37 diverging lens ray diagram
A diverging lens is a lens that diverges rays of light that are traveling parallel to ... The focal point is denoted by the letter F on the diagrams below. Diverging Lenses As such, the rules for how light behaves when going through a diverging lens is a little bit different. You will be expected to be able to draw a Ray Diagram of a converging and diverging lens on our upcoming test without the rules.
03.10.2020 · 1. Concave lens is also known as 2. Mirror used as rear view mirror 3. Mirror used by dentist 6. A point on principal axis of lens where all rays of light parallel to the principal axis meets or appear to meet. 7. The image which can be obtained on screen. Answer. Answer: Across: 4. Refraction 5. One 8. Converging lens. Down: 1. Diverging lens ...
Diverging lens ray diagram
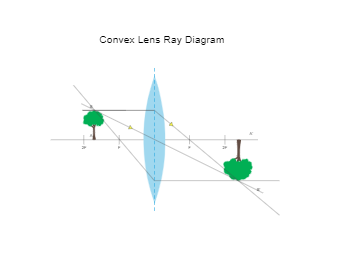
Convex (converging) and concave (diverging) lenses are drawn as, V W To understand image formation we use ray diagrams. Here is an example for aconvex lens: F The image of the top of the object is formed where the light rays cross. In a perfect lens all the rays from a point on the object will meet at one other point - so we only need to draw two rays! Section 1: Introduction (Refraction and ... A diverging lens ray diagram follows three basic rules: Any ray of light that is parallel to the principal axis of the lens will pass through its focal point after refraction. Any incident ray of light that passes through the focus of the lens before getting refracted will emerge parallel to the principal axis on refraction. 23.04.2020 · For a Concave mirror, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object AB is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes t
Diverging lens ray diagram. 7. Make a ray diagram for an object placed closer to a diverging (concave) lens than the focal point. Is the magnification greater or less than 1? Can the magnification for a diverging lens ever be greater than 1? Explain. 8. Show by making ray diagrams that for any image, the magnification, M, is the ratio of image to object distances: M ... View Notes - Diverging Lenses - Ray Diagrams from GEO 111 at Vilniaus Gedimino technikos universitetas. 3/6/2011 Diverging Lenses - Ray Diagrams h om e - a bout - te rm s - cre dits - fe e dback T Earlier in Lesson 5, we learned how light is refracted by double concave lens in a manner that a virtual image is formed.We also learned about three simple rules of refraction for double concave lenses: . Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the focal point (i.e., in a direction such that its ... diverging lens focal length f optic axis A B A´ image distance q object distance p Figure 7.3: Using a ray diagram to locate the virtual image formed by a diverging lens. The dotted lines show the trajectories that the photons appear to follow, according to the observer. The gray lines indicate the relationships between the second and third ...
Show by a ray diagram that a diverging lens cannot form a real image of an object placed anywhere on its principal axis. Solution: Question: 15. Draw a ray diagram to show how a converging lens can form a real and enlarged image of an object. Solution: The above figure shows the image formed is real, enlarged and inverted. Question: 16. A lens forms an upright and diminished image of an object ... The above diagram shows the behavior of two incident rays approaching parallel to the principal axis of the double concave lens. Just like the double convex ... Emerson Foo (https://www.youtube.com/user/emersonfoo) & Wong Yann (https://www.youtube.com/user/MrWongYann) made an original music video on the Electromagnet... , ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by double concave lenses (i.e., diverging lenses) ...
The diagram below shows a light ray parallel to the principal axis of a spherical convex (diverging) mirror. Point F is the virtual focal point of the mirror and C is the centre of curvature. After the light ray is reflected, it will pass through point Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are: A real image is formed by a converging lens. If a weak diverging lens is placed between the converging lens and the image, where is the new image ...15 pages Find Answer to MCQ A diverging lens always has the same ray diagram, which forms a - (a) curved image - (b) large image - (c) fat image - (d) smaller image - Geometrical Optics MCQs - MCQtimes.com
Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a diverging lens. A diverging lens always form an upright virtual image.
Ray Diagram for Object Located in Front of the Focal Point. In the three cases described above - the case of the object being located beyond 2F, the case of the object being located at 2F, and the case of the object being located between 2F and F - light rays are converging to a point after refracting through the lens. In such cases, a real image is formed.
The ray diagram constructed earlier for a diverging lens revealed that the image of the object was virtual, upright, reduced in size and located on the same side. Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the focal point (i.e., in a direction such.
03.08.2020 · Draw a ray diagram to show its path and also mark angle of incidence and angle of emergence. (CBSE 2013) Answer: Angle of incidence = 0, angle of emergence = 0. Based on Refraction by spherical lens. Question 29. What is the difference between a convex lens (converging lens) and a concave lens (diverging lens) ? (CBSE 2012) Answer:
Show clearly by a ray diagram how the lens corrects the defects. Answer: Diverging lens is used for correcting myopia. Following is the ray diagram of the correction of myopia: a) The image formation for a myopic eye will happen in the front of the retina. b) F is the far point of a myopic eye which is less than infinity. c) The concave lens is placed in the front of the eye which forms a ...
13.03.2018 · The ray diagram below shows that when rays of light from a distant object pass through a diverging lens they spread out, so that they appear to come from an image which is closer to the lens and reduced in size compared to the object. This is called a virtual image, because the rays of light don’t actually form an image.
A tutorial on how to draw ray diagrams for a diverging lens.
23.04.2020 · For a Concave mirror, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object AB is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes t
A diverging lens ray diagram follows three basic rules: Any ray of light that is parallel to the principal axis of the lens will pass through its focal point after refraction. Any incident ray of light that passes through the focus of the lens before getting refracted will emerge parallel to the principal axis on refraction.
Convex (converging) and concave (diverging) lenses are drawn as, V W To understand image formation we use ray diagrams. Here is an example for aconvex lens: F The image of the top of the object is formed where the light rays cross. In a perfect lens all the rays from a point on the object will meet at one other point - so we only need to draw two rays! Section 1: Introduction (Refraction and ...




0 Response to "37 diverging lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment