37 plant cell cytoskeleton diagram
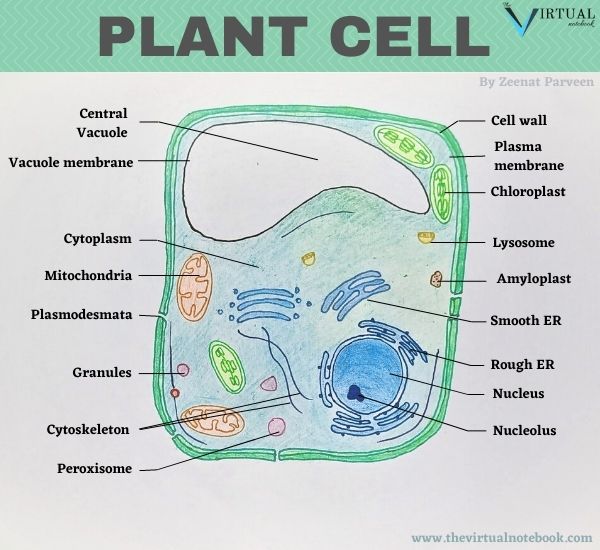
The central vacuoles are found in the cytoplasmic layer of cells of a variety of different organisms, but larger in the plant cells. Structure of plant cell vacuoles. These are large, vesicles filled with fluid, within the cytoplasm of a cell. It is made up of 30% fluid of the cell volume but can fill up to 90% of the cell's intracellular space. Cytoskeleton And Cell Membrane. The cell membrane allows the substances in and the cytoskeleton helps the substance move once it is inside the cell. In eukaryotic cells, the cytoskeleton may be in the form of three types of filaments: actin filaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. A bacteria diagram in actual fact helps us to profit […]
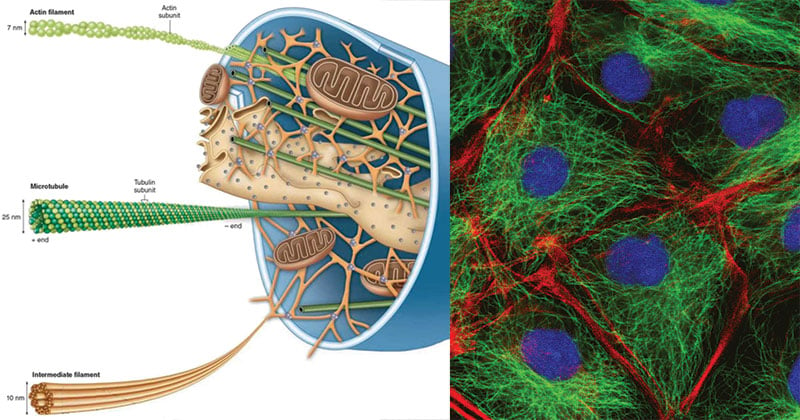
The cytoskeleton has three different types of protein elements. From narrowest to widest, they are the microfilaments (actin filaments), intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Microfilaments are often associated with myosin. They provide rigidity and shape to the cell and facilitate cellular movements.
