36 action potential diagram labeled
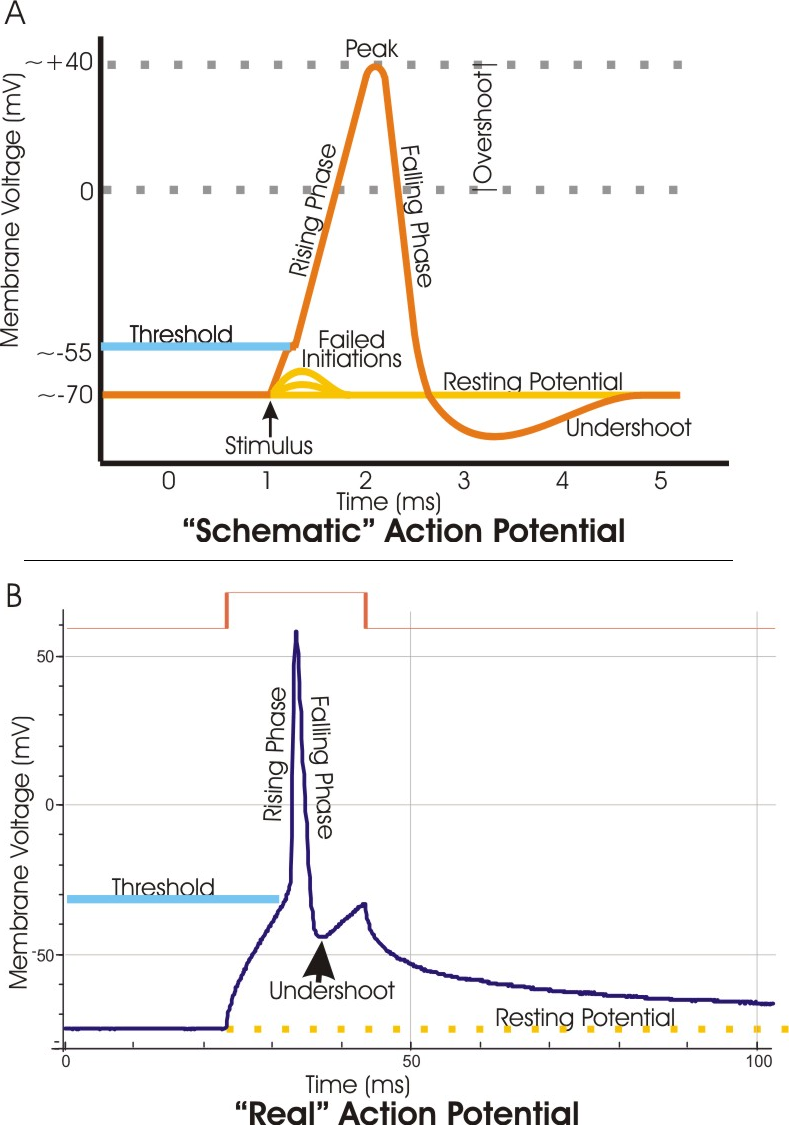
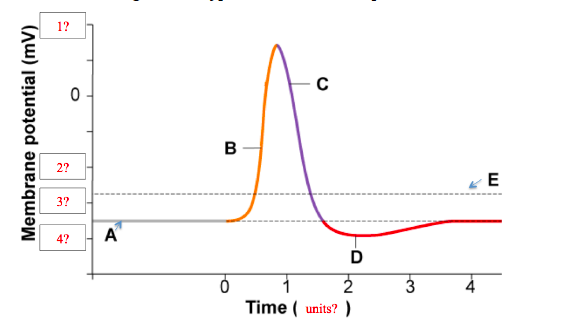
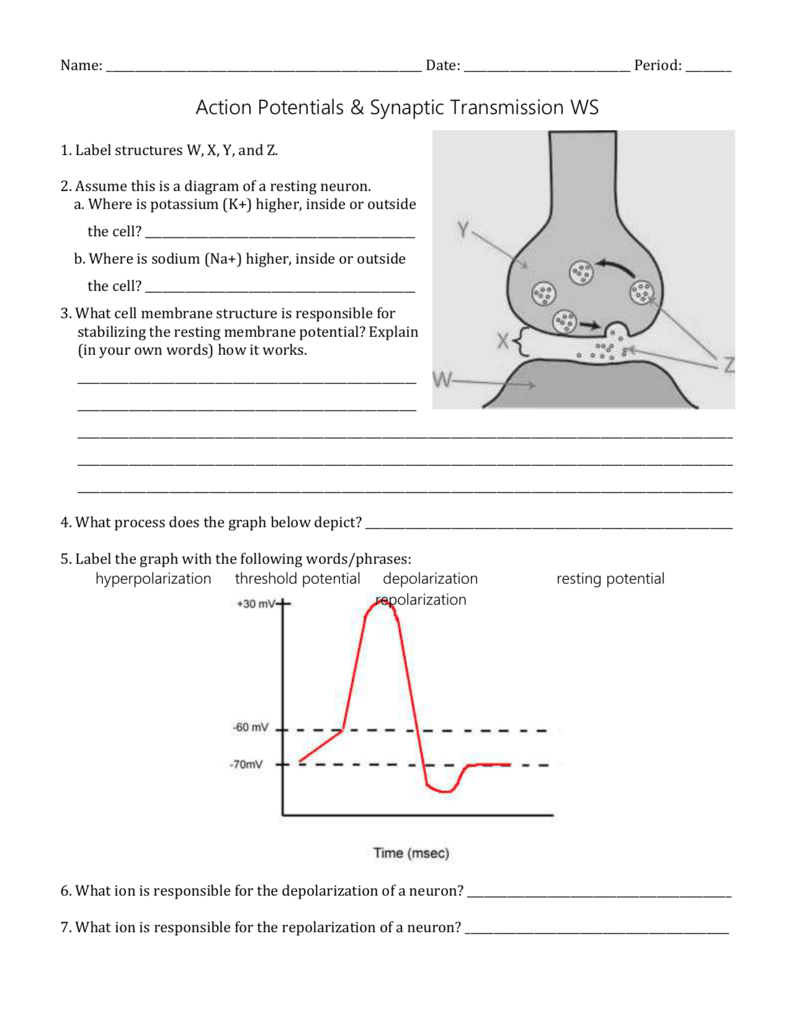
The ions, in this case, are cations of sodium, calcium, and potassium. These two diagrams each show a channel protein embedded in the cell membrane. In the. A ... If depolarization reaches -55 mV, then the action potential continues and runs all the way to +30 mV, at which K + causes repolarization, including the hyperpolarizing overshoot. Also, those changes are the same for every action potential, which means that once the threshold is reached, the exact same thing happens.
The action potential thus moves along the axon as a wave of depolarization traveling away from the cell body. • Label where the action potential is in these two diagrams: Page 17. Conduction Velocity Depends on Diameter and Myelination of the Axon • Conduction velocity is the speed with which an action potential is propagated.

