35 co molecular orbital diagram
23:32In this video we are discuss about MO Diagram and Characteristics of CO Molecule MO diagrams of ...19 Oct 2019 · Uploaded by Chem Academy Molecular orbital diagram of CO and charge localisation. Ask Question Asked 1 year, 5 months ago. Active 1 year, 5 months ago. Viewed 110 times ... My question concerns the interpretation of the Molecular Orbital of CO. I think I find it clear how you build it but I have some concerns about how you rationalize it.
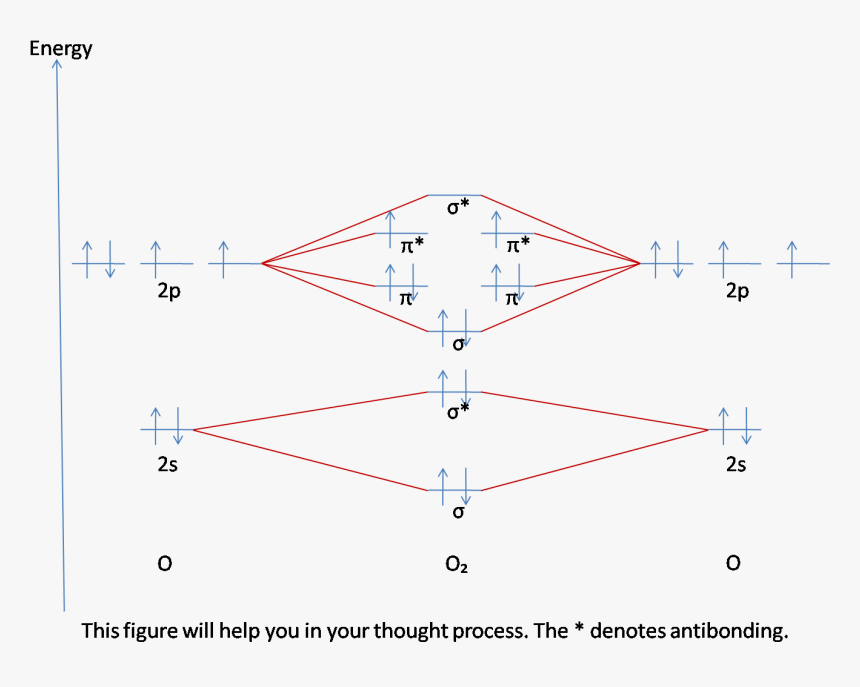
18.03.2018 · Also see here... Bond order for "NO"^+ Order by bond length: "NO", "NO"^(+), "NO"^(-) Is "CO" a Lewis acid? "O"_2 is well-known to be paramagnetic, and it is one of the successes of molecular orbital theory. You can see that "CO" is not (as it has zero unpaired electrons), but "NO" is (it has one unpaired electron). Well, the MO diagram for "O"_2 is: The bond order is already calculated in the ...

Co molecular orbital diagram
The Molecule · CO is a very stable 10-valence-electron molecule, isoelectronic with [CN]– and with N2, which has a slightly lower bond dissociation energy than ... HÜCKEL MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY In general, the vast majority polyatomic molecules can be thought of as consisting of a collection of twoelectron bonds between pairs of atoms. So the qualitative picture of σ and πbonding and antibonding orbitals that we developed for a diatomic like CO can be carried over give a qualitative starting point for describing the C=O bond in acetone, for ... 06.11.2021 · H2CO Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram. So far, we have covered many structural aspects of the formaldehyde molecule by using hybrid orbitals and VSEPR theory. In addition, we have a molecular orbital theory (MOT), the most in-depth analysis of chemical bonding using quantum mechanical properties. MOT describes electron density and distribution in molecules similar to atomic …