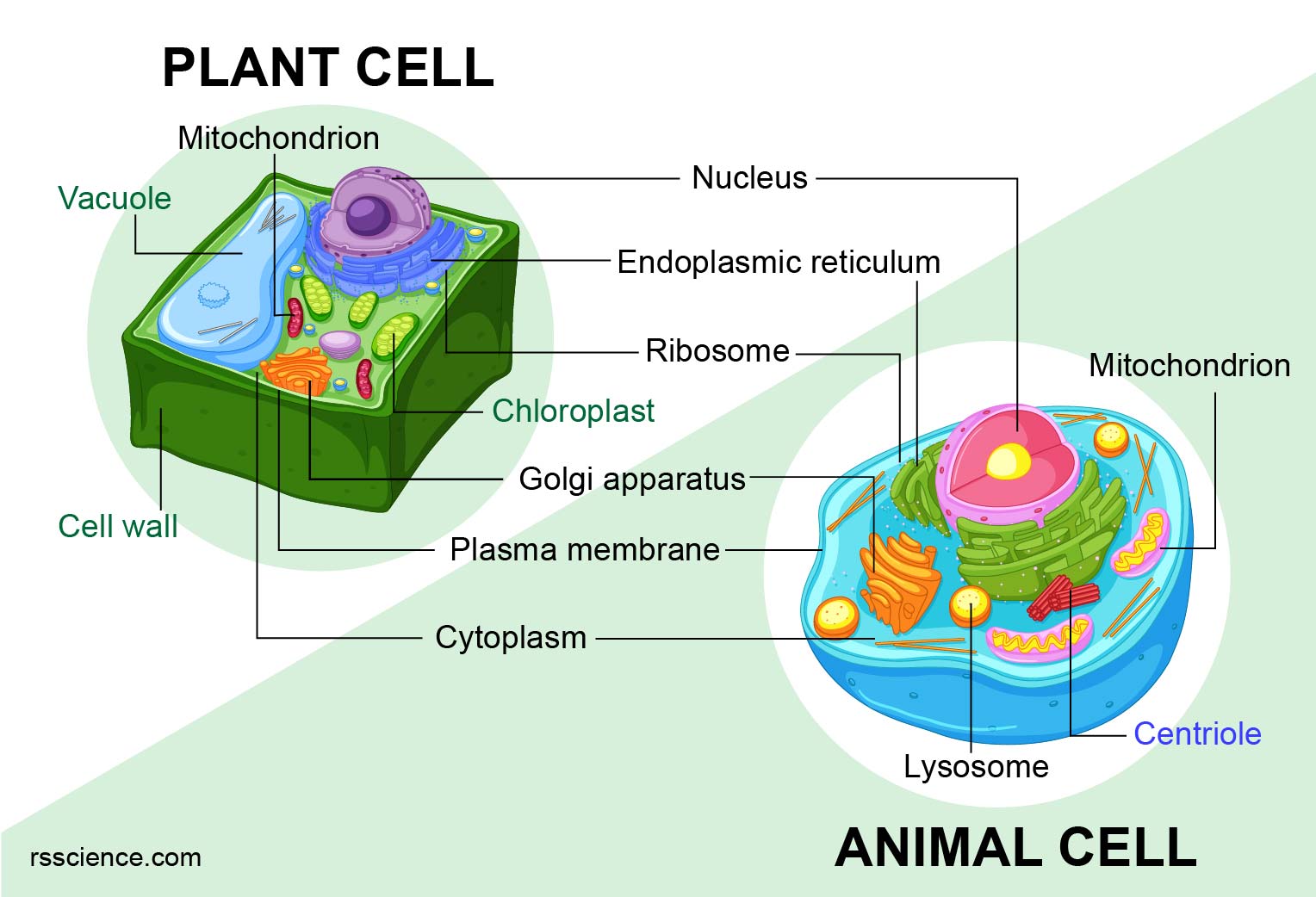
Plant cell cytoskeleton diagram
The cytoskeleton supports the cell, gives it shape, organizes and suspends the organelles within the cytoplasm, and has roles in molecule transport, cell division, cell signaling, and cell movement. Functionally, you can say the cytoskeleton network is equal to a cell's muscle, bone, blood vessel, and nervous systems in combination. The parts of a plant cell include the cell wall, the cell membrane, the cytoskeleton. Leaves take in energy via sunlight and capture carbon dioxide from the air. Animal Cell Diagram Unlabeled — UNTPIKAPPS. Animal Cell Diagram Unlabeled — UNTPIKAPPS. pictures of plant and animal cells for kids to fill out …. Functions of cytoskeleton in plant cells involve cell support and shape.. Cytoskeleton is an elaborate network of filamentous proteinaceous structures (a network of microtubules and microfilaments) present in the cytoplasm.Collectively it is referred as the cytoskeleton.
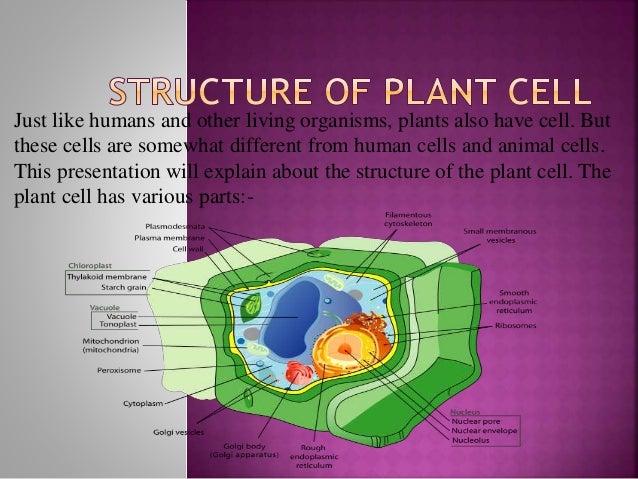
Plant cell cytoskeleton diagram. The cytoskeleton is a complex network of fibers that supports the interior of a cell. Cross-linked by molecular connectors into systems that support cellular membranes, it holds internal structures, such as the nucleus, in place and controls various kinds of cell movement. Virtually all eukaryotic cells, including plant cells, have a cytoskeleton.. Cytoskeletal systems extend internally from ... Nov 27, 2021 · Plant Cell Diagram/Structure of Plant cell. The majority of plant cells are larger than animals’ cells. They generally are rectangular or cube-like in shape. Plant cells also contain structural organelles that aren’t found in animals’ cells, including the cells’ vacuoles, the cell wall, and the plastids, e. Chloroplast. ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about Cytoskeleton:- 1. Meaning of Cytoskeleton 2. Components of Cytoskeleton. Meaning of Cytoskeleton: Earlier idea of cell was that it was a collection of some cell organelles suspended in cell sap. But with the advancement of microscopic techniques and the discovery of electron microscopy the idea of cell […] CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CHART PLANT CELL ANIMAL CELL . 1. Cell Wall •(Plants only) inflexible barrier "protecting" the ... Cytoskeleton Network of fine tubes and threads. Provides internal structural support. Cilia, Pilli, and Flagella ... CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CHART Author:
The cytoskeleton is located in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells, and archaeans, extending from the nucleus to the cell membrane. Parts and Structure The cytoskeleton consists of three different types of protein fibers: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. cell structure 3d model of plant cell cytoskeleton stock pictures, royalty-free photos & images. 3d illustration protein or enzyme 3d illustration protein or enzyme cytoskeleton stock pictures, royalty-free photos & images. Bovine pulmonary arthery cells Bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells in culture. The diagram below shows the general structure of a plant cell when viewed under and electron microscope. _____ 40m. ... There is a network of fine filaments or fibres that run through the cytoplasm of the cell. This is known as the cytoskeleton. There are three types of fibre: microfilaments. The cytoskeleton is not a static structure but is able to disassemble and reassemble its parts in order to enable internal and overall cell mobility. Types of intracellular movement supported by the cytoskeleton include transportation of vesicles into and out of a cell, chromosome manipulation during mitosis and meiosis , and organelle migration.
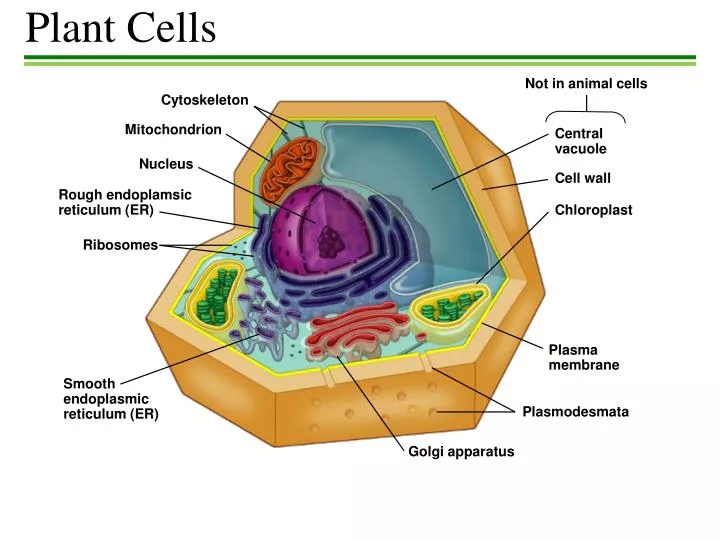
These cells tend to be larger than the cells of bacteria (prokaryotic) Have a defined nucleus. Found in organisms made up of many cells. Example: Plant and Animal cells. Structure: Eukaryotic. Cell Membrane. Cell Wall (plant cells only) Centrosome. Centriole (animal cells only) Chloroplast (plant cells only) Cytoplasm. Cytoskeleton. Cytosol ... Jan 13, 2021 · Plant cells and animal cells share many of the same structures, but each type of cell also has unique structures. Animal and plant cells have some of the same cell components in common including a nucleus, Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, peroxisomes, cytoskeleton, and cell (plasma) membrane. A cytoskeleton gives an animal cell its shape. The cytoskeleton is an important part of the cell structure. It spans the cytoplasm to provide support, shape, elasticity, and protection to the contents of the cell, much like the larger skeleton found in many living organisms. It was historically thought that only eukaryotic cells contained this ... cytoplasm cytoskeleton Parts of a plant cell: cell wall - provides rigid structure and protection; made of cellulose (dark green) cell membrane - surrounds the internal cell parts; controls passage of materials in and out of the cell cytoplasm - everything inside of the cell membrane except for the nucleus (light green)
A diagram of a plant cell with the organelles labeled. The plant cell has many different features that allow it to carry out its functions. ... The cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and tubules found throughout the cytoplasm of the cell. It has many functions; it gives the cell shape, ...
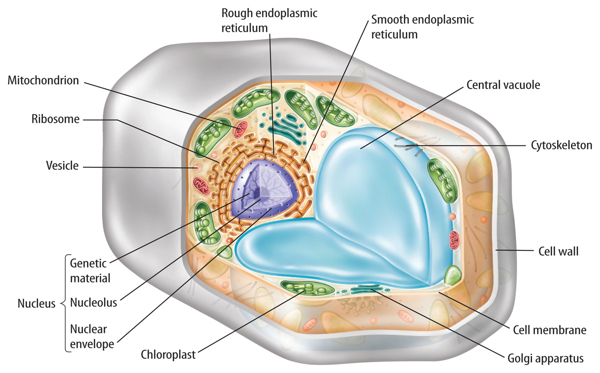
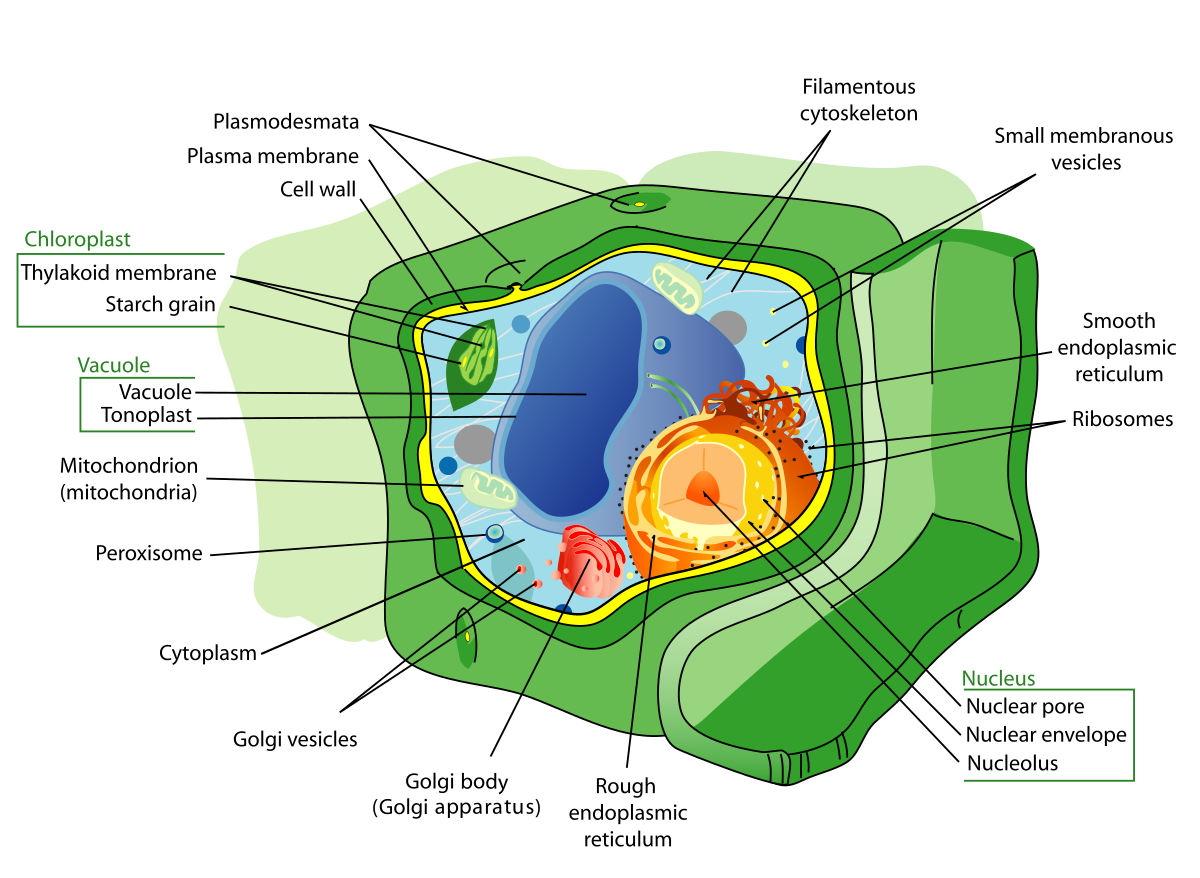
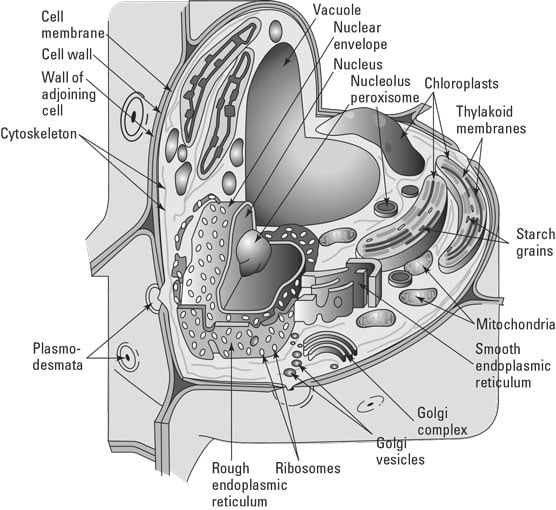
A plant cell diagram, like the one above, shows each part of the plant cell including the chloroplast, cell wall, plasma membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, etc.A plant cell diagram is a great way to learn the different components of the cell for your upcoming exam. Plants are able to do something animals can't: photosynthesize.Plant cells are able to do this because plant cells have ...
structure bestows rigidity to the plant, provides a porous medium for the circulation and distribution of water, minerals, and other nutrients, and houses specialized molecules that regulate growth and protect the plant from disease. Secondary cell wall . The secondary plant cell wall, which is often deposited inside the primary cell wall as a
48+ Plant Cell Diagram Microfilaments Images. If all the organelles were removed from a cell, the plasma membrane and the cytoplasm would not be the only components left. Structure and functions of microfilaments microfilaments are the leanest filaments of the cytoskeleton present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells with a diameter of about 5 ...
Similarly, during cell division, the cytoskeleton helps move chromosomes. The foundation of a house is one reference to the cytoskeleton. Like the frame of a house, the cytoskeleton is the cell's "core," which holds structures in place, provides support and gives the cell a definite shape. Cytoskeleton Diagram (image will be uploaded soon).
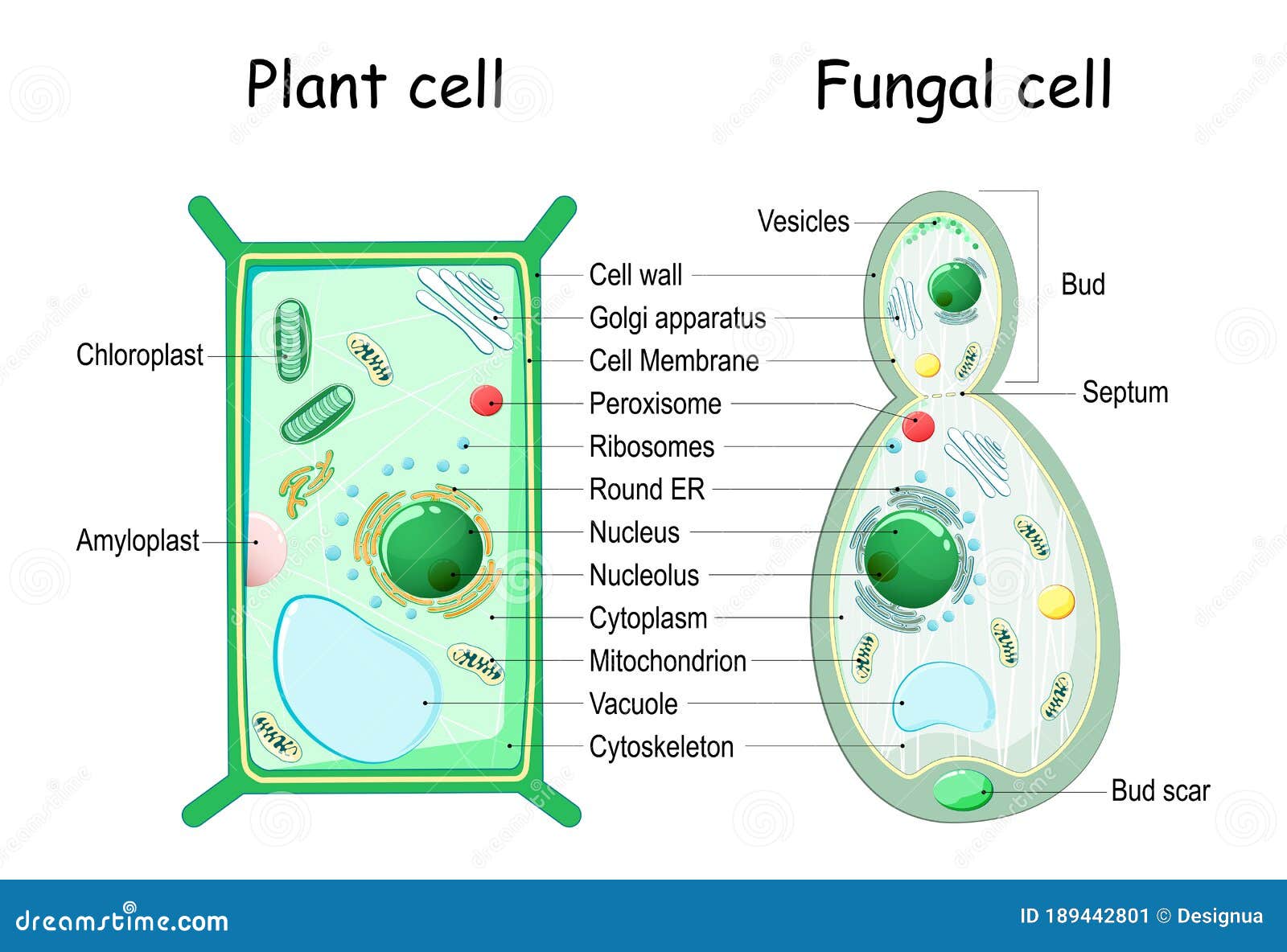
Plant Cell And Fungal Yeast Cell Structure Stock Vector Illustration Of Cytoskeleton Endoplasmic 189442801
The cytoskeleton gives animal cells structure, strength, and the ability to change shape and move. In animal cells, the cytoskeleton is a network of filaments that gives the cell its shape and forms the support network for cell functions, such as cell division. In addition to giving cells shape and support, the cytoskeleton creates particular ...
• cytoskeleton • Has DNA • No cell wall • Fixed shape • Shape can change • 10-30 um • 10-100 um • Golgi apparatus • Nucleus • Cytoplasm • Ribosomes ... Plant Cells Animal Cells Venn Diagram of Plant and Animal Cells. KEY Directions: Write in the similarities and differences between plant and animal cells.
The Cytoskeleton and Plant Cell Structure. STUDY. Flashcards. Learn. Write. Spell. Test. PLAY. Match. Gravity. Created by. sarah_st_clair PLUS. Terms in this set (28) What are the three main things that plant cell have? Plant cells have a cell wall, and often have plastids such as chloroplasts and a large central
The cytoskeleton of a biological cell is the framework of tiny tubes and filaments that forms the internal structure of the cell, helping to maintain the shape of the cell and hold the contents i.e. organelles in position and suitably inter-connected. Structure of the cytoskeleton: The main three components of the cytoskeleton are (in order of increasing size) microfilaments, intermediate ...
The plant cell diagram below displays various parts of the cell including nucleus, cytoskeleton, cell wall, membrane, centrosome, central vacuole, chloroplast and others. Lets explain what each component is responsible for: The nucleus is the commanding center of the cell controlling various functions of the cell and containing DNA.
Jan 11, 2002 · The eukaryotic cytoskeleton is a dynamic filamentous network with various cellular and developmental functions. Plant cells display a singular architecture, necessitating a structurally and functionally unique cytoskeleton and plant specific control mechanisms.
Functions of cytoskeleton in plant cells involve cell support and shape.. Cytoskeleton is an elaborate network of filamentous proteinaceous structures (a network of microtubules and microfilaments) present in the cytoplasm.Collectively it is referred as the cytoskeleton.
The parts of a plant cell include the cell wall, the cell membrane, the cytoskeleton. Leaves take in energy via sunlight and capture carbon dioxide from the air. Animal Cell Diagram Unlabeled — UNTPIKAPPS. Animal Cell Diagram Unlabeled — UNTPIKAPPS. pictures of plant and animal cells for kids to fill out ….
The cytoskeleton supports the cell, gives it shape, organizes and suspends the organelles within the cytoplasm, and has roles in molecule transport, cell division, cell signaling, and cell movement. Functionally, you can say the cytoskeleton network is equal to a cell's muscle, bone, blood vessel, and nervous systems in combination.

123rf Millions Of Creative Stock Photos Vectors Videos And Music Files For Your Inspiration And Projects Plant Cell Plant Cell Model Cell Diagram
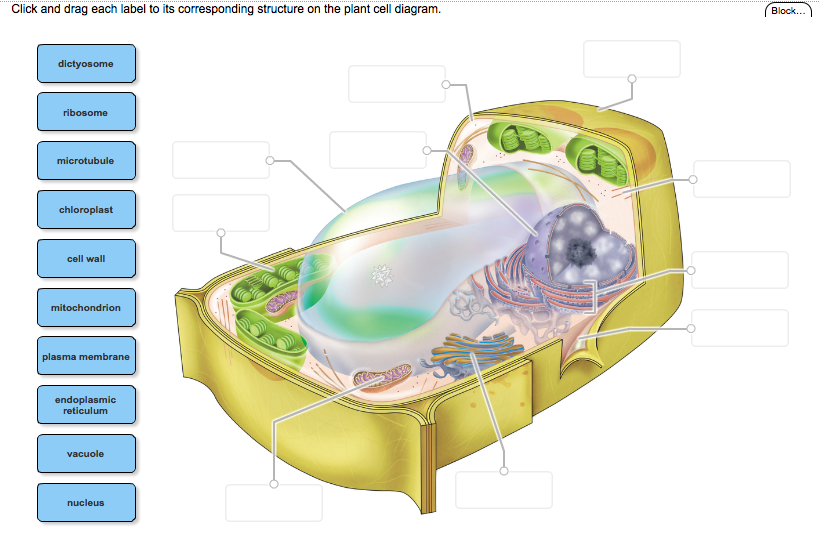

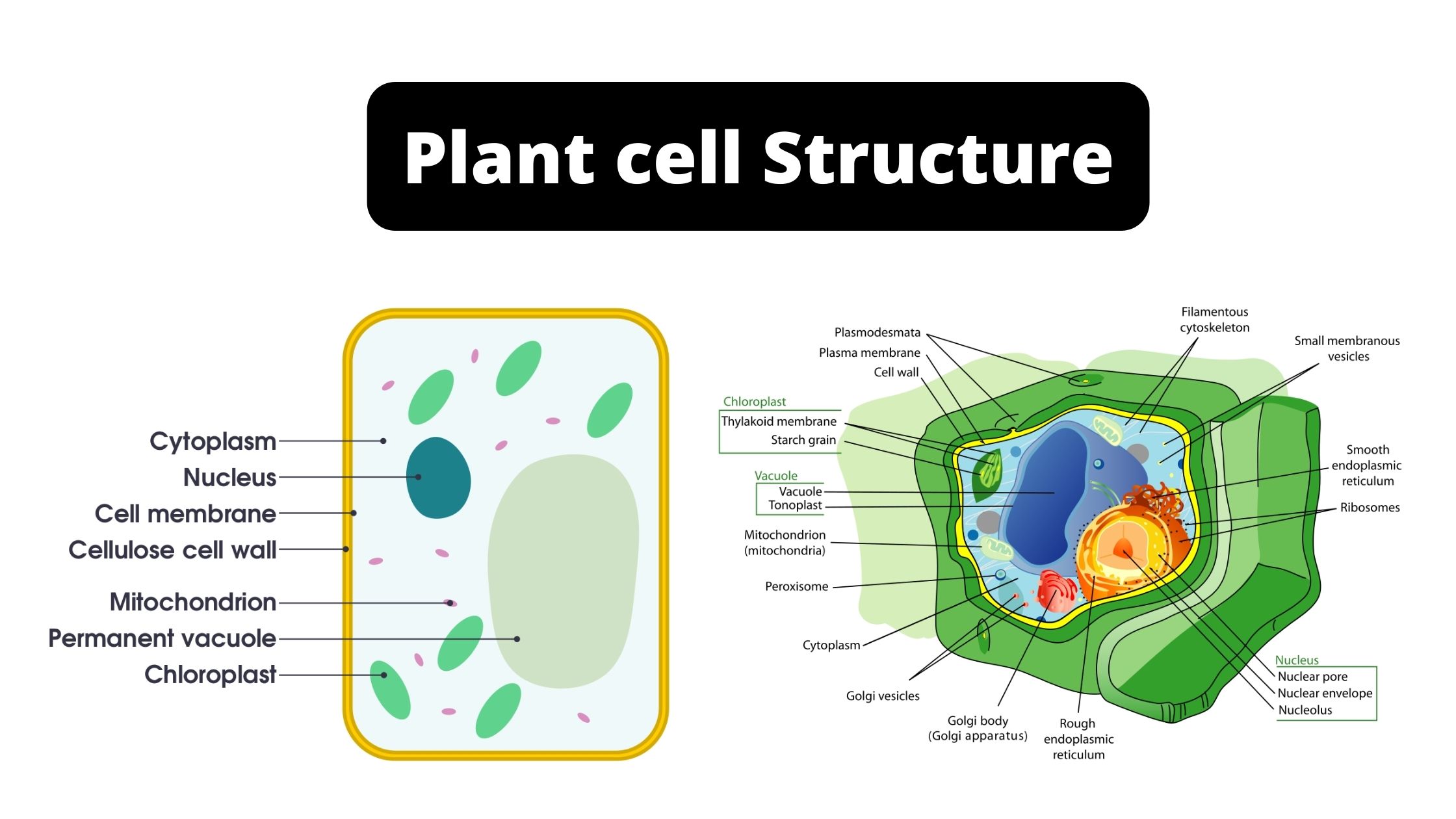



/animal-cells-vs-plant-cells-373375_final-5b462d7fc9e77c00375014f1.png)














0 Response to "37 plant cell cytoskeleton diagram"
Post a Comment