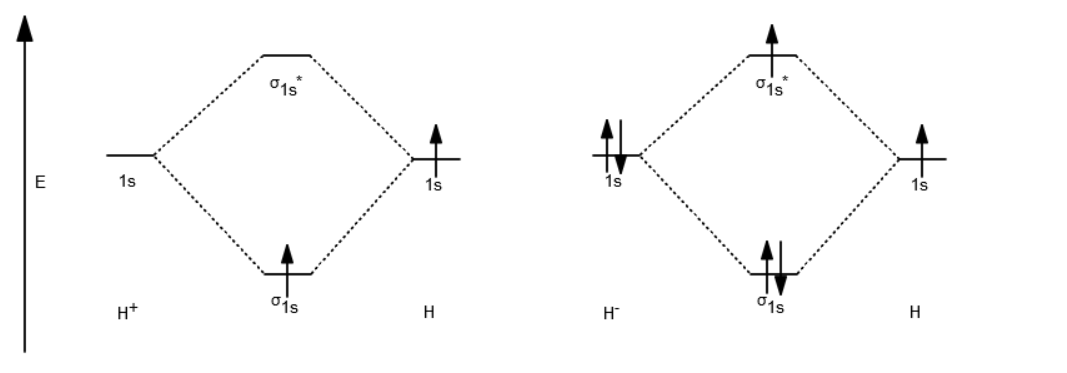
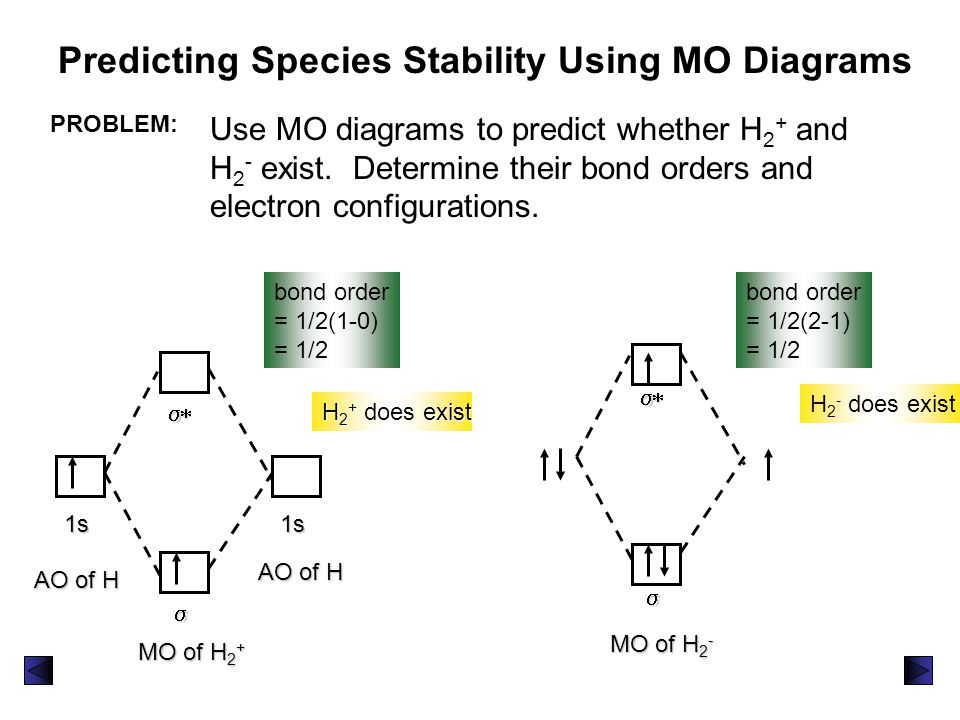
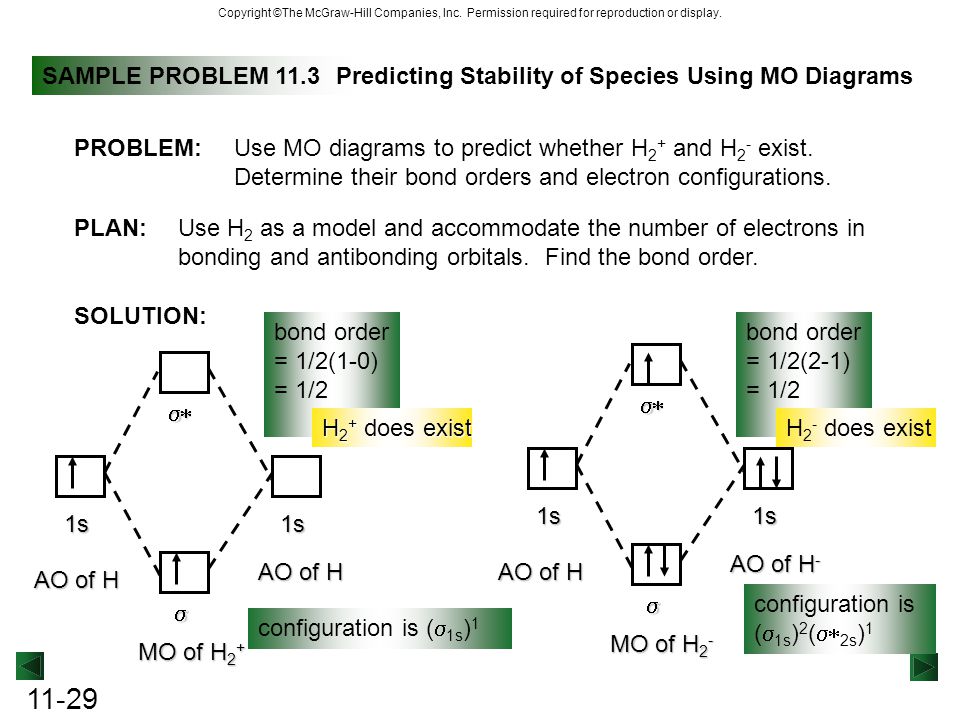
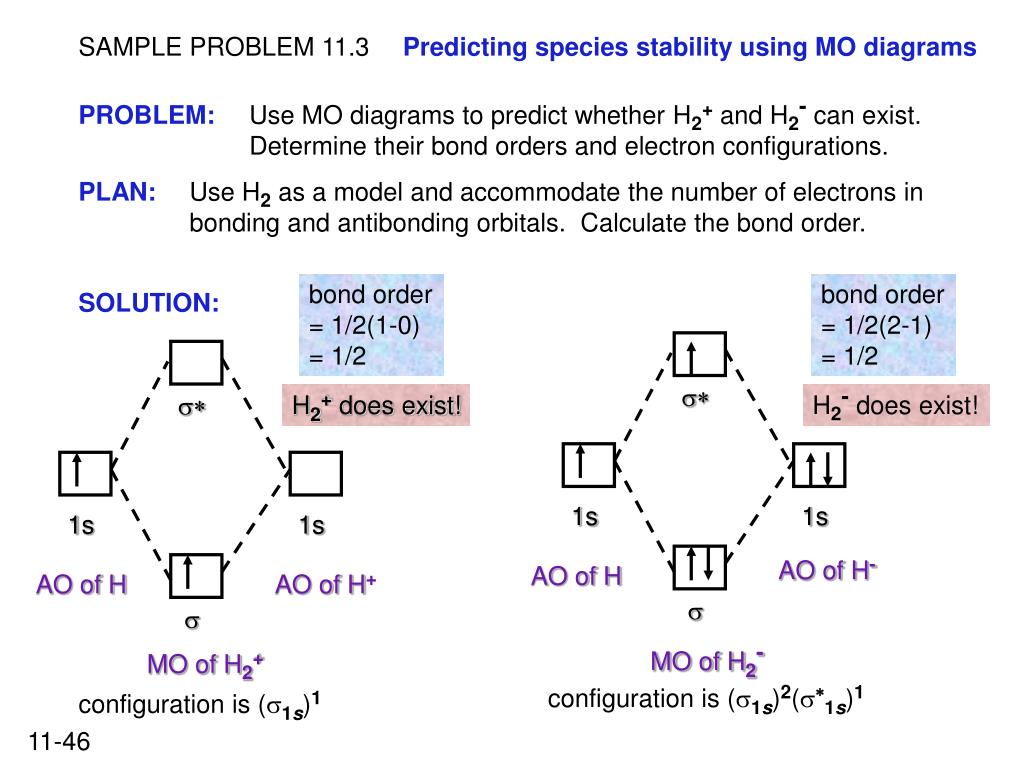
37 use the mo diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether h2- exists.
Use an MO diagram to find the bond order and predict whether H2- exists. Molecular orbitals: Molecular orbitals are gotten by joining the nuclear orbitals on the particles in the atom. Problem Details. Use an MO diagram to find the bond order and predict whether H 2− exists. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Bond Order Concept Videos. All Chemistry Practice Problems MO Theory: Bond Order Practice Problems. Q. Draw Lewis structures and MO diagrams for CN+, CN, and CN-. According to the Lewis model, which species is ...
Valence Bond Model vs. Molecular Orbital Theory . Because arguments based on atomic orbitals focus on the bonds formed between valence electrons on an atom, they are often said to involve a valence-bond theory.. The valence-bond model can't adequately explain the fact that some molecules contains two equivalent bonds with a bond order between that of a single bond and a double bond.

Use the mo diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether h2- exists.
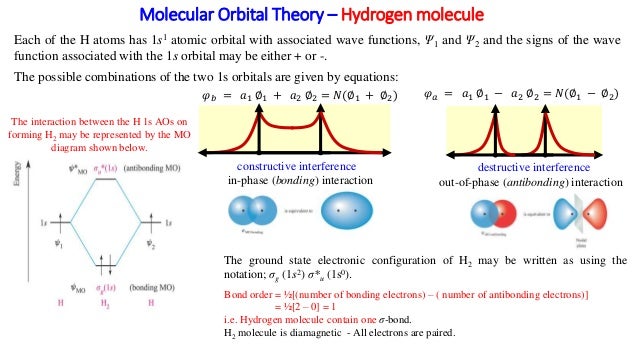
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H–F nb σ σ* Energy H –13.6 eV 1s F –18.6 eV –40.2 eV 2s 2p So H–F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms; in diatomic nitrogen (N≡N) for example, the bond order is 3, while in acetylene (H−C≡C−H), the bond order between the two carbon atoms is 3 and the C−H bond order is 1. Bond order indicates the stability of a bond. In a more advanced context, bond order does not need ... For this, we need to determine the bond order for each species. The bond order tells us the stability of a bond: a higher bond order means the bond is more stable. Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons present. Step 2: Draw the molecular orbital diagram. Step 3: Calculate the bond order of the molecule/ion.
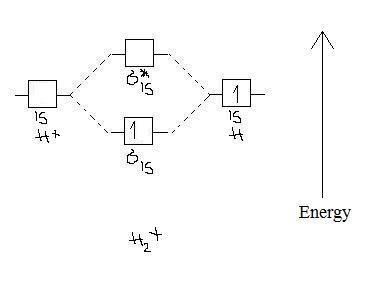
Use the mo diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether h2- exists.. Question: Use an MO diagram to find the bond order and predict whether H2- exists. This problem has been solved! See the answer ... 2) Stability of molecules in terms of bond order. Bond order is defined as half of the difference between the number of electrons present in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Bond Order = ½ ( N b – Na) The molecule is stable if N b > Na ie. bond order is positive. The molecule is unstable if N b < Na i.e. the bond order is negative or zero. Use the MO diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether H2 exists. Enter the bond order as a decimal number, eg. 0.5. 1.0, 1.5, etc ?* ???Y-average energy H2ls ; Question: Use the MO diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether H2 exists. Enter the bond order as a decimal number, eg. 0.5. 1.0, 1.5, etc ?* ???Y-average ... 1 Apr 2017 · 1 answerI'm assuming you mean H−2 vs. H+2 . Well, build the molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, ...
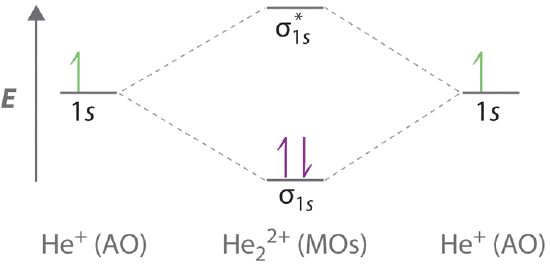
Bond order is a simple calculation, based on the number of bonding versus antibonding electrons ... There would be four electrons to fill into our molecular orbital diagram and that would force us to fill in the bonding sigma MO and the anti-bonding sigma-star MO. What we gain in the bonding sigma MO, we lose in the anti-bonding sigma-star MO. - The MO diagram typically includes valence-shell molecular orbitals only. - The MO diagram can be used to calculate bond order and predict the stability of a species. - The MO diagram shows the relative energy and number of electron in each MO. 2 answersIn order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2- is to ... By this trick you can find out the bond order of any molecules given in +2 ... 3 Feb 2021 — Figure 3: Schematic represenation of antibonding molecular orbital σ*(1s) ... Bond order = 1/2 (#e- in bonding MO - #e- in antibonding MO).
For this, we need to determine the bond order for each species. The bond order tells us the stability of a bond: a higher bond order means the bond is more stable. Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons present. Step 2: Draw the molecular orbital diagram. Step 3: Calculate the bond order of the molecule/ion. Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms; in diatomic nitrogen (N≡N) for example, the bond order is 3, while in acetylene (H−C≡C−H), the bond order between the two carbon atoms is 3 and the C−H bond order is 1. Bond order indicates the stability of a bond. In a more advanced context, bond order does not need ... MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H–F nb σ σ* Energy H –13.6 eV 1s F –18.6 eV –40.2 eV 2s 2p So H–F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
9 8 Molecular Orbital Theory Does Not Predict A Stable Diatomic Helium Molecule Chemistry Libretexts

M O Bonding Beyond The Oxo Wall Spectroscopy And Reactivity Of Cobalt Iii Oxyl And Cobalt Iii Oxo Complexes Andris 2019 Angewandte Chemie International Edition Wiley Online Library

Use Molecular Orbital Theory To Predict Whether Or Not Each Of The Following Molecules Or Ions Should Exist In A Relatively Stable Form Li 2 Li 2 2 C 2 2 Be 2 2 A Will Exist















0 Response to "37 use the mo diagram given to find the bond order and predict whether h2- exists."
Post a Comment