Action potential diagram labeled
Compound Action Potential . The top trace in the diagram opposite shows the A-alpha only peak over a longer time course. The stimulus necessary to initiate an action potential in small axons is larger than for larger diameter axons. As the stimulus is increased, smaller axons begin to generate their action potential, and these potentials are ... Action potential curve and phases (diagram) Hypopolarization is the initial increase of the membrane potential to the value of the threshold potential.The threshold potential opens voltage-gated sodium channels and causes a large influx of sodium ions. EKG or ECG waveform parts are explained clearly to make EKG interpretation easy. Learn the meaning of each component of an EKG wave with this step-by-step labeled diagram of the conduction system of the heart. Provides information on atrial depolarization and the P wave, ventricular depolarization a
Action potential diagram labeled. What has been described here is the action potential, which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in Figure 12.5.7. It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication. The change in the membrane voltage from -70 mV at rest to +30 mV at the end of depolarization is a 100-mV change. When that voltage becomes less negative, the channel begins to allow ions to cross the membrane (Figure 4). This is a two part diagram. Both diagrams show a ... Draw the generic action potential curve for a nerve, and briefly explain the curve. Voltage-gated sodium channels are _____. a. closed at -60 mV. b. open at -60 mV. c. inactivated at -70 mV. d ... An action potential is a rapid rise and fall in voltage or membrane potential across a cellular membrane. Explore action potential chart/graph for more ...
E. In the diagram, which labeled structure is the marginal branch of the right coronary artery? B. In the diagram, which labeled structure is the circumflex branch of the left coronary artery? D. Describe what is happening during the phase of the cardiac action potential labeled 2 in the diagram. Phase 2 is the plateau phase which occurs due to ... In physiology, an action potential (AP) occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls: this depolarization then ...Membrane potential · Threshold potential · Cardiac action · Saltatory conduction Quiz & Worksheet Goals. You can see how much you know about: A segment that shows a phase where the neuron is less likely to fire an action potential. The normal membrane potential of the cell ... Neuron action potentials: The creation of a brain signal. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Email. Neuron membrane potentials.
The Action Potential. Resting membrane potential describes the steady state of the cell, which is a dynamic process that is balanced by ion leakage and ion pumping. Without any outside influence, it will not change. To get an electrical signal started, the membrane potential has to change. 13 Aug 2020 — Key Terms · action potential.: A brief reversal of membrane potential. · repolarization: Also called the falling phase, · absolute refractory ... EKG or ECG waveform parts are explained clearly to make EKG interpretation easy. Learn the meaning of each component of an EKG wave with this step-by-step labeled diagram of the conduction system of the heart. Provides information on atrial depolarization and the P wave, ventricular depolarization a Action potential curve and phases (diagram) Hypopolarization is the initial increase of the membrane potential to the value of the threshold potential.The threshold potential opens voltage-gated sodium channels and causes a large influx of sodium ions.
Compound Action Potential . The top trace in the diagram opposite shows the A-alpha only peak over a longer time course. The stimulus necessary to initiate an action potential in small axons is larger than for larger diameter axons. As the stimulus is increased, smaller axons begin to generate their action potential, and these potentials are ...
If There S A Mutation Causing The Resting Membrane Potential Of A Neuron To Be 50 Rather Than 70 Would The Height Of The Action Potential Graph Be Different Quora

Nerve Action Potential Nerve Signals Are Rapid Changes In The Membrane Potential That Spread Rapidly Along The Nerve Fiber Membrane By Action Potential Ppt Download

Diagram Of Synaptic Transmission Okinawa Institute Of Science And Technology Graduate University Oist
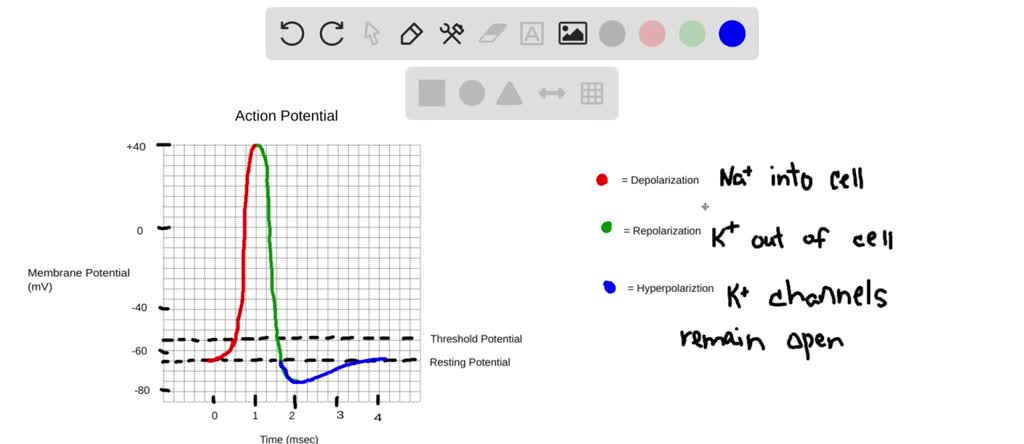
Solved Draw And Label An Action Potential Including Which Ions Are Moving Through The Membrane And In Which Direction They Are Flowing In Each Phase How Does Each Iona S Conductance Change With Each
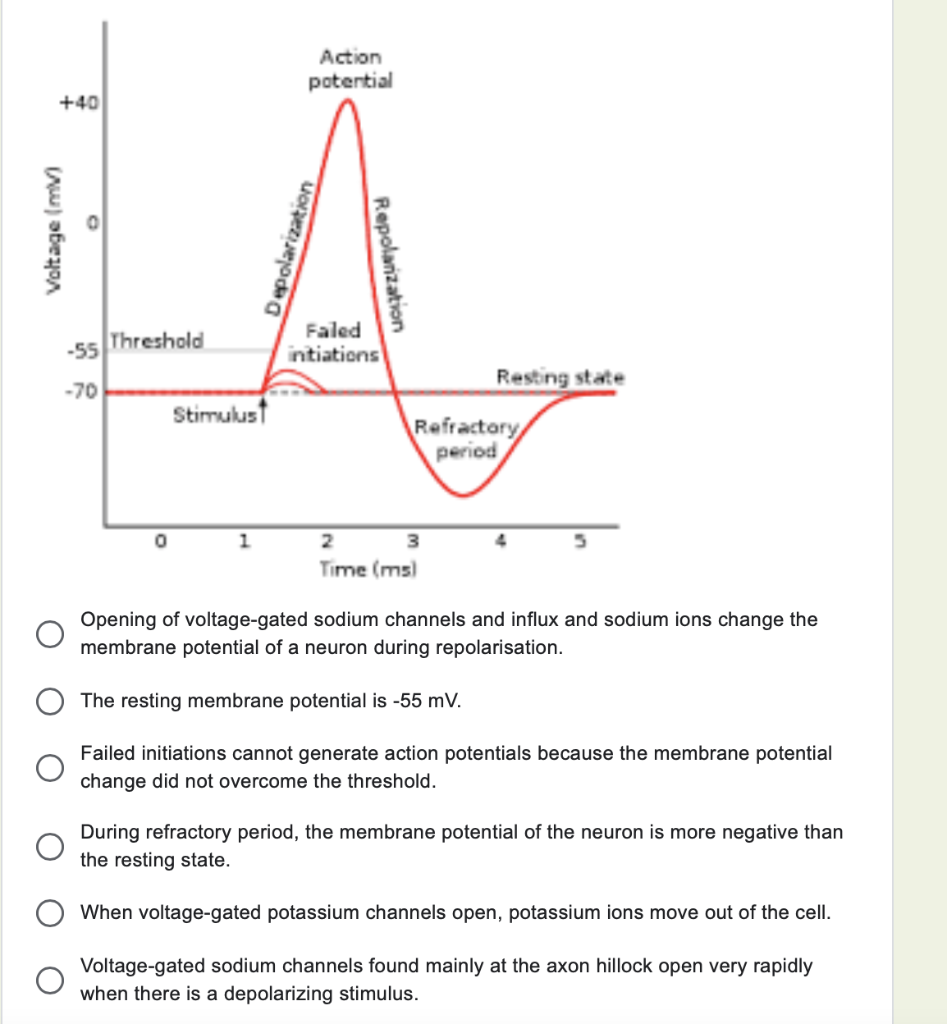




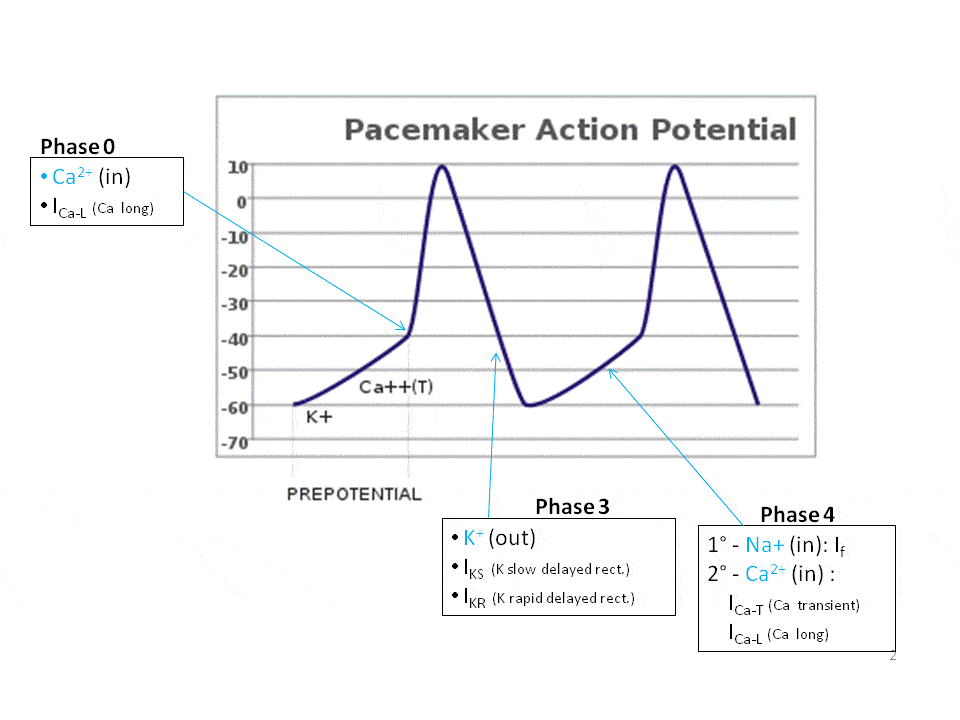
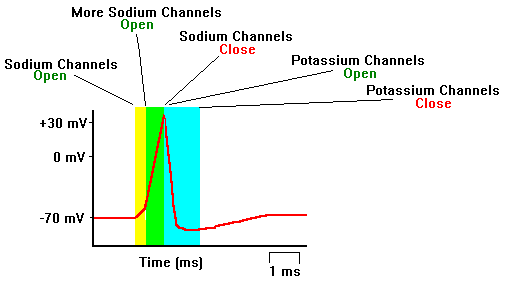



:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11524/Action_potential_ions.png)


:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11522/Action_potential_curve.png)



:format(jpeg)/images/article/en/action-potential/pJRivfYxfsvi7mIh8xRQg_Action_potential_curve.png)







0 Response to "36 action potential diagram labeled"
Post a Comment