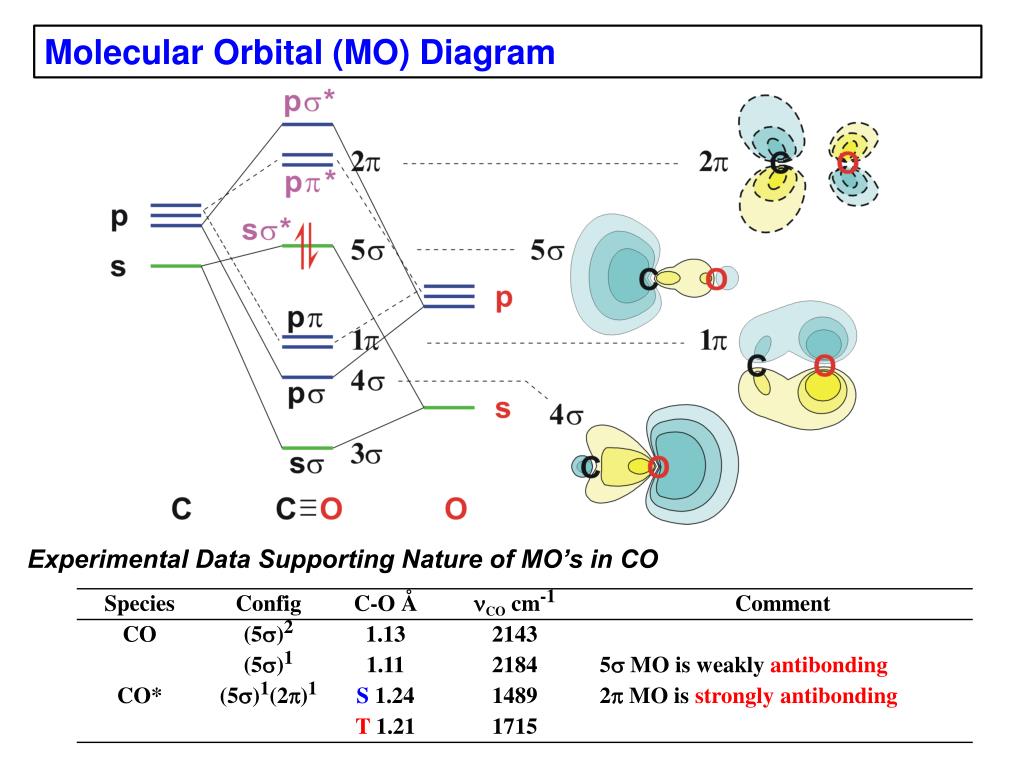
Co molecular orbital diagram. Molecular Orbital Diagram of CO. TAGS; Molecular Orbital Diagram; Previous article Wohl-Ziegler Bromination. Next article Molecular Orbital Diagram of NO. All About Chemistry. https://allaboutchemistry.net. Hello Reader! Thanking for reading this post, If you find it to be informative, pls share it and visit our website. 04.11.2021 · Phosgene is a colorless gaseous compound known as carbonyl chloride and has a molecular weight of 98.92 gram/mol. It is non-flammable in nature and bears a suffocating odor. It has a boiling point (b.p.) of around 8.3 0C. Phosgene is acyl chloride. The below reaction shows the process of formation of COCl2 from CO and Cl2: CO + Cl2 —> COCl2 (exothermic reaction, temp between 50 … The energy diagram for this process is shown below. The hybridized orbitals are higher in energy than the s orbital, but lower in energy than the p orbitals. atomic orbitals hybridized orbitals Carbon has 4 valence electrons. Add these electrons to the atomic and molecular orbitals. This hybridization gives tetrahedral geometry. The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide, CO, is show below. Which overlap is strongest? During the axial overlap of p-p orbitals, the electron density increases around the axis, so the bond formed is the strongest. Therefore, the strongest bond formed is when p-p orbital overlap occurs. Final answer: The correct answer is Option B- 2p ...
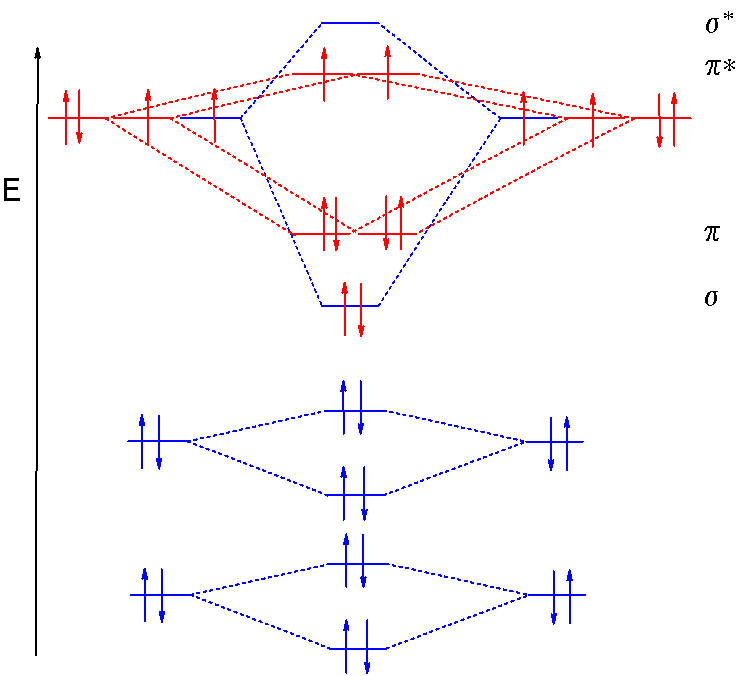
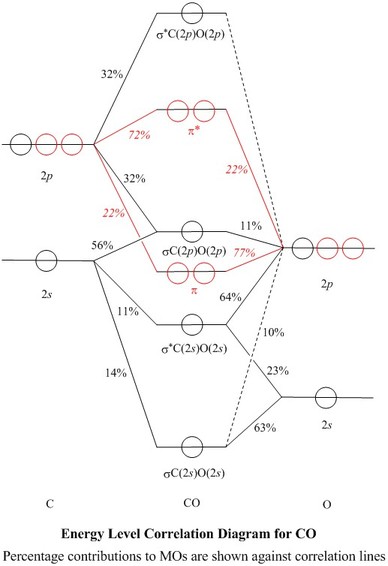
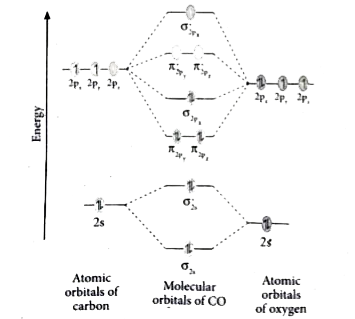
The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide is very similar to that of molecular nitrogen. Carbon, with 4 valence electrons, and oxygen with 6 valence ... Orbital-orbital Interactions and Symmetry Adapted Linear Combinations; ... Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. CONTROLS > Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. In carbon monoxide (CO, isoelectronic with dinitrogen) the oxygen 2s orbital is much lower in energy than the carbon 2s orbital and therefore the degree of ... 19 Mar 2021 — Carbon monoxide MO diagram ... Carbon monoxide is an example of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule where both atoms are second-row elements. The ...
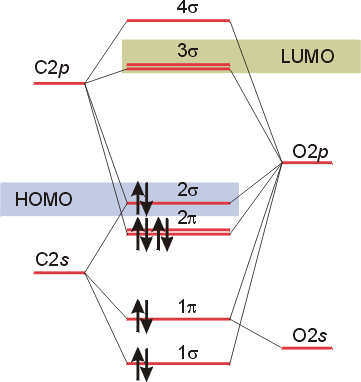
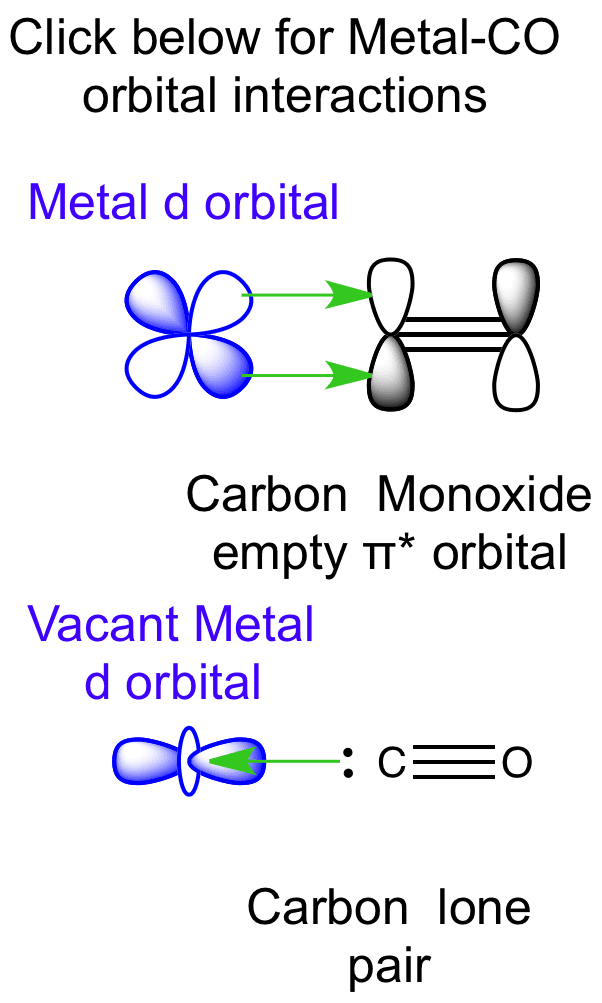
12-12 This video describes the molecular orbital theory diagram of CO, placing emphasis on how MO theory differs for homo and heteronuclear diatomics A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. . combinations such as CO and NO show that the 3σg MO is higher in energy. Mulliken came up with theory known as Molecular Orbital Theory to explain questions like above. Point out key differences between the diagrams and use the diagram to explain why $\ce{CO}$ acts as a two-electron donor through carbon rather than through oxygen. Understandably, the key difference between these molecules is that $\ce{CO}$ is heteronuclear, and thus will have differences in energy between the molecular orbital and the atoms. According to Merriam-Webster and the Online Etymology Dictionary, the word "molecule" derives from the Latin "moles" or small unit of mass.. Molecule (1794) – "extremely minute particle", from French molécule (1678), from New Latin molecula, diminutive of Latin moles "mass, barrier". A vague meaning at first; the vogue for the word (used until the late 18th century only in Latin form) can ...
In the case of CO, the 2s atomic orbital on Oxygen is much lower in energy than the 2s atomic orbital in carbon. The discrepancy in energies allows the π2px & π2py bonding molecular orbitals to sink lower in energy than the “ σ*2s MO” in the MO diagram of CO.
In chemistry, orbital hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals (with different energies, shapes, etc., than the component atomic orbitals) suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory.For example, in a carbon atom which forms four single bonds the valence-shell s orbital combines with three ...

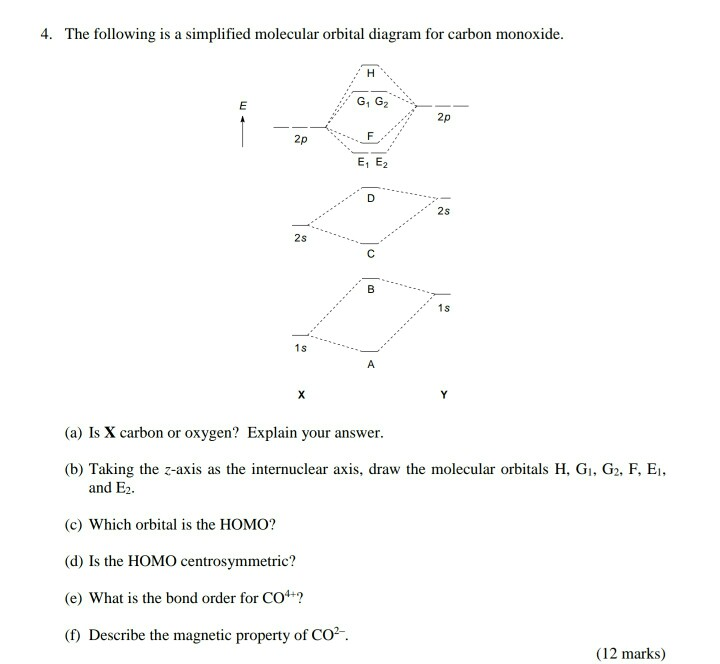
Question 13 Molecular Orbitals For Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules Using The Above Molecular Orbital Diagram For Co Homeworklib
Molecular orbital diagram of co. Tricky chemistry basics. A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao method in particular. The course introduces the three key spectroscopic ...
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
06.11.2021 · H2CO Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram. So far, we have covered many structural aspects of the formaldehyde molecule by using hybrid orbitals and VSEPR theory. In addition, we have a molecular orbital theory (MOT), the most in-depth analysis of chemical bonding using quantum mechanical properties. MOT describes electron density and distribution in molecules similar to atomic …
HÜCKEL MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY In general, the vast majority polyatomic molecules can be thought of as consisting of a collection of twoelectron bonds between pairs of atoms. So the qualitative picture of σ and πbonding and antibonding orbitals that we developed for a diatomic like CO can be carried over give a qualitative starting point for describing the C=O bond in acetone, for ...
The Molecule · CO is a very stable 10-valence-electron molecule, isoelectronic with [CN]– and with N2, which has a slightly lower bond dissociation energy than ...












0 Response to "35 co molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment