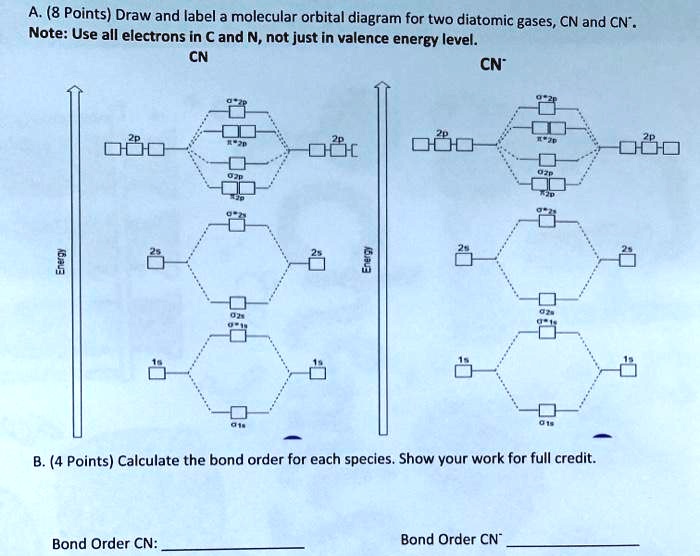
36 cn molecular orbital diagram
Answer (1 of 8): You didn't specify the kind of theory you are considering. VB theory (Lewis dots) will give a different bond order than MO theory. In VB theory, you end up getting three bonds and a pair of electrons on one atom, C\underline{=}N: so three (Or maybe four if you put the lone pair ... Molecular orbital diagram for oxygen gas (o2).fill from the bottom up, with 12 electrons total.bonding order is 2, and it is paramagnetic.sigma2s(2),sigma2s*. Building molecular orbital diagrams for homonuclear and heteronuclear diatomic molecules; (1) e n = 13.6 z e f f 2 n 2 e v. Six lgo (ligand group orbitals) that have symmetries that match ...
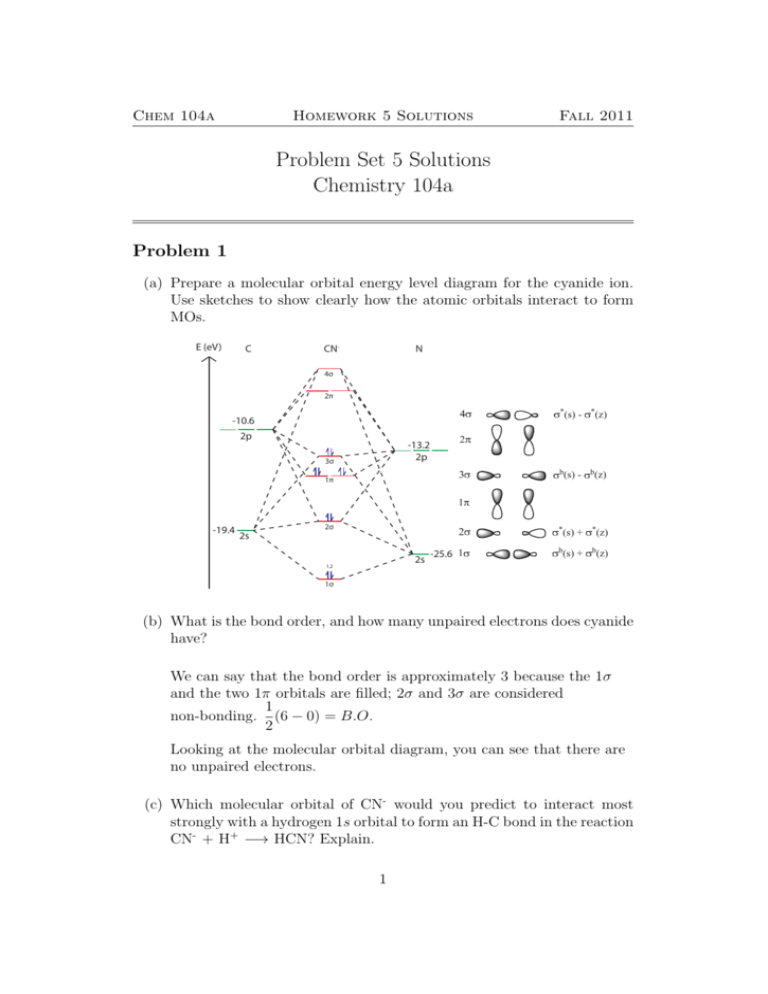
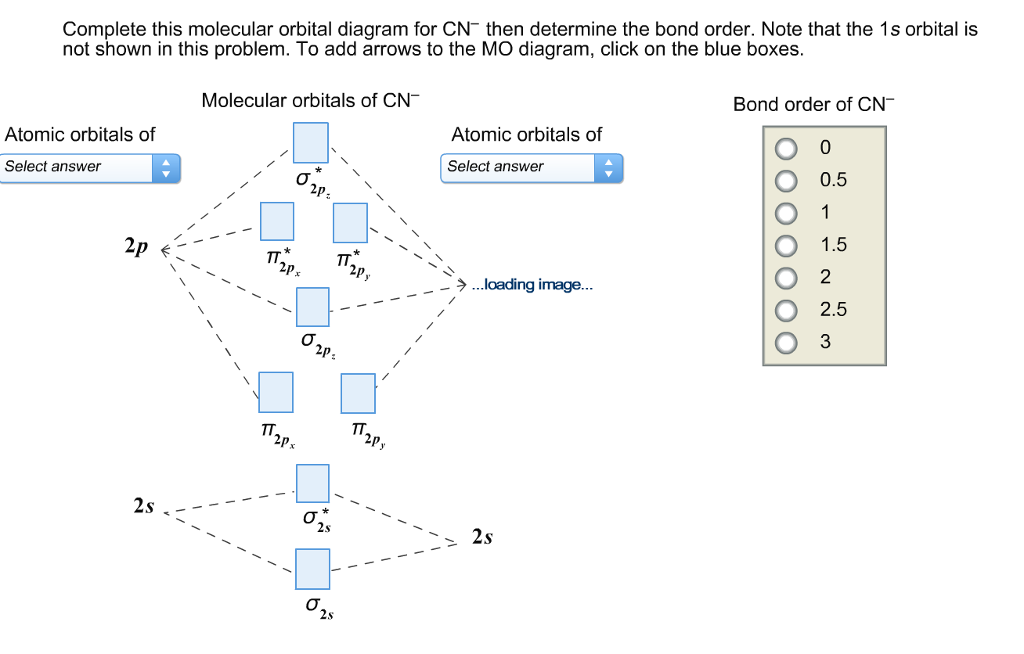
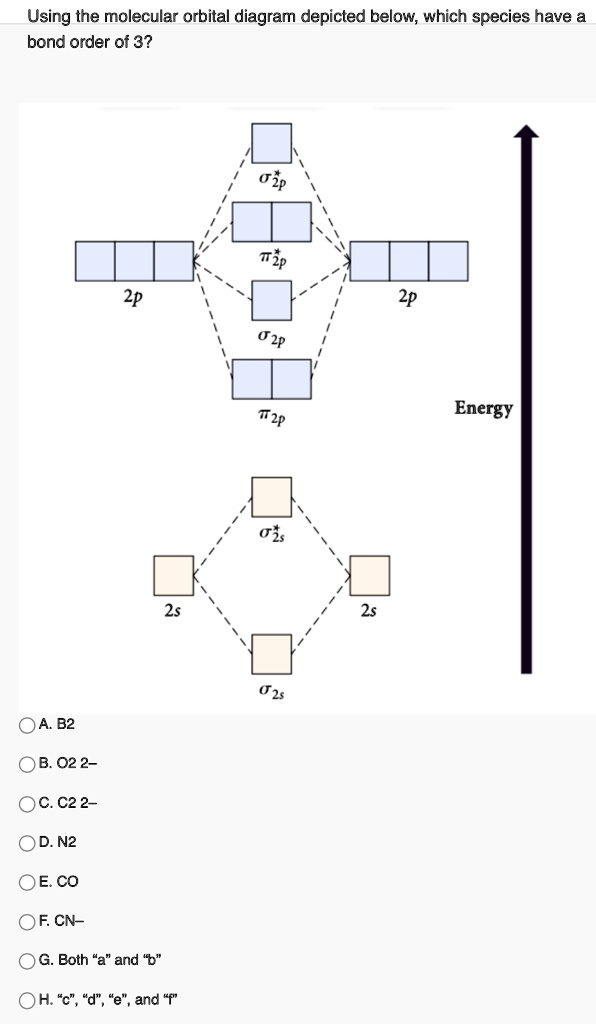
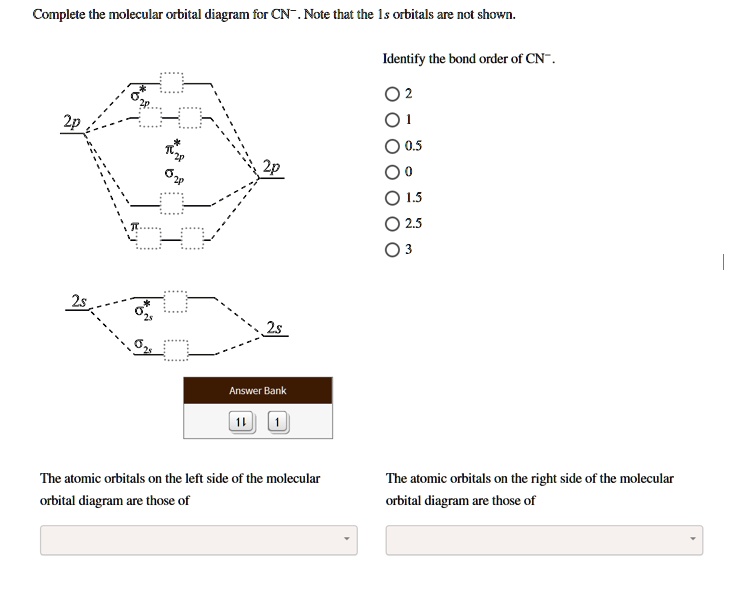
Bond order = n bonding electrons − n antibonding electrons 2. Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There are 8 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, therefore B. O. = 8 − 2 2 = 3. Here's a guide on how to construct MO diagrams, in case you need help. 57.6K views.

Cn molecular orbital diagram
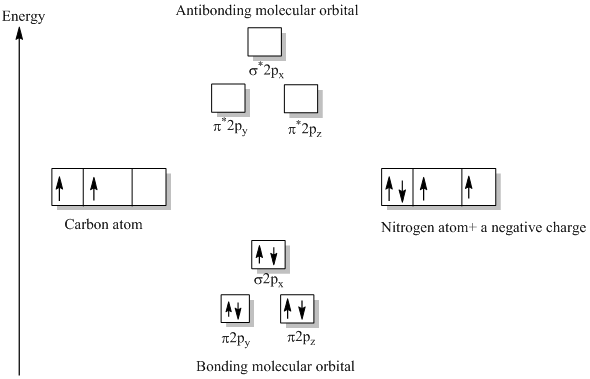
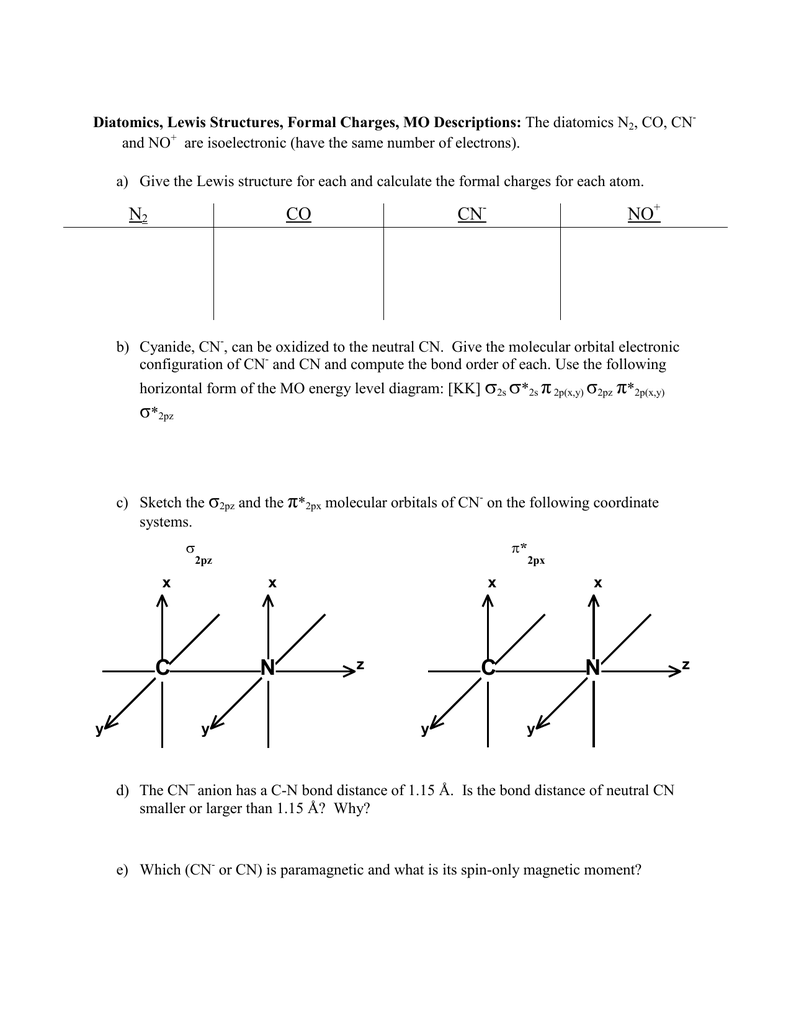
The occupied molecular orbitals and conduction molecular orbitals contain DOS. In bulk particles, DOS is a continuous function of energy, while in CNTs (and other 1D nanoparticles), DOS is made of discontinuous spikes, ascending and then descending sharply—the Van hove singularities ( Figure 39 ; v1, v2 and v3 are DOS for HOMO and c1, c2 and c3 for LUMO). The molecular orbital energy level diagram provided shows the energies of the orbitals for the valence electrons in the free radical CN. Indicate on this diagram the ground state electronic configuration of CN using the arrow notation for electron spins. * C has 4 valence electrons and N has 5 valence electrons, giving a total of 9 Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of cn. 1. find the valence electron of each atom in the cn molecule. clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. find if the molecule homo nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. clearly, cn is hetero orbital. 3.
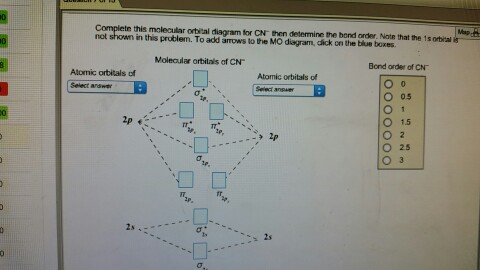
Cn molecular orbital diagram. 3 Jan 2021 — Just as with atomic orbitals, we create an energy-level diagram by listing the molecular orbitals in order of increasing energy. Use the molecular orbital diagram to figure out the electronic configuration for CN. Which of the following statements is correct?a) CN is diamagnetic.b) CN− is paramagnetic.c) If an electron is removed to give CN+, the bond order increases.d) The π*2p orbital is the highest energy orbital containing an electron in CNe) If an electron is added to give CN−, the bond length decreases. 29 Cn Molecular Orbital Diagram Wiring Diagram List. Create a molecular orbital diagram of the linear bef2 molecule. for be use a basis set that consists of the 2s, 2px, 2py, 2pz atomic orbitals. unlike in question 4. i am wondering if my molecular orbital for bef2 is correct: i too don't know how to get a picture in the mo diagram that you show looks okay. Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN. O2 01 OOOOO 25- 0 2s Answer Bank The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of.
