39 construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species
Transcribed image text: Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V(H2O)63+ Co(CN)63 - Mn(H2O)62+. This problem has been solved! See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V ( H 2 O ) 3 + 6 V (H2O)63+ Co ( CN ) 3 − 6 Co (CN)63− Mn ( H 2 O ) 2 + 6 Mn (H2O)62+ Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in ...
Transcribed image text: Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V(H_2O)_6^3+ b) Fe(CN)_6^4- c) FeCl_6^3-.
Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species
Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. Cr4+ This board is unable to make drawings/diagrams available. species coefficient is "1" then "1" needs to be entered in the field before that species. Answer to Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. The presence of a solid solution type cubic structure in which cation sites were randomly occupied was observed. 133 Finally, for the characterization of surface species and substrate–surface interactions on metal NPs, the groups of Pruski and Emsley have shown that dynamic nuclear polarization surface enhanced NMR can be a very useful tool for the further increase of the sensitivity of SS ... how to construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species start by determining how many d electrons each metal species possesses. Make sure that degenerate orbitals obey Hund\'s rule of maximum multiplicity.
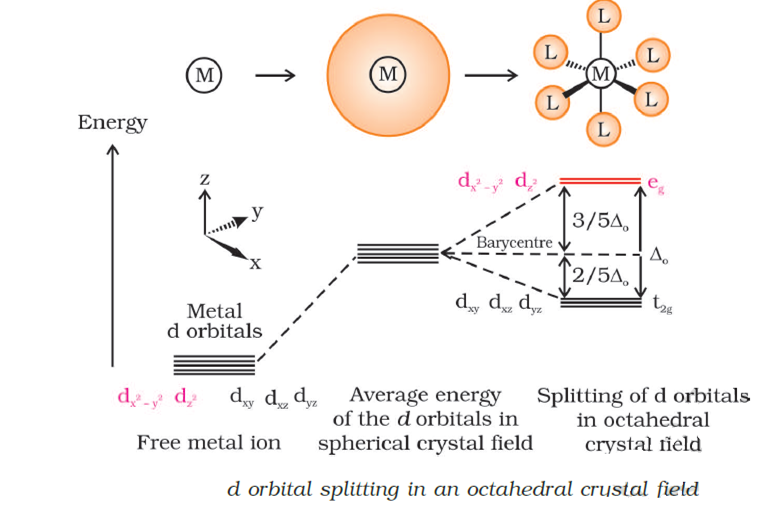
Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. Crystal Field Splitting in an Octahedral Field eg Energy 3/5 o o 2/5 o t2g e g - The higher energy set of orbitals (d z2 and d x2-y2) t 2g - The lower energy set of orbitals (d xy, d yz and d xz) Δ o or 10 Dq - The energy separation between the two levels The eThe eg orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0 6orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0.6 Δo The t2gorbitals to be stabilized to the ... Transcribed image text: Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species, a) V(H_2O)_6^3+ Co(CN)_6^3- FeCl_6^3-. Construct the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. Lecture 9 crystal field theory for octahedral. Crystal Field Theory Chemistry Libretexts Cfse the stability that results from placing a transition metal ion in the crystal field generated by a set of ligands. Question: Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. This problem has been solved! See the answerSee the ...
FREE Expert Solution. Octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram → d-orbital electrons. high-spin - electrons can occupy the upper level (eg) low-spin - electrons can pair up with the electrons on the lower level (t2g) Recall that: weak field ligands → high spin → lowΔ or crystal field splitting energy values. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V (H2O)63+ Co (CN)63 - Mn (H2O)62+. Construct the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. Since the oxalate ligand is fairly low in the series a weak field ligand at this point you may not have studied ligand field theory yet which explains why it is a weak ligand. Cr4 mnh2o62 asked by katie on march 30 2012 chemistry based on crystal field ... Transcribed image text: Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species, V(H_20)^3+_6 Fe(CN)^4-_6 FeCle^3-_6.
Transcribed image text: Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. a)V(H_2O)6^3+ b)Co(CN)6^3- c) FeCl_6^3-. Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. Cr4+ Mn (H2O)6^2+. Nov 14, · Basically, the question is referring to the compound K3 [Fe (C2O4)3]. It asks what is the electron configuration in this comound, I got it to be d5. Fe in the compound is Fe (III) so 23 electrons -> d5. Question: Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V(H_2O)_6^3+ Co(CN)_6^3- Mn(H_2O)_6^2+ ... Crystal field theory was established in 1929 treats the interaction of metal ion and ligand as a purely electrostatic phenomenon where the ligands are considered as point charges in the vicinity of the atomic orbitals of the central atom. Development and extension of crystal field theory taken into account the partly covalent nature of bonds ...
how to construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species start by determining how many d electrons each metal species possesses. Make sure that degenerate orbitals obey Hund\'s rule of maximum multiplicity.
The presence of a solid solution type cubic structure in which cation sites were randomly occupied was observed. 133 Finally, for the characterization of surface species and substrate–surface interactions on metal NPs, the groups of Pruski and Emsley have shown that dynamic nuclear polarization surface enhanced NMR can be a very useful tool for the further increase of the sensitivity of SS ...
Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. Cr4+ This board is unable to make drawings/diagrams available. species coefficient is "1" then "1" needs to be entered in the field before that species. Answer to Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species.





0 Response to "39 construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species"
Post a Comment