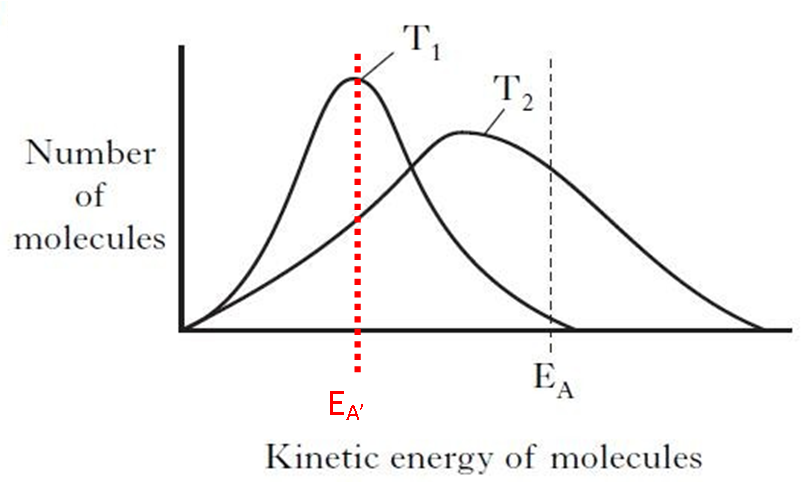
It's time to learn a little more about a chemical reaction. How do molecules have to be arranged and how much energy do they have to collide with? What's a c...

Answer The Following In Brief How A Catalyst Increases The Rate Of Reaction Explain With The Help Of A Potential Energy Diagram For Catalyzed And Uncatalyzed Reactions Chemistry Shaalaa Com
Catalysis is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher reaction . This effect can be illustrated with an energy profile diagram.
Energy diagrams are useful to illustrate the effect of a catalyst on reaction rates. Catalysts decrease the activation energy required for a reaction to proceed (shown by the smaller magnitude of the activation energy on the energy diagram in Figure 7.14 ), and therefore increase the reaction rate.
Adding a catalyst has exactly this effect of shifting the activation energy. A catalyst provides an alternative route for the reaction. That alternative route has a lower activation energy. Showing this on an energy profile: A word of caution! Be very careful if you are asked about this in an exam. The correct form of words is
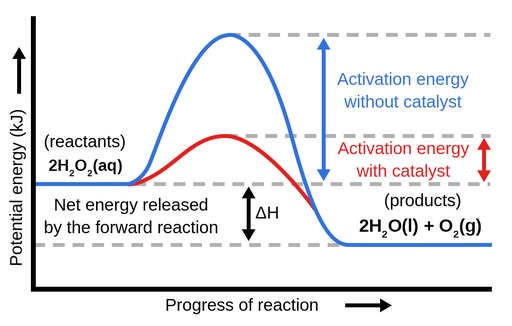
Label the energy diagram and answer the question that follows% (1). The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide is exothermic. The reaction is catalyzed by iodide ion. The equation for the uncatalyzed reaction is. 2 H 2 O 2 (l) 2 H 2 O (l) + O 2 (g) Sketch a possible graph for this reaction, first without a catalyst and then with a catalyst.
Thermochemistry and Energy Diagrams. The activation energy ( Ea) of this reaction is. - 80 kJ. 240 kJ. 40 kJ. 160 kJ. 80 kJ.
Consider the following energy diagram showing a reaction with and without a catalyst.. High B D D Energy А Low Start of reaction End of reaction Fill in the blank with the appropriate letter (A, B, C, etc.). The heat of reaction would be represented by ; Question: Consider the following energy diagram showing a reaction with and without a ...
Diagrams like this are described as energy profiles.In the diagram above, you can clearly see that you need an input of energy to get the reaction going. Once the activation energy barrier has been passed, you can also see that you get even more energy released, and so the reaction is overall exothermic.
Ppt Topic 06 Kinetics 6 2a Collision Theory 6 2b Maxwell Boltzmann Catalysts Powerpoint Presentation Id 2604073

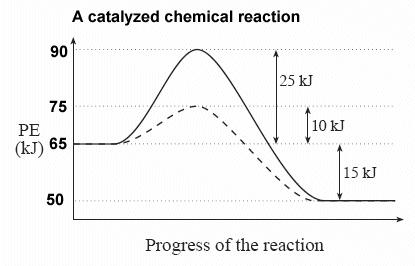
15 The Energy Diagram Represents A Chemical Reaction Carried Out Both With A Catalyst And Without A Catalyst What Is The Enthalpy Change For The Catalysed Reaction A 125kj Mol B


















0 Response to "39 energy diagram with catalyst"
Post a Comment