Molecular orbital theory is also able to explain the presence of Figure \(\ PageIndex{6}\): Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for HCl. to describe the bonding in the cyanide ion (CN −). mix atomic orbitals on different atoms to get Molecular Orbitals. The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion). molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest a double bond. c. The 2s, 2s *, 2p, and 2p * orbitals exhibit C v symmetry, with the NF bond axis the infinite-fold rotation axis. The 2p and 2p * orbitals exhibit Cs symmetry. The latter do not possess C2 rotation axes coincident to the Molecular Orbital Diagram. Molecular Orbital Theory is slightly different from VBT and orbital hybridization. Here, AOs from different atoms inside the molecule can come together to form molecular orbitals or MOs. Therefore, valence electrons are shared inside the molecule. The electronic configuration of both C and N are as follows: Carbon (atomic no:6) We're being asked to complete the molecular orbital diagram of CN-and then determine the bond order. To do so, we shall follow these steps: Step 1: Calculate the total valence electrons present. Step 2: Fill the molecular orbitals with electrons. Step 3: Determine the bond order. Step 1: Calculate the total valence electrons present. Group Valence Electrons
Figure 3-1 Molecular orbitals of Cr(CO) 6 (Only interactions between Ligand (σ- and π*) orbitals and metal d-orbitals are shown.) Simplified MO energy level diagram for Cr(CO) 6. Note the empty π* orbitals. Only three are involved in overlap with metal d orbitals. This video is about MO Diagram #3 - CN- Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3. [math]\text{Bond order} = \frac{n_{\text{bonding electrons}}-n_{\text{antibonding electrons}}}{2}[/math] Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There ...
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
The hybrid orbitals are more prominent outward so that their ability to overlap is stronger than that of normal orbitals. Molecular Formula: A chemical formula is a brief way of expressing the number and type of atoms that make up a particular chemical compound.
CN + has 12 electrons (6 from carbon, 7 for nitrogen, -1 for positive charge). So, we have configuration. (σ1s) 2,(σ ∗1s) 2,(σ2s) 2,(σ ∗2s) 2,(π) 4. So, bond order = 21. . (a−b) a is the number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals and b is the number of electrons in antibondng molecular orbitals. Bond Order = 21.
Cyanide (CN-) lewis structure, Molecular orbital diagram, bond order, formal charge, and its hybridization Home > Chemistry Article > CN- lewis structure and its molecular orbital diagram Cyanide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CN‾ ion.
The molecular orbital configuration of C N + is K K σ (2 s) 2, σ ∗ (2 s) 2, π (2 p x ) 2, π (2 p y ) 2. Bond order is 2 . All the electrons are paired and ion is diamagnetic.
The π orbitals largely remain untouched by this. From there we can use the fact, that carbon monoxide is isoelectronic with dinitrogen. We have to skew the energies of the atomic orbitals. The energy of the atomic orbitals is decreasing from left to right in the period; therefore carbon will have slightly elevated levels and oxygen's are lowered.
Jul 09, 2018 · Cyanide Molecular Orbital Diagram. MO Theory: the bonding orbital will be lower in energy, the an7bonding The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion ). The molecular orbital diagram of (if order of molecular orbital is like that in) is as shown below. We must remember that total number of electrons in ...
How to make molecular Orbital diagramhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UYC-ndQ6Lww&t=6s
MO Diagram of CN-<. Theoretical chemistry research group focusing on development of methods, and calculations in the areas of ionic liquids, photochemistry and catalysis. step 9. Molecular Orbital Mixing. More detail was added to this answer in response to input and questions from students in the class of 2008.
Hybridization of CN- = 0.5 ( 2+1-0+1) = 2 The number corresponds to sp hybridization. Thus both atoms, that is, Carbon and Nitrogen, have sp hybridization in CN-. The sp orbitals of both these atoms overlap with each other and form triple bonds. CN- Molecular Geometry
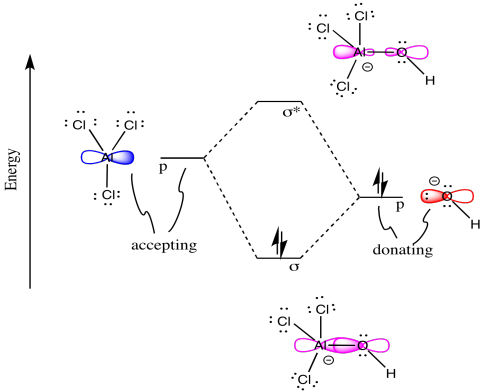
As Geoff already pointed out in the comments, the connection between a molecular orbital theory (MO) point of view and a Lewis picture (LT) is tenuous at best. Maybe the best example for this is the mentioned $\ce{{}^{-}CN}$ and obviously the isoelectronic $\ce{CO}$. But there are many more molecules.
Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of cn. 1. find the valence electron of each atom in the cn molecule. clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. find if the molecule homo nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. clearly, cn is hetero orbital. 3.
The molecular orbital energy level diagram provided shows the energies of the orbitals for the valence electrons in the free radical CN. Indicate on this diagram the ground state electronic configuration of CN using the arrow notation for electron spins. * C has 4 valence electrons and N has 5 valence electrons, giving a total of 9
The occupied molecular orbitals and conduction molecular orbitals contain DOS. In bulk particles, DOS is a continuous function of energy, while in CNTs (and other 1D nanoparticles), DOS is made of discontinuous spikes, ascending and then descending sharply—the Van hove singularities ( Figure 39 ; v1, v2 and v3 are DOS for HOMO and c1, c2 and c3 for LUMO).
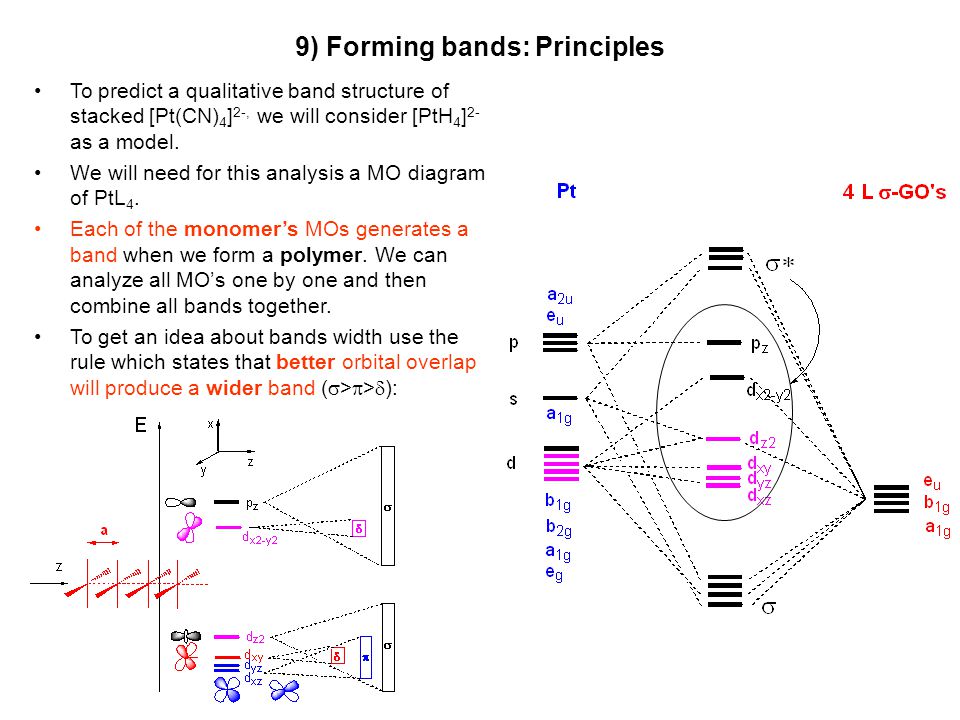


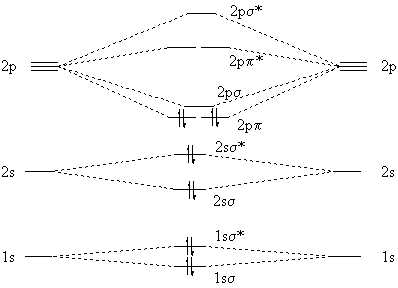





![d-orbital energy levels in planar [M II F 4 ] 2− , [M II (NH ...](https://pubs.rsc.org/image/article/2020/DT/d0dt02022b/d0dt02022b-f1_hi-res.gif)


0 Response to "36 cn molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment