36 diagram of the sun labeled
Dec 13, 2021 · Diagram showing the six layers of the Sun. The layers of the Sun shown in the diagram above include a label for each of the six layers. The labels on the diagram are as follows Core Radiative zone...
Sep 13, 2016 · Diagram: Below is a diagram of the Sun, originally developed by NASA for educational purposes. Visible, IR and UV radiation – The light that we see coming from the Sun is visible, but if you ...
[/caption] This image contains all of the largest objects in the Solar System. You can print this diagram of the Solar System, as well as this handy list of all the planets. The Sun – The ...
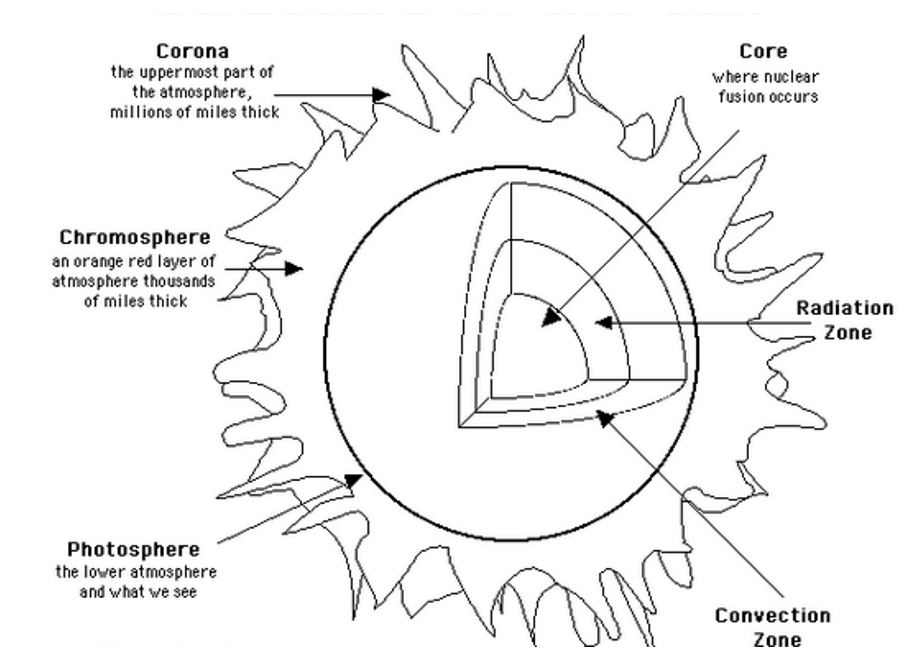
Diagram of the sun labeled
Name The Solar System The Sun Understanding Main Ideas Label the diagram of the sun below. 1. 3. cow Building Vocabulary Date Class Match each term with its description by writing the letter of the correct description
The diagram represents the apparent path of the Sun as observed at four locations, A through D, on Earth's surface on the same date. The present positions of the Sun represent the same time of day at each location. The zenith (the position directly overhead) is shown for an observer at each location. [Diagrams are not drawn to scale.]
an area on the Sun where magnetic fields are concentrated; sunspots, prominences, flares, and CMEs all tend to occur in active regions. apparent brightness. a measure of the amount of light received by Earth from a star or other object—that is, how bright an object appears in the sky, as contrasted with its luminosity.
Diagram of the sun labeled.
The parts of the inner layer are: 1. Core. It is the innermost layer of the sun, which is extremely dense where nuclear fusion generates energy in terms of photons by converting hydrogen into helium. The core is approximately 20% of the size of the solar interior and is found to be the hottest part of the sun. 2.
Lunar Eclipse Diagram Labeled. A brief illustrated discussion of lunar eclipses, including total, partial and penumbral As shown in the diagram below, two lines can be drawn from the bottom of the Sun . The two shadow regions were appropriately darkened and labeled by. Partial eclipses occur when the umbral shadow of the Moon misses the Earth ...
7. solar flare a. the layer of the sun's atmosphere that gives off visible light 8. core 9. Question: The Solar System The Sun Understanding Main Ideas Label the diagram of the sun below. Building Vocabulary Match each term with its description by writing the letter of the correct description in the right column on the line next to the term in ...
Diagram of lunar eclipse. Relative scale is correct! 2017 eclipse path visualization. Note that eclipses don't happen every month because the moon's orbit is tilted 5 degrees out of the earth-sun plane. So we really only get eclipse seasons twice a year (when the sun is on the "line of nodes" in the diagram below). Constellations
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is one of the most important tools in the study of stellar evolution.Developed independently in the early 1900s by Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell, it plots the temperature of stars against their luminosity (the theoretical HR diagram), or the colour of stars (or spectral type) against their absolute magnitude (the observational HR diagram, also known ...
Aug 04, 2017 · A collection of diagrams of the sun are available in the following 101 Diagramss to help you learn about the structures of the sun. The images that we have collected in the following images below show basic layers of the sun. The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is by far the biggest thing in the solar system.
The diagram is a model of the sky (celestial sphere) for an observer at 50° N latitude. The Sun's apparent path on June 21 is shown. 6. On the diagram mark with a dot the position of Polaris as viewed by the observer. Label this dot "Polaris." 7. On the diagram mark with a dot the position of the observer's zenith. Label this dot ...
This diagram illustrates the path of the sun and the altitude of the noon sun on the celestial sphere for an observer in New York State (latitude 43N) at the beginning of each season. Label each month for the paths drawn in the diagram below Spring Summer Fall Winter NW SE NE 6/21 12/21 E 3/21
Answer (1 of 2): During sunrise and sunset, the rays have to travel a larger part of the atmosphere because they are very close to the horizon. Therefore, light other than red is mostly scattered away. Most of the red light, which is the least scattered, enters our eyes. Hence, the sun and the sk...
Oct 10, 2012 · This graphic shows a model of the layers of the Sun, with approximate mileage ranges for each layer: for the inner layers, the mileage is from the sun's core; for the outer layers, the mileage is from the sun's surface. The inner layers are the Core, Radiative Zone and Convection Zone. The outer layers are the Photosphere, the Chromosphere, the Transition Region and the Corona.
This apparent path of the Sun was observed on the first day of A)above position 1 B)below position 3 C)between position 1 and position 2 D)between position 2 and position 3 3.Positions 1, 2, and 3 in the diagram below represent the noon Sun above the horizon on three different days during the year, as viewed from Binghamton, New York.
Jan 23, 2013 · Anatomy of the Sun. The Sun's Core - Energy is generated via thermonuclear reactions creating extreme temperatures deep within the Sun's core. The Convection Zone - Energy continues to move toward the surface through convection currents of the heated and cooled gas. The Chromosphere - This relatively thin layer of the Sun is sculpted by ...
A Diagram of the Earth-Sun Relationship Notice that the Earth’s tilt is always directed towards one place in space (in this model, it is towards the left. But notice all you need to do is move your perspective to underneath or some other side, and saying the pole tilts towards “the left” becomes meaningless.
Hello, At page below we bring you particular amazing photos we have collected so they might helpful, for today we choose to be focus related with Layers Sun Diagram Worksheet. Talking related with Layers Sun Diagram Worksheet, scroll the page to see particular related pictures to inform you more. structure of the sun diagram worksheet, plant life cycle reproducibles and black widow spider life ...
Moon phases diagram. Moon phases diagram/image credits: StarChild team at Nasa. As seen in the diagram, when the earth is between the moon and the sun, then we see a full moon. When the moon is between the earth and the sun, we have a new moon. If they are perfectly aligned, then we have a solar eclipse.
Lunar Eclipse Diagram. This shows the geometry of a lunar eclipse. When the Sun, Earth, and Moon, are precisely aligned, a lunar eclipse will occur. During an eclipse the Earth blocks sunlight from reaching the Moon. Earth creates two shadows: the outer, pale shadow called the penumbra, and the dark, inner shadow called the umbra.
The structure of the sun is made up of four layers. At the very center is the dense, hot core. Around the core lie two layers: a thick layer called the radiative zone and a thinner, cooler layer called the convective zone. Surrounding all of them is the sun's surface layer, known as the photosphere.
Label the neap and spring tides drawn below. spring neap Earth Sun Moon Why does the lineup of the Earth, sun, and moon impact the tides? The gravitation pull is increased when they are lined up together. Ho w can you tell/ remember the difference between a neap and a spring tide from a diagram? Neap Tides are perpendicular
This diagram features pictures of the Sun, Earth and Moon, as well as circular lines denoting Earth and the Moon's orbits around the Sun and Earth respectively. To complete the activity, students must identify and label each of the three bodies and two orbits. This would be a good activity to give pupils at the start of a series of lessons on ...
Astronomy. Read the definitions, then label the diagram below. Definitions. Sun - The Sun is a star at the center of our Solar System. Mercury - Mercury is the planet closest to the Sun. Venus - Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is the hottest planet. Earth - Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the planet we live on.
The sun’s atmosphere consists of the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the corona. The inner layer of the sun’s atmosphere is called the photosphere. Photo means “light,” so the photosphere is the sphere that gives off visible light. ... Label the diagram of the sun below.
The Sun’s rotation rate differs according to latitude: as seen from the Earth, the equatorial region rotates with a period of about 27 days, while the rotational period closer to the poles is about 32 days (Table 2–1). _____ * The Sun’s rotational period as observed from Earth is known as the synodic period . Because the Earth moves about
The diagram represents four apparent paths of the Sun, labeled A, B, C, and D, observed in Jamestown, New York. The June 21 and December 21 sunrise and sunset positions are indicated. Letter S identifies the Sun's position on path C at a specific time of day. Compass directions are indicated along the horizon.
File:Sun diagram.svg. Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 600 × 600 pixels. Other resolutions: 240 × 240 pixels | 480 × 480 pixels | 768 × 768 pixels | 1,024 × 1,024 pixels | 2,048 × 2,048 pixels | 1,800 × 1,800 pixels. This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown below.
0 Response to "36 diagram of the sun labeled"
Post a